Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
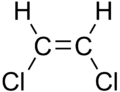
1,2-Dichloroethylene
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
1,2-Dichloroethylene or 1,2-DCE is the name for a pair of organochlorine compounds with the molecular formula C2H2Cl2. The two compounds are isomers, each being colorless liquids with a sweet odor. It can exist as either of two geometric isomers, cis-1,2-dichloroethene or trans-1,2-dichloroethene, but is often used as a mixture of the two. They have modest solubility in water. These compounds have some applications as a degreasing solvent.[1] In contrast to most cis-trans compounds, the Z isomer (cis) is more stable than the E isomer (trans) by 0.4 kcal/mol.[4]
Remove ads
Production, uses and reactions
cis-DCE, the Z isomer, is obtainable by the controlled chlorination of acetylene:
- C2H2 + Cl2 → C2H2Cl2
Industrially both isomers arise as byproducts of the production of vinyl chloride, which is produced on a vast scale. Unlike 1,1-dichloroethylene, the 1,2-dichloroethylene isomers do not polymerize.[1]
trans-1,2-DCE has applications including electronics cleaning, precision cleaning, and certain metal cleaning applications.[5]
Both isomers participate in Kumada coupling reactions. trans-1,2-Dichloroethylene participates in cycloaddition reactions.[6]
Remove ads
Safety and environmental concerns
These compounds have "moderate oral toxicity to rats".[1]
The dichloroethylene isomers occur in some polluted waters and soils, as the decomposition products of trichloroethylene. Significant attention has been paid to their further degradation, e.g. by iron particles.[7][8]
See also
- 1,1-Dichloroethene
- 1,2-Dichloroethane, which is also often abbreviated as 1,2-DCE
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads