Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Kura–Araxes culture
Archaeological culture from the Caucasus region From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
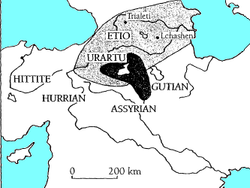
The Kura–Araxes culture (also named Kur–Araz culture, Mtkvari–Araxes culture, Early Transcaucasian culture, Shengavitian culture[1][2]) was an archaeological culture that existed from about 4000 BC until about 2000 BC,[3] which has traditionally been regarded as the date of its end; in some locations it may have disappeared as early as 2600 or 2700 BC.[4] The earliest evidence for this culture is found on the Ararat plain; it spread north in the Caucasus by 3000 BC.[5]
Altogether, the early Transcaucasian culture enveloped a vast area about 1,000 km by 500 km,[6] and mostly encompassed the modern-day territories of the Armenia, eastern Georgia, Azerbaijan, northwestern Iran, the northeastern Caucasus, eastern Turkey, and as far as northern Syria.[7][8]
The name of the culture is derived from the Kura and Araxes river valleys. Some local variations of the Kura–Araxes culture are sometimes known as Shengavitian, Karaz (Erzurum), Pulur (after a site renamed later as Sakyol), and Yanik Tepe (Iranian Azerbaijan, near Lake Urmia) cultures.[9] It gave rise to the Khirbet Kerak-ware culture found in the Levant and Trialeti culture of the South Caucasus and Armenian highlands. In Nakhchivan region of Azerbaijan and nearby areas, Kura-Araxes culture was followed by Nakhchivan culture.
This civilization was characterized by an agricultural sedentary economy with more than a thousand settlements covering the fertile riverside valleys, high plateaus and high mountain zones of the Armenian highlands and neighboring regions. The Early Bronze Age artificial hill-settlements were characterized by multiple cultural layers, which in some places spread to tens of meters (Mokhrablur of Nakhijevan, Norsun-Tepe).[10][11]
Remove ads
Genetics
Summarize
Perspective

Ancient DNA analysis has provided insights into the genetic composition of individuals associated with the Kura-Araxes culture. The Y-chromosome haplogroups identified in Kura–Araxes individuals include G2b, J-CTS1460 (x2), J-Z1842, and R1b1-M415 (xM269), reflecting a mixture of lineages with deep Near Eastern and Caucasian origins. Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) analysis indicates diverse maternal lineages, with haplogroups including H, H1u, K3, N1b1a, R1a1, T2a1b2b, T2h, U1a1a, U3a2, U3b1a1, U3b2, and X2f. These haplogroups suggest genetic connections between Kura–Araxes populations and neighboring regions such as Anatolia, the Near East, and the Caucasus. Genomic studies indicate that Kura–Araxes individuals shared a significant portion of their ancestry with Caucasus hunter-gatherers (CHG) and Anatolian Chalcolithic populations. The data indicate a largely stable genetic profile over time, with limited gene flow from Steppe populations, distinguishing them from later Bronze Age groups that incorporated more Yamnaya-related ancestry.[13][14][15]
Remove ads
Early history
Summarize
Perspective

The formative processes of the Kura–Araxes cultural complex, and the date and circumstances of its rise, have been long debated.
Shulaveri–Shomu culture preceded the Kura–Araxes culture in the area. There were many differences between these two cultures[example needed], so the connection was not clear. Later it was suggested that the Sioni culture of eastern Georgia possibly represented a transition from the Shulaveri to the Kura–Arax cultural complex.
At many sites the Sioni culture layers can be seen as intermediary between Shulaver–Shomu–Tepe layers and the Kura–Araxes layers.[16] This kind of stratigraphy warrants a chronological place of the Sioni culture at around 4000 BCE.[17]
Some scholars consider the Kartli and Kakheti areas as key to forming the earliest phase of the Kura–Araxes culture.[17] To a large extent, this appears as an indigenous culture of Caucasus that was formed over a long period, and at the same time incorporating foreign influences.
There are some indications (such as at Arslantepe) of the overlapping in time of the Kura-Araxes and Uruk cultures; such contacts may go back even to the Middle Uruk period.[18]
Some scholars have suggested that the earliest manifestation of the Kura–Araxes phenomenon should be dated at least to the last quarter of the 5th millennium BC. This is based on the recent data from Ovçular Tepesi, a late Chalcolithic settlement located in Nakhchivan by the Arpaçay river.[19]

Remove ads
Expansion
Summarize
Perspective
Rather quickly, elements of Kura–Araxes culture started to proceed westward to the Erzurum plain, southwest to Cilicia, and to the southeast into the area of Lake Van, and below the Urmia basin in Iran, such as to Godin Tepe. Finally, it proceeded into the present-day Syria (Amuq valley), and as far as Palestine.
Its territory corresponds to large parts of modern Armenia, Azerbaijan, Chechnya, Dagestan, Georgia, Ingushetia, North Ossetia, and parts of Iran and Turkey.[7][8][21]
At Sos Hoyuk, in Erzurum Province, Turkey, early forms of Kura–Araxes pottery were found in association with local ceramics as early as 3500–3300 BC. During the Early Bronze Age in 3000–2200 BC, this settlement was part of the Kura-Araxes phenomenon.[22]
At Arslantepe, Turkey, around 3000 BCE, there was widespread burning and destruction, after which Kura–Araxes pottery appeared in the area.[23]
According to Geoffrey Summers, the movement of Kura–Araxes peoples into Iran and the Van region, which he interprets as quite sudden, started shortly before 3000 BC, and may have been prompted by the 'Late Uruk Collapse' (end of the Uruk period), taking place at the end of Uruk IV phase c. 3100 BC.[24]
Iranian sites
There are many important Kura-Araxes sites along the Araxes river, south of which is modern Iran. Kultepe, Azerbaijan, in Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic close to Araxes river, has already been known for a long time.[25][26] In Iran, the excavations especially accelerated in the 21st century. Kul Tepe Jolfa, a related site, is seen as an important gateway for Kura-Araxes culture on its way south towards Lake Urmia area. Ancient obsidian trade and distribution are particularly revealing of cultural connections, and Kul Tepe Jolfa was an important transshipment point for the movement of Caucasian obsidian to Iranian sites. This trade was probably conducted by groups of mobile pastoralists from Iran.[27]
Also in Iran downstream the Araxes river, two additional sites from the same period have recently been excavated, Kohne Pasgah and Kohne Tepesi.[28]
Many other Iranian sites have come to light recently and have been excavated already.[28]
Remove ads
Cultural connections
Summarize
Perspective
The Kura–Araxes culture and main other contemporary cultures c. 3000 BC.[29]
Kura–Araxes culture is closely linked to the approximately contemporaneous Maykop culture of the North Caucasus. The two cultures seem to have influenced one another.[30][31]
Economy
The economy was based on farming and livestock-raising (especially of cattle and sheep).[32] They grew grain and orchard crops, and are known to have used implements to make flour. They raised cattle, sheep, goats, dogs, and in later phases, horses.[32]
Before the Kura-Araxes period, horse bones were not found in Transcaucasia. Later, beginning about 3300 BCE, they became widespread, with signs of domestication.[33]
There is evidence of trade with Mesopotamia as well as Asia Minor.[32] It is, however, considered above all to be indigenous to the Caucasus, and its major variants characterized (according to Caucasus historian Amjad Jaimoukha) later major cultures in the region.[32]
It was at this period that the irrigation systems built on the slopes of the Aragats and Geghama mountains were formed and at the sources of canals, artificial water pools and springs, dragon stones (vishapakar) made from one piece basalt were erected. Another prerequisite for unprecedented economic development was copper production. A large number of weapon and tools made of arsenical bronze are attested by both the finds near Yerevan and the stone and clay molds found in various ancient sites of Shengavit civilization (Shengavit, Margahovit, etc.). In the Shengavit ancient site, weight standards similar to those used in the Levant were found, which testify to Armenia's involvement in the newly formed international trade relations in the Early Bronze Age. The weapons that were found were arrows, daggers, battle axes, spears and other weapons made of obsidian, flint, bone and bronze.[34][35][36]
Settlements
Archaeological evidence of inhabitants of the Kura–Araxes culture showed that ancient settlements were found along the Hrazdan river, as shown by drawings at a mountainous area in a cave nearby.[37] Structures in settlements have not revealed much differentiation, nor was there much difference in size or character between settlements,[5] facts that suggest they probably had a poorly developed social hierarchy for a significant stretch of their history. Some, but not all, settlements were surrounded by stone walls.[5] Among the settlements with an area of 1–10 ha, the central ones were surrounded by fortified walls built of stone (Shengavit, Garni, Persi, Khorenia-Javakhk) and of mud-brick (Mokhrablur, Goy-tepe, Gudaberteke), with artificial puddles (Norabats, Kvatskhelebi, Khizannat-gora). The Shengavit fortified wall is noteworthy with its stone foundations, reinforced with rectangular masonry walls and a tiled secret passage leading to Hrazdan river. The central urban areas, which are characterized by dense construction (Shengavit, Mokhrablur, etc.), were surrounded by satellite residences.[citation needed]
The Kura–Araxes built mud-brick houses, originally round, but later developing into subrectangular designs with structures of just one or two rooms, multiple rooms centered around an open space, or rectilinear designs.[5] The mud-brick was made from sandy clay with the help of mold forms and dried in the sun. It was the main building material from which 10 to 11 walls, temples, residential and economic buildings and hydro-engineering structures were built. The foundations of the houses were made of river stones, cracked or unprocessed basalt (Shengavit, Harich, Karaz, Amiranis-gora, etc.), on which mud-brick walls were raised. Round buildings with a diameter of 4–10 m and rectangular floorplan were widespread. The latter had a flat, log roof, and the buildings with round floorplan had primitive roofs of "hazarashen" type, covered with clay mud-bricks with reed, with a skylights hole in the centre of the roof, that solved the issues of light and ventilation of the house (Shengavit, Mokhrablur). The floors were of rammed earth. There were also plaster covered, up to 10 cm thick (Shengavit) and red painted (Garakepek-Tepe) floors. There are found samples of attempts to enliven the monotonous clay walls with decoration and with shaped arrangement of bricks of different color and to enlighten the monotonous appearance of the walls with various colors (Shengavit, Mokhrablur in Nakhijevan, Yanik-tepe, etc).[35]
At some point[when?] the culture's settlements and burial grounds expanded out of lowland river valleys and into highland areas.[38] Although some scholars have suggested that this expansion demonstrates a switch from agriculture to pastoralism and that it serves as possible proof of a large-scale arrival of Indo-Europeans, facts such as that settlement in the lowlands remained more or less continuous suggest merely that the people of this culture were diversifying their economy to encompass crop and livestock agriculture.[38]
Shengavit Settlement is a prominent Kura–Araxes site in the present-day Yerevan area in Armenia. It was inhabited from about 3200 BC cal to 2500 BC cal. Later, in the Middle Bronze Age, it was used irregularly until 2200 BC cal. The town occupied an area of six hectares, which is large for Kura-Araxes sites.
Metallurgy
In the earliest phase of the Kura–Araxes culture, metal was scarce. In comparison, the preceding Leilatepe culture's metalwork tradition was far more sophisticated.[39] Especially after 3000 BC, a significant increase in the use of metal objects occurred at Kura–Araxes sites. Also the variation in copper alloys increased during this time. The rich tomb of a woman at Kvazchela is a good example of this, which is quite similar to the 'royal tomb' from Arslantepe. The use of an arsenical component up to 25% in copper objects resulted in a shiny greyish, silvery colour. So it's quite possible that these unusually high arsenical alloys were intended to imitate silver.[40]
The Kura–Araxes culture would later display "a precocious metallurgical development, which strongly influenced surrounding regions".[41] They worked copper, arsenic, silver, gold,[5] tin, and bronze.[38]
Their metal goods were widely distributed, from the Volga, Dnieper and Don-Donets river systems in the north to Syria and Palestine in the south and Anatolia in the west.
Pottery

Their pottery was distinctive. The spread of their pottery along trade routes into surrounding cultures was much more impressive than any of their achievements domestically.[5] It was painted black and red, using geometric designs. Examples have been found as far south as Syria and Israel, and as far north as Dagestan and Chechnya.[42] The spread of this pottery, along with archaeological evidence of invasions, suggests that the Kura-Araxes people may have spread outward from their original homes and, most certainly, had extensive trade contacts. Jaimoukha believes that its southern expanse is attributable primarily to Mitanni and the Hurrians.[32]
According to Giulio Palumbi (2008), the typical red-black ware of Kura–Araxes culture originated in eastern Anatolia, and then moved on to the Caucasus area. But then these cultural influences came back to Anatolia mixed in with other cultural elements from the Caucasus.[43]
Köhne Shahar is a very large Kura–Araxes archaeological site in Iran located close to the Turkish border. Situated in a narrow valley at the altitude of 1905 m, it was excavated in 2012–2014. It was located on the trade route between Iran and Anatolia.[44]
Viticulture
Viticulture and wine-making were widely practised in the area from the earliest times. Viticulture even goes back to the earlier Shulaveri-Shomu culture.
The earliest evidence of domesticated grapes in the world has been found at Gadachrili Gora, near the village of Imiri, Marneuli Municipality, in southeastern Republic of Georgia; carbon-dating points to the date of about 6000 BC.[45][46]
Grape pips dating back to the V-IVth millennia BC were found in Shulaveri; others dating back to the IVth millennium BC were found in Khizanaant Gora—all in this same 'Shulaveri area' of the Republic of Georgia.[47]
A theory has been suggested by Stephen Batiuk that the Kura-Araxes folk may have spread Vitis vinifera vine and wine technology to the "Fertile Crescent"—to Mesopotamia and the Eastern Mediterranean.[48] The spread of the wine-goblet form, such as represented by the Khirbet Kerak ware, is clearly associated with these peoples. The same applies to the large ceramic vessels used for grape fermentation.
Religion
The bearers of the Shengavit culture had a complex religious system. In the central part of the Mokhrablur settlement III construction horizon, a volume-spatial creation was uncovered: a structure-tower with a rectangular plan (7.4 m × 5.5 m [24 ft × 18 ft]) constructed with hard tuff, in the eastern part of which a 3.9 m-long (13 ft) one-piece basalt altar was placed. Near this stone structure, clay buildings and ash pits were uncovered, in which the ashes of the sacred hearths had been accumulated. Many tufa idols and clay hearths were excavated in the Shengavit settlement.
In 2012 a complex cult system was excavated—a room with a rectangular plan, designed specifically for ritual ceremonies, inside which a clay altar decorated with relief ornaments on its front was uncovered. A statue of an idol was affixed into the altar and goblets for libation were placed in front of the heart. To the right from the stairs, leading to the semi-subterranean room of the shrine, two clay–packed basins were found, in which the ashes from sacred fires were kept. A phallic pendant-idol was found in the shrine, which was the identifying symbol of the priestess. The adjacent room of the complex reflects household activities of the time. A similar cultic complex was found at the ancient site of Pulur (Sakyol). At the inside of the religious structures, terracotta cult hearths unique to the Shengavit culture were located in the altars front. They had diameters of up to a meter, with the edges of the inner space resembling a ship bow divided into three, the upper platforms red-painted and decorated with geometric figures. Statuettes of women and men and worshiped animals like horses, bulls, and rams were found near these hearths. The horseshoe-shaped mobile shrines with ram protomes, threelegged pedestals, phallus-shaped pendant figures were also of religious nature.[49][50]

Burial customs
One of the spheres of religious practice was the burial ritual. Outside the settlements, burial grounds were formed in their immediate vicinity. Both individual tombs with earthen and tiled walls, as well as wide ancestral tombs with stone walls were revealed, in which the deceased (Joghaz) of the upper-class family were sequentially buried. In the final stage of this civilization, collective burials were performed, which included human sacrifices. These tombs contain numerous artifacts that indications of social stratification: gold and silver jewelry, bronze tools and weapons, imported valuable items.[51]
Inhumation practices are mixed. Flat graves are found but so are substantial kurgan burials, the latter of which may be surrounded by dolmen. This points to a heterogeneous ethno-linguistic population (see section below).[citation needed]
Analyzing the situation in the Kura-Araxes period, T. A. Akhundov notes the lack of unity in funerary monuments, which he considers more than strange in the framework of a single culture; for the funeral rites reflect the deep culture-forming foundations and are weakly influenced by external customs. There are non-kurgan and kurgan burials, burials in ground pits, in stone boxes and crypts, in the underlying ground strata and on top of them; using both the round and rectangular burials; there are also substantial differences in the typical corpse position.[52] Burial complexes of Kura–Araxes culture sometimes also include cremation.[53]
Here one can come to the conclusion that the Kura–Araxes culture developed gradually through a synthesis of several cultural traditions, including the ancient cultures of the Caucasus and nearby territories.
Late Kura–Araxes sites often featured Kurgans of greatly varying sizes, with larger, wealthier kurgans surrounded by smaller kurgans containing less wealth. These kurgans also contained a wide assortment metalworks.[4] This trend suggests the eventual emergence of a marked social hierarchy.[4] Their practice of storing relatively great wealth in burial kurgans was probably a cultural influence from the more ancient civilizations of the Fertile Crescent to the south.[4]
In the 3rd millennium BC one particular group of mounds of the Kura–Araxes culture is remarkable for their wealth. This was the final stage of culture's development. These burial mounds are known as the Martqopi (or Martkopi) period mounds. Those on the left bank of the river Alazani are often 20–25 meters high and 200–300 meters in diameter. They contain especially rich artefacts, such as gold and silver jewelry.[54]
Remove ads
Ethno-linguistic makeup
While it is unknown what languages were present in Kura–Araxes, the two most widespread theories suggest a connection with Hurro-Urartian[55][56][57][58] and/or Anatolian languages.[59][60][failed verification][61][62][63] The Kartvelian[64][65] and Northeast Caucasian languages[66] were likely spoken in the region as well.
A 2023 study using Bayesian linguistic phylogenetics in conjunction with archaeological, ethnoecological, and human population genetic data suggests that Proto-Karto-Zan (i.e. Proto-Georgian-Zan) prior to its split into Georgian and Zan was spoken by pre-Kura-Araxes and Kura-Araxes farmers that thrived in the watershed of Mtkvari (Kura) River during the Copper and Bronze Ages.[65]
Remove ads
See also
References
Sources
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads