Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
International Organization for Standardization
International standards development organization From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO /ˈaɪsoʊ/;[3] French: Organisation internationale de normalisation; Russian: Международная организация по стандартизации) is an independent, non-governmental, international standard development organization composed of representatives from the national standards organizations of member countries.[4][5]
Membership requirements are given in Article 3 of the ISO Statutes.[6]
ISO was founded on 23 February 1947, and (as of July 2024[update]) it has published over 25,000 international standards covering almost all aspects of technology and manufacturing. It has over 800 technical committees (TCs) and subcommittees (SCs) to take care of standards development.[7]
The organization develops and publishes international standards in technical and nontechnical fields, including everything from manufactured products and technology to food safety, transport, IT, agriculture, and healthcare.[7][8][9][10] More specialized topics like electrical and electronic engineering are instead handled by the International Electrotechnical Commission.[11] It is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland.[7] The three official languages of ISO are English, French, and Russian.[2]
Remove ads
Name and abbreviations
The International Organization for Standardization in French is Organisation internationale de normalisation and in Russian, Международная организация по стандартизации (Mezhdunarodnaya organizatsiya po standartizatsii).
A common misconception is that ISO is an abbreviation for "International Standardization Organization" or a similar title in another language. In fact, the letters do not officially represent an acronym or initialism. The organization provides this explanation of the name:
Because 'International Organization for Standardization' would have different acronyms in different languages (IOS in English, OIN in French), our founders decided to give it the short form ISO. ISO is derived from the Greek word isos (ίσος, meaning "equal"). Whatever the country, whatever the language, the short form of our name is always ISO.[7]
During the founding meetings of the new organization, however, the Greek word explanation was not invoked, so this meaning may be a false etymology.[12]
Both the name ISO and the ISO logo are registered trademarks and their use is restricted.[13]
Remove ads
History

The organization that is known today as ISO began in 1926 as the International Federation of the National Standardizing Associations (ISA), which primarily focused on mechanical engineering. The ISA was suspended in 1942 during World War II but, after the war, the ISA was approached by the recently formed United Nations Standards Coordinating Committee (UNSCC) with a proposal to form a new global standards body.[14]
In October 1946, ISA and UNSCC delegates from 25 countries met in London and agreed to join forces to create the International Organization for Standardization. The organization officially began operations on 23 February 1947.[15][16]
ISO Standards were originally known as ISO Recommendations (ISO/R), e.g., "ISO 1" was issued in 1951 as "ISO/R 1".[17]
Remove ads
Structure and organization
Summarize
Perspective
ISO is a voluntary organization whose members are recognized authorities on standards, each one representing one country. Members meet annually at a General Assembly to discuss the strategic objectives of ISO. The organization is coordinated by a central secretariat based in Geneva.[18]
A council with a rotating membership of 20 member bodies provides guidance and governance, including setting the annual budget of the central secretariat.[18][19]
The technical management board is responsible for more than 250 technical committees, who develop the ISO standards.[18][20][21][22]
Joint technical committee with IEC
ISO has a joint technical committee (JTC) with the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) to develop standards relating to information technology (IT). Known as JTC 1 and entitled "Information technology", it was created in 1987 and its mission is "to develop worldwide Information and Communication Technology (ICT) standards for business and consumer applications."[23][24]
There was previously also a JTC 2 that was created in 2009 for a joint project to establish common terminology for "standardization in the field of energy efficiency and renewable energy sources".[25] It was later disbanded.
Membership
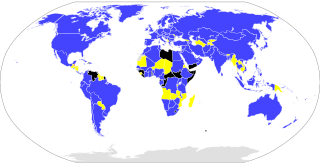
ISO member countries with a national standards body and ISO voting rights
Correspondent members (countries without a national standards body)
Subscriber members (countries with small economies)
other places with an ISO 3166-1 code who are not members of ISO
As of 2022[update], there are 167 national members representing ISO in their country, with each country having only one member.[7][26]
ISO has three membership categories,[1]
- Member bodies are national bodies considered the most representative standards body in each country. These are the only members of ISO that have voting rights.
- Correspondent members are countries that do not have their own standards organization. These members are informed about the work of ISO, but do not participate in standards promulgation.
- Subscriber members are countries with small economies. They pay reduced membership fees, but can follow the development of standards.
Participating members are called "P" members, as opposed to observing members, who are called "O" members.
Financing
ISO is funded by a combination of:[27]
- Organizations that manage the specific projects or loan experts to participate in the technical work
- Subscriptions from member bodies, whose subscriptions are in proportion to each country's gross national product and trade figures
- Sale of standards
Remove ads
International standards and other publications
Summarize
Perspective
International standards are the main products of ISO. It also publishes technical reports, technical specifications, publicly available specifications, technical corrigenda (corrections), and guides.[28][29]
International standards
- These are designated using the format ISO[/IEC] [/ASTM] [IS] nnnnn[-p]:[yyyy] Title, where nnnnn is the number of the standard, p is an optional part number, yyyy is the year published, and Title describes the subject. IEC for International Electrotechnical Commission is included if the standard results from the work of ISO/IEC JTC 1 (the ISO/IEC Joint Technical Committee). ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) is used for standards developed in cooperation with ASTM International. yyyy and IS are not used for an incomplete or unpublished standard and, under some circumstances, may be left off the title of a published work.
Technical reports
- These are issued when a technical committee or subcommittee has collected data of a different kind from that normally published as an International Standard,[28] such as references and explanations. The naming conventions for these are the same as for standards, except TR prepended instead of IS in the report's name.
For example:
- ISO/IEC TR 17799:2000 Code of Practice for Information Security Management
- ISO/TR 19033:2000 Technical product documentation – Metadata for construction documentation
Technical and publicly available specifications
- Technical specifications may be produced when "the subject in question is still under development or where for any other reason there is the future but not immediate possibility of an agreement to publish an International Standard". A publicly available specification is usually "an intermediate specification, published prior to the development of a full International Standard, or, in IEC may be a 'dual logo' publication published in collaboration with an external organization".[28] By convention, both types of specification are named in a manner similar to the organization's technical reports.
For example:
- ISO/TS 16952-1:2006 Technical product documentation – Reference designation system – Part 1: General application rules (later withdrawn and replaced by ISO/TS 81346-3:2012, which was later withdrawn)
- ISO/PAS 11154:2006 Road vehicles – Roof load carriers (later revised in ISO 11154:2023, which does not have the "PAS" abbreviation in its name)
Technical corrigenda
- When partnering with IEC in their joint technical committee, ISO also sometimes issues "technical corrigenda" (where "corrigenda" is the plural of corrigendum). These are amendments made to existing standards to correct minor technical flaws or ambiguities.[28]
ISO guides
- These are meta-standards covering "matters related to international standardization".[28] They are named using the format "ISO[/IEC] Guide N:yyyy: Title".
For example:
- ISO/IEC Guide 2:2004 Standardization and related activities – General vocabulary
- ISO/IEC Guide 65:1996 General requirements for bodies operating product certification (since revised and reissued as ISO/IEC 17065:2012 Conformity assessment — Requirements for bodies certifying products, processes and services).[30]
Document copyright
ISO documents have strict copyright restrictions and ISO charges for most copies. As of 2020[update], the typical cost of a copy of an ISO standard is about US$120 or more (and electronic copies typically have a single-user license, so they cannot be shared among groups of people).[31] Some standards by ISO and its official U.S. representative (and, via the U.S. National Committee, the International Electrotechnical Commission) are made freely available.[32][33]
Remove ads
Standardization process
Summarize
Perspective
A standard published by ISO/IEC is the last stage of a long process that commonly starts with the proposal of new work within a committee. Some abbreviations used for marking a standard with its status are:[34][35][36][37][38][39][40]
- PWI – Preliminary Work Item
- NP or NWIP – New Proposal / New Work Item Proposal (e.g., ISO/IEC NP 23007)
- AWI – Approved new Work Item (e.g., ISO/IEC AWI 15444-14)
- WD – Working Draft (e.g., ISO/IEC WD 27032)
- CD – Committee Draft (e.g., ISO/IEC CD 23000-5)
- FCD – Final Committee Draft (e.g., ISO/IEC FCD 23000-12)
- DIS – Draft International Standard (e.g., ISO/IEC DIS 14297)
- FDIS – Final Draft International Standard (e.g., ISO/IEC FDIS 27003)
- PRF – Proof of a new International Standard (e.g., ISO/IEC PRF 18018)
- IS – International Standard (e.g., ISO/IEC 13818-1:2007)
Abbreviations used for amendments are:[34][35][36][37][38][39][40][41]
- NP Amd – New Proposal Amendment (e.g., ISO/IEC 15444-2:2004/NP Amd 3)
- AWI Amd – Approved new Work Item Amendment (e.g., ISO/IEC 14492:2001/AWI Amd 4)
- WD Amd – Working Draft Amendment (e.g., ISO 11092:1993/WD Amd 1)
- CD Amd / PDAmd – Committee Draft Amendment / Proposed Draft Amendment (e.g., ISO/IEC 13818-1:2007/CD Amd 6)
- FPDAmd / DAM (DAmd) – Final Proposed Draft Amendment / Draft Amendment (e.g., ISO/IEC 14496-14:2003/FPDAmd 1)
- FDAM (FDAmd) – Final Draft Amendment (e.g., ISO/IEC 13818-1:2007/FDAmd 4)
- PRF Amd – (e.g., ISO 12639:2004/PRF Amd 1)
- Amd – Amendment (e.g., ISO/IEC 13818-1:2007/Amd 1:2007)
Other abbreviations are:[38][39][41][42]
- TR – Technical Report (e.g., ISO/IEC TR 19791:2006)
- DTR – Draft Technical Report (e.g., ISO/IEC DTR 19791)
- TS – Technical Specification (e.g., ISO/TS 16949:2009)
- DTS – Draft Technical Specification (e.g., ISO/DTS 11602-1)
- PAS – Publicly Available Specification
- TTA – Technology Trends Assessment (e.g., ISO/TTA 1:1994)
- IWA – International Workshop Agreements (e.g., IWA 1:2005)
- Cor – Technical Corrigendum (e.g., ISO/IEC 13818-1:2007/Cor 1:2008)
- Guide – a guidance to technical committees for the preparation of standards
International Standards are developed by ISO technical committees (TC) and subcommittees (SC) by a process with six steps:[36][43]
- Stage 1: Proposal stage
- Stage 2: Preparatory stage
- Stage 3: Committee stage
- Stage 4: Enquiry stage
- Stage 5: Approval stage
- Stage 6: Publication stage
The TC/SC may set up working groups (WG) of experts for the preparation of a working drafts. Subcommittees may have several working groups, which may have several Sub Groups (SG).[44]
It is possible to omit certain stages, if there is a document with a certain degree of maturity at the start of a standardization project, for example, a standard developed by another organization. ISO/IEC directives also allow the so-called "Fast-track procedure". In this procedure, a document is submitted directly for approval as a draft International Standard (DIS) to the ISO member bodies or as a final draft International Standard (FDIS), if the document was developed by an international standardizing body recognized by the ISO Council.[36]
The first step, a proposal of work (New Proposal), is approved at the relevant subcommittee or technical committee (e.g., SC 29 and JTC 1 respectively in the case of MPEG, the Moving Picture Experts Group). A working group (WG) of experts is typically set up by the subcommittee for the preparation of a working draft (e.g., MPEG is a collection of seven working groups as of 2023). When the scope of a new work is sufficiently clarified, some of the working groups may make an open request for proposals—known as a "call for proposals". The first document that is produced, for example, for audio and video coding standards is called a verification model (VM) (previously also called a "simulation and test model"). When a sufficient confidence in the stability of the standard under development is reached, a working draft (WD) is produced. This is in the form of a standard, but is kept internal to working group for revision. When a working draft is sufficiently mature and the subcommittee is satisfied that it has developed an appropriate technical document for the problem being addressed, it becomes a committee draft (CD) and is sent to the P-member national bodies of the SC for the collection of formal comments. Revisions may be made in response to the comments, and successive committee drafts may be produced and circulated until consensus is reached to proceed to the next stage, called the "enquiry stage".
After a consensus to proceed is established, the subcommittee will produce a draft international standard (DIS), and the text is submitted to national bodies for voting and comment within a period of five months. A document in the DIS stage is available to the public for purchase and may be referred to with its ISO DIS reference number.[45]
Following consideration of any comments and revision of the document, the draft is then approved for submission as a Final Draft International Standard (FDIS) if a two-thirds majority of the P-members of the TC/SC are in favour and if not more than one-quarter of the total number of votes cast are negative. ISO will then hold a ballot among the national bodies where no technical changes are allowed (a yes/no final approval ballot), within a period of two months. It is approved as an International Standard (IS) if a two-thirds majority of the P-members of the TC/SC is in favour and not more than one-quarter of the total number of votes cast are negative. After approval, the document is published by the ISO central secretariat, with only minor editorial changes introduced in the publication process before the publication as an International Standard.[34][36]
Except for a relatively small number of standards,[32] ISO standards are not available free of charge, but rather for a purchase fee,[46] which has been seen by some as unaffordable for small open-source projects.[47]
The process of developing standards within ISO was criticized around 2007 as being too difficult for timely completion of large and complex standards, and some members were failing to respond to ballots, causing problems in completing the necessary steps within the prescribed time limits. In some cases, alternative processes have been used to develop standards outside of ISO and then submit them for its approval. A more rapid "fast-track" approval procedure was used in ISO/IEC JTC 1 for the standardization of Office Open XML (OOXML, ISO/IEC 29500, approved in April 2008), and another rapid alternative "publicly available specification" (PAS) process had been used by OASIS to obtain approval of OpenDocument as an ISO/IEC standard (ISO/IEC 26300, approved in May 2006).[48]
As was suggested at the time by Martin Bryan, the outgoing convenor (chairman) of working group 1 (WG1) of ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 34, the rules of ISO were eventually tightened so that participating members that fail to respond to votes are demoted to observer status.
The computer security entrepreneur and Ubuntu founder, Mark Shuttleworth, was quoted in a ZDNet blog article in 2008 about the process of standardization of OOXML as saying: "I think it de-values the confidence people have in the standards setting process", and alleged that ISO did not carry out its responsibility. He also said that Microsoft had intensely lobbied many countries that traditionally had not participated in ISO and stacked technical committees with Microsoft employees, solution providers, and resellers sympathetic to Office Open XML:[49]
When you have a process built on trust and when that trust is abused, ISO should halt the process... ISO is an engineering old boys club and these things are boring so you have to have a lot of passion ... then suddenly you have an investment of a lot of money and lobbying and you get artificial results. The process is not set up to deal with intensive corporate lobbying and so you end up with something being a standard that is not clear.
International Workshop Agreements
International Workshop Agreements (IWAs) are documents that establish a collaboration agreement that allow "key industry players to negotiate in an open workshop environment" outside of ISO in a way that may eventually lead to development of an ISO standard.[42]
Remove ads
Products named after ISO
On occasion, the fact that many of the ISO-created standards are ubiquitous has led to common use of "ISO" to describe the product that conforms to a standard. Some examples of this are:
- Disk images ending in the file extension "ISO" to signify that they are using the ISO 9660 standard file system as opposed to another file system—hence disc images commonly being referred to as "ISOs".
- The sensitivity of a photographic film to light (its "film speed") is described by ISO 6, ISO 2240, and ISO 5800. Hence, the speed of the film often is referred to by its ISO number.
- As it was originally defined in ISO 518, the flash hot shoe found on cameras often is called the "ISO shoe".
- ISO 11783, the communication protocol for the agriculture industry, which is marketed as ISOBUS.
- ISO 13216, the standardized attachment points for child safety seats, which is marketed as ISOFIX.
- ISO 668, the standardized intermodal containers, sometimes called "ISO containers".
Remove ads
ISO awards
ISO presents several awards to acknowledge the valuable contributions made in the realm of international standardization:[50]
- The Lawrence D. Eicher Award: This award acknowledges outstanding standards development. It is available to all ISO and ISO/IEC technical committees.
- The ISO Next Generation Award: Aimed at young professionals from ISO member nations, this award highlights those who advocate for sustainability-centric standardization and emphasize the importance of partnerships.
- The ISO Excellence Award: Dedicated to recognizing the endeavors of ISO's technical professionals, any individual nominated as an expert, project leader, or convenor in a committee working group is eligible for this award.
Remove ads
See also
Summarize
Perspective
- Countries in the International Organization for Standardization – Members of ISO
- Ecma International – Standards organization for information and communication systems
- European Committee for Standardization (CEN) – Standards organization
- Global Reporting Initiative – International standards organization – for sustainability information and linking up with reporting on their 17#GlobalGoals indicators
- GOST – CIS technical standards – a set of technical standards maintained by the Euro-Asian Council for Standardization, Metrology, and Certification
- IEEE Standards Association – Operating unit within IEEE
- Institute of Environmental Sciences and Technology
- Interface 2010 – the Interface Marketing Supplier Integration Institute
- International Classification for Standards – Classification system for technical standards
- The International Customer Service Institute – International partnership organisation for sharing of best practices in customer service
- International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) – International standards organization
- International healthcare accreditation – International healthcare accreditation organisation
- International Telecommunication Union – Specialized agency of the United Nations
- Internet Engineering Task Force – Open internet standards organization
- List of ISO standards
- Standardization – Implementation of technical standards based on the consensus of different parties
- Standards organization – Organization that develops standards
- Terminology planning policy
ISO divisions
Some of the 834 Technical Committees of the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) include:[7]
- ISO/TC 37 - Language and terminology – Terminology and other language content resources
- ISO/TC 46 - Information and documentation - Libraries, archives, indexing and information science
- ISO/TC 68 - Financial services - Banking, securities and financial services
- ISO/TC 176 - Quality management and quality assurance
- ISO/TC 211 - Geographic information/Geomatics - Geographic data and information
- ISO/TC 215 - Health informatics - Health-related data/information
- ISO/TC 262 - Risk management - Risk management
- ISO/TC 289 - Brand evaluation - Brand evaluation and valuation
- ISO/TC 292 - Security and resilience - Security of society
Remove ads
References
Further reading
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads

