Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
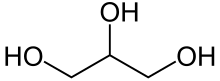
Glycerol
Chemical compound widely used in food and pharmaceuticals From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Glycerol (/ˈɡlɪsərɒl/)[6] is a simple triol compound. It is a colorless, odorless, sweet-tasting, viscous liquid. The glycerol backbone is found in lipids known as glycerides. It is also widely used as a sweetener in the food industry and as a humectant in pharmaceutical formulations. Because of its three hydroxyl groups, glycerol is miscible with water and is hygroscopic in nature.[7]
Modern use of the word glycerine (alternatively spelled glycerin) refers to commercial preparations of less than 100% purity, typically 95% glycerol.[8]
Remove ads
Structure
Although achiral, glycerol is prochiral with respect to reactions of one of the two primary alcohols. Thus, in substituted derivatives, the stereospecific numbering labels the molecule with a sn- prefix before the stem name of the molecule.[9][10][11]
Production
Summarize
Perspective
Natural sources
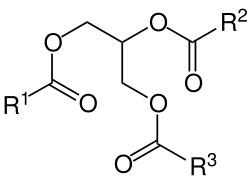
Glycerol is generally obtained from plant and animal sources where it occurs in triglycerides, esters of glycerol with long-chain carboxylic acids. The hydrolysis, saponification, or transesterification of these triglycerides produces glycerol as well as the fatty acid derivative:
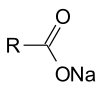
Triglycerides can be saponified with sodium hydroxide to give glycerol and fatty sodium salt or soap.
Typical plant sources include soybeans or palm. Animal-derived tallow is another source. From 2000 to 2004, approximately 950,000 tons per year were produced in the United States and Europe; 350,000 tons of glycerol were produced in the U.S. alone.[12] Since around 2010, there is a large surplus of glycerol as a byproduct of biofuel, enforced for example by EU directive 2003/30/EC that required 5.75% of petroleum fuels to be replaced with biofuel sources across all member states.[7] Crude glycerol produced from triglycerides is of variable quality, with a selling price as low as US$0.02–0.05 per kilogram in 2011.[13] It can be purified in a rather expensive process by treatment with activated carbon to remove organic impurities, alkali to remove unreacted glycerol esters, and ion exchange to remove salts. High purity glycerol (greater than 99.5%) is obtained by multi-step distillation; a vacuum chamber is necessary due to its high boiling point (290 °C).[7]
Consequently, glycerol recycling is more of a challenge than its production, for instance by conversion to glycerol carbonate[14] or to synthetic precursors, such as acrolein and epichlorohydrin.[15]
Synthetic glycerol
Although more expensive than production from plant or animal triglycerides, glycerol can be synthesized by various routes. During World War II, synthetic glycerol processes became a national defense priority because it is a precursor to nitroglycerine. Epichlorohydrin is the most important precursor. Chlorination of propylene gives allyl chloride, which is oxidized with hypochlorite to dichlorohydrin, which reacts with a strong base to give epichlorohydrin. Epichlorohydrin can be hydrolyzed to glycerol. Chlorine-free processes from propylene include the synthesis of glycerol from acrolein and propylene oxide.[7]
Remove ads
Applications
Summarize
Perspective
Food industry
In food and beverages, glycerol serves as a humectant, solvent, and sweetener, and may help preserve foods. It is also used as filler in commercially prepared low-fat foods (e.g., cookies), and as a thickening agent in liqueurs. Glycerol and water are used to preserve certain types of plant leaves.[16] As a sugar substitute, it has approximately 27 kilocalories per teaspoon (sugar has 20) and is 60% as sweet as sucrose.[citation needed] It does not feed the bacteria that form dental plaque and cause dental cavities.[citation needed] As a food additive, glycerol is labeled as E number E422. It is added to icing (frosting) to prevent it from setting too hard.
As used in foods, glycerol is categorized by the U.S. Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics as a carbohydrate. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) carbohydrate designation includes all caloric macronutrients excluding protein and fat. Glycerol has a caloric density similar to table sugar, but a lower glycemic index and different metabolic pathway within the body.
It is also recommended as an additive when polyol sweeteners such as erythritol and xylitol are used, as its heating effect in the mouth will counteract these sweeteners' cooling effect.[17]
Medical
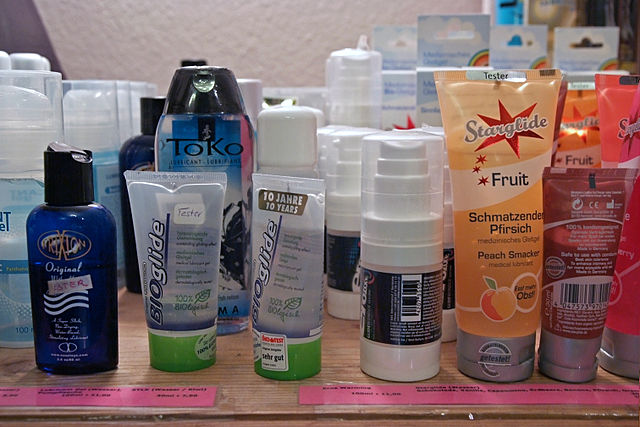




Glycerol is used in medical, pharmaceutical and personal care preparations, often as a means of improving smoothness, providing lubrication, and as a humectant.
Ichthyosis and xerosis have been relieved by the topical use of glycerin.[18][19] It is found in allergen immunotherapies, cough syrups, elixirs and expectorants, toothpaste, mouthwashes, skin care products, shaving cream, hair care products, soaps, and water-based personal lubricants. In solid dosage forms like tablets, glycerol is used as a tablet holding agent. For human consumption, glycerol is classified by the FDA among the sugar alcohols as a caloric macronutrient. Glycerol is also used in blood banking to preserve red blood cells prior to freezing.[20]
Taken rectally, glycerol functions as a laxative by irritating the anal mucosa and inducing a hyperosmotic effect,[21] expanding the colon by drawing water into it to induce peristalsis resulting in evacuation.[22] It may be administered undiluted either as a suppository or as a small-volume (2–10 ml) enema. Alternatively, it may be administered in a dilute solution, such as 5%, as a high-volume enema.[23]
Taken orally (often mixed with fruit juice to reduce its sweet taste), glycerol can cause a rapid, temporary decrease in the internal pressure of the eye. This can be useful for the initial emergency treatment of severely elevated eye pressure.[24]
In 2017, researchers showed that the probiotic Limosilactobacillus reuteri bacteria can be supplemented with glycerol to enhance its production of antimicrobial substances in the human gut. This was confirmed to be as effective as the antibiotic vancomycin at inhibiting Clostridioides difficile infection without having a significant effect on the overall microbial composition of the gut.[25]
Glycerol solutions have been used for the preservation and storage of tissue grafts at ambient conditions as an alternative to frozen storage.[26]
Glycerol has also been incorporated as a component of bio-ink formulations in the field of bioprinting.[27] The glycerol content acts to add viscosity to the bio-ink without adding large protein, saccharide, or glycoprotein molecules.
Botanical extracts
When utilized in tincture method extractions, specifically as a 10% solution, glycerol prevents tannins from precipitating in ethanol extracts of plants (tinctures). It is also used as an "alcohol-free" alternative to ethanol as a solvent in preparing herbal extractions. It is less extractive when utilized in a standard tincture methodology. Alcohol-based tinctures can also have the alcohol removed and replaced with glycerol for its preserving properties. Such products are not "alcohol-free" in a scientific or FDA regulatory sense, as glycerol contains three hydroxyl groups. Fluid extract manufacturers often extract herbs in hot water before adding glycerol to make glycerites.[28][29]
When used as a primary "true" alcohol-free botanical extraction solvent in non-tincture based methodologies, glycerol has been shown to possess a high degree of extractive versatility for botanicals including removal of numerous constituents and complex compounds, with an extractive power that can rival that of alcohol and water–alcohol solutions.[30] That glycerol possesses such high extractive power assumes it is utilized with dynamic (critical) methodologies as opposed to standard passive "tincturing" methodologies that are better suited to alcohol. Glycerol does not denature or render a botanical's constituents inert as alcohols (ethanol, methanol, and so on) do. Glycerol is a stable preserving agent for botanical extracts that, when utilized in proper concentrations in an extraction solvent base, does not allow inverting or reduction-oxidation of a finished extract's constituents, even over several years.[citation needed] Both glycerol and ethanol are viable preserving agents. Glycerol is bacteriostatic in its action, and ethanol is bactericidal in its action.[31][32][33]
Electronic cigarette liquid

Glycerin, along with propylene glycol, is a common component of e-liquid, a solution used with electronic vaporizers (electronic cigarettes). This glycerol is heated with an atomizer (a heating coil often made of Kanthal wire), producing the aerosol that delivers nicotine to the user.[34]
Antifreeze
Like ethylene glycol and propylene glycol, glycerol is a non-ionic kosmotrope that forms strong hydrogen bonds with water molecules, competing with water-water hydrogen bonds. This interaction disrupts the formation of ice. The minimum freezing point temperature is about −38 °C (−36 °F) corresponding to 70% glycerol in water.
Glycerol was historically used as an anti-freeze for automotive applications before being replaced by ethylene glycol, which has a lower freezing point. While the minimum freezing point of a glycerol-water mixture is higher than an ethylene glycol-water mixture, glycerol is not toxic and is being re-examined for use in automotive applications.[35][36]
In the laboratory, glycerol is a common component of solvents for enzymatic reagents stored at temperatures below 0 °C (32 °F) due to the depression of the freezing temperature. It is also used as a cryoprotectant where the glycerol is dissolved in water to reduce damage by ice crystals to laboratory organisms that are stored in frozen solutions, such as fungi, bacteria, nematodes, and mammalian embryos. Some organisms like the moor frog produce glycerol to survive freezing temperatures during hibernation.[37]
Chemical intermediate
Glycerol is used to produce a variety of useful derivatives.
Nitration gives nitroglycerin, an essential ingredient of various explosives such as dynamite, gelignite, and propellants like cordite. Nitroglycerin under the name glyceryl trinitrate (GTN) is commonly used to relieve angina pectoris, taken in the form of sub-lingual tablets, patches, or as an aerosol spray.
Trifunctional polyether polyols are produced from glycerol and propylene oxide.
Oxidation of glycerol affords mesoxalic acid.[38] Dehydrating glycerol affords hydroxyacetone.
Chlorination of glycerol gives the 1-chloropropane-2,3-diol:
- HOCH(CH2OH)2 + HCl → HOCH(CH2Cl)(CH2OH) + H2O
The same compound can be produced by hydrolysis of epichlorohydrin.[39]
Epoxidation by reaction with epichlorohydrin and a Lewis acid yields Glycerol triglycidyl ether.[40][41]
Vibration damping
Glycerol is used as fill for pressure gauges to damp vibration. External vibrations, from compressors, engines, pumps, etc., produce harmonic vibrations within Bourdon gauges that can cause the needle to move excessively, giving inaccurate readings. The excessive swinging of the needle can also damage internal gears or other components, causing premature wear. Glycerol, when poured into a gauge to replace the air space, reduces the harmonic vibrations that are transmitted to the needle, increasing the lifetime and reliability of the gauge.[42]
Niche uses
Entertainment industry
Glycerol is used by set decorators when filming scenes involving water to prevent an area meant to look wet from drying out too quickly.[43]
Glycerine is also used in the generation of theatrical smoke and fog as a component of the fluid used in fog machines as a replacement for glycol, which has been shown to be an irritant if exposure is prolonged.
Ultrasonic couplant
Glycerol can be sometimes used as replacement for water in ultrasonic testing, as it has favourably higher acoustic impedance (2.42 MRayl versus 1.483 MRayl for water) while being relatively safe, non-toxic, non-corrosive and relatively low cost.[44]
Internal combustion fuel
Glycerol is also used to power diesel generators supplying electricity for the FIA Formula E series of electric race cars.[45]
Research on additional uses
Research continues into potential value-added products of glycerol obtained from biodiesel production.[46] Examples (aside from combustion of waste glycerol):
- Hydrogen gas production.[47]
- Glycerine acetate is a potential fuel additive.[48]
- Additive for starch thermoplastic.[49][50]
- Conversion to various other chemicals:
- Propylene glycol[51]
- Acrolein[52][53][54]
- Ethanol[55][56]
- Epichlorohydrin,[57] a raw material for epoxy resins
Remove ads
Metabolism
Summarize
Perspective
Glycerol is a precursor for synthesis of triacylglycerols and of phospholipids in the liver and adipose tissue. When the body uses stored fat as a source of energy, glycerol and fatty acids are released into the bloodstream.
Glycerol is mainly metabolized in the liver. Glycerol injections can be used as a simple test for liver damage, as its rate of absorption by the liver is considered an accurate measure of liver health. Glycerol metabolism is reduced in both cirrhosis and fatty liver disease.[58][59]
Blood glycerol levels are highly elevated during diabetes, and is believed to be the cause of reduced fertility in patients who suffer from diabetes and metabolic syndrome. Blood glycerol levels in diabetic patients average three times higher than healthy controls. Direct glycerol treatment of testes has been found to cause significant long-term reduction in sperm count. Further testing on this subject was abandoned due to the unexpected results, as this was not the goal of the experiment.[60]
Circulating glycerol does not glycate proteins as do glucose or fructose, and does not lead to the formation of advanced glycation endproducts (AGEs). In some organisms, the glycerol component can enter the glycolysis pathway directly and, thus, provide energy for cellular metabolism (or, potentially, be converted to glucose through gluconeogenesis).
Before glycerol can enter the pathway of glycolysis or gluconeogenesis (depending on physiological conditions), it must be converted to their intermediate glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate in the following steps:
ATP
ADP
The enzyme glycerol kinase is present mainly in the liver and kidneys, but also in other body tissues, including muscle and brain.[61][62][63] In adipose tissue, glycerol 3-phosphate is obtained from dihydroxyacetone phosphate with the enzyme glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
Remove ads
Toxicity and safety
Summarize
Perspective
Glycerol has very low toxicity when ingested; its LD50 oral dose for rats is 12600 mg/kg and 8700 mg/kg for mice. It does not appear to cause toxicity when inhaled, although changes in cell maturity occurred in small sections of lung in animals under the highest dose measured. A sub-chronic 90-day nose-only inhalation study in Sprague Dawley rats exposed to 0.03, 0.16 and 0.66 mg of glycerin per liter of air for 6-hour continuous sessions revealed no treatment-related toxicity other than minimal metaplasia of the epithelium lining at the base of the epiglottis in rats exposed to 0.66 mg/L glycerin.[64][65]
Glycerol intoxication
Excessive consumption by children can lead to glycerol intoxication.[66] Symptoms of intoxication include hypoglycemia, nausea and a loss of consciousness. While intoxication as a result of excessive glycerol consumption is rare and its symptoms generally mild, occasional reports of hospitalization have occurred.[67] In the United Kingdom in August 2023, manufacturers of syrup used in slush ice drinks were advised to reduce the amount of glycerol in their formulations by the Food Standards Agency to reduce the risk of intoxication.[68] A 2025 study reported that between 2018 and 2024, at least 21 children aged 2–7 in the UK and Ireland received emergency treatment for symptoms of glycerol intoxication following the consumption of slush ice drinks.[69][70]
Food Standards Scotland advises that slush ice drinks containing glycerol should not be given to children under the age of 4, owing to the risk of intoxication. It also recommends that businesses do not use free refill offers for the drinks in venues where children under the age of 10 are likely to consume them, and that products should be appropriately labelled to inform consumers of the presence of glycerol.[71]
Remove ads
Historical cases of contamination with diethylene glycol
On 4 May 2007, the FDA advised all U.S. makers of medicines to test all batches of glycerol for diethylene glycol contamination.[72] This followed an occurrence of hundreds of fatal poisonings in Panama resulting from a falsified import customs declaration by Panamanian import/export firm Aduanas Javier de Gracia Express, S. A. The cheaper diethylene glycol was relabeled as the more expensive glycerol.[73][74] Between 1990 and 1998, incidents of DEG poisoning reportedly occurred in Argentina, Bangladesh, India, and Nigeria, and resulted in hundreds of deaths. In 1937, more than one hundred people died in the United States after ingesting DEG-contaminated elixir sulfanilamide, a drug used to treat infections.[75]
Remove ads
Etymology
The origin of the gly- and glu- prefixes for glycols and sugars is from Ancient Greek γλυκύς glukus which means sweet.[76] Name glycérine was coined ca. 1811 by Michel Eugène Chevreul to denote what was previously called "sweet principle of fat" by its discoverer Carl Wilhelm Scheele. It was borrowed into English ca. 1838 and in the 20th c. displaced by 1872 term glycerol featuring an alcohols' suffix -ol.
Remove ads
Properties
Table of thermal and physical properties of saturated liquid glycerin:[77][78]
Remove ads
See also
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads