Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
North China
Region of China From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
North China (Chinese: 华北) is a geographical region of the People's Republic of China, consisting of five provincial-level administrative divisions, namely the direct-administered municipalities Beijing and Tianjin, the provinces Hebei and Shanxi, and the autonomous region Inner Mongolia (although the four prefectures east of the Greater Khingan Range are sometimes regarded as parts of Northeast China).
This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|
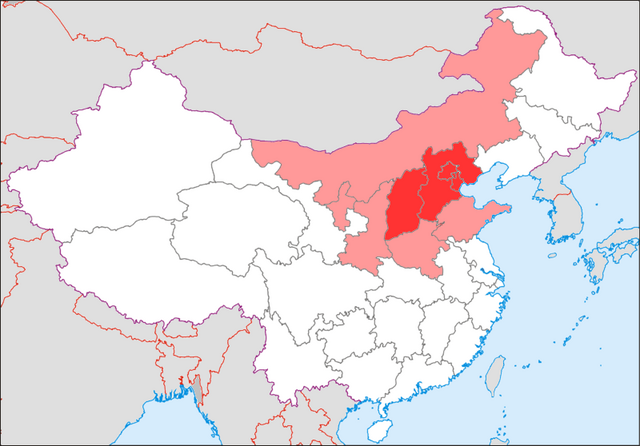
Part of the larger region of Northern China (Beifang), it lies north of the Qinling–Huaihe Line,[3] with its heartland in the North China Plain. Most inhabitants here speak variants of Northern Chinese languages such as Mandarin, which includes the Beijing dialect and its cousin variants. The Beijing dialect is largely the basis of Standard Chinese (or Standard Mandarin), the official language of the People's Republic of China. Jin Chinese and Mongolian are also widely spoken due to the political and cultural history of the area.
Remove ads
History
Summarize
Perspective
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (December 2016) |
In prehistory, the region was home to the Yangshao and Longshan cultures. Peking Man was found near modern-day Beijing.

The main agricultural lands of China lay in the area known as the Central Plain, an area bordered by the Yangtze River to its south and the Yellow River to its north. Further north of the Yellow River lies the Gobi Desert and steppe lands that extend west across Eurasia. This region has long, harsh winters. It has relatively little in the way of water resources.[4]: 132
Despite these challenges, some forms of agriculture have been successful in this region, especially animal husbandry, certainly of horse and camel, and possibly other types of animals. The crops Panicum Miliaceum and Setaria Italica, both types of millet grain, are believed to be indigenous to northern China. Panicum Miliaceum is known from the Cishan culture in Hebei province, recovered as Phytoliths from pits in stratigraphic sections. Sediments from the pits have radiocarbon dates from 8500 to 7500 BCE. Archaeological evidence of charred grains found in early Holocene layers in Hebei province at Nanzhuangtou and Cishan has led scholars to revise the earliest dates associated with millet by about two millennia. Millet sites are concentrated along the boundaries of the Loess and Mongolian Plateau, separated by a mountain chain from the Huabei Plain and the Dongbei Plain, North China's main alluvial plains, located to the west. Millet cultivation was similarly situated relative to the Qinling Mountains at Dadiwan, and the Yitai Mountains at Yuezhuang. Macrofossil evidence (charred grains of foxtail and broomcorn millet) has been recovered from Xinglonggou in Inner Mongolia, Xinle in Liaoning, Cishan in Hebei, and Dadiwan in Gansu, among other sites in Eastern and Central China.[5]
Remove ads
Administrative divisions in the PRC
Remove ads
Cities with urban area over one million in population
- Provincial capitals in bold.
See also
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads

