Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
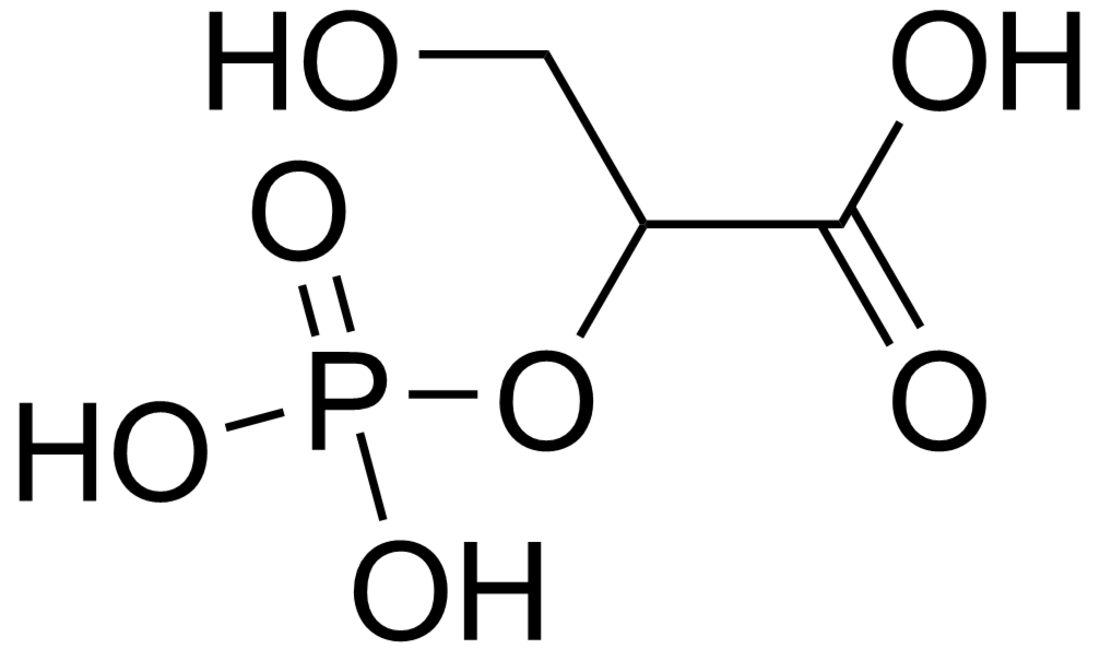
2-Phosphoglyceric acid
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
2-Phosphoglyceric acid (2PG), or 2-phosphoglycerate, is a glyceric acid which serves as the substrate in the ninth step of glycolysis. It is catalyzed by enolase into phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP), the penultimate step in the conversion of glucose to pyruvate.
Remove ads
In glycolysis
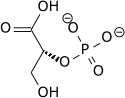
| 3-phospho-D-glycerate | Phosphoglyceromutase | 2-phospho-D-glycerate | Enolase | phosphoenolpyruvate | ||
 |
 |
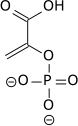 | ||||
| H2O | ||||||
 |
 | |||||
| H2O | ||||||
| Phosphoglyceromutase | Enolase | |||||
Compound C00197 at KEGG Pathway Database. Enzyme 5.4.2.1 at KEGG Pathway Database. Compound C00631 at KEGG Pathway Database. Enzyme 4.2.1.11 at KEGG Pathway Database. Compound C00074 at KEGG Pathway Database.
Click on genes, proteins and metabolites below to link to respective articles.[§ 1]
Glycolysis and Gluconeogenesis edit
- The interactive pathway map can be edited at WikiPathways: "GlycolysisGluconeogenesis_WP534".
Remove ads
See also
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads