Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Aluminium iodide
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Aluminium iodide is a chemical compound containing aluminium and iodine. Invariably, the name refers to a compound of the composition AlI
3, formed by the reaction of aluminium and iodine[4] or the action of HI on Al metal. The hexahydrate is obtained from a reaction between metallic aluminum or aluminum hydroxide with hydrogen iodide or hydroiodic acid. Like the related chloride and bromide, AlI
3 is a strong Lewis acid and will absorb water from the atmosphere. It is employed as a reagent for the scission of certain kinds of C-O and N-O bonds. It cleaves aryl ethers and deoxygenates epoxides.[5]
Remove ads
Structure
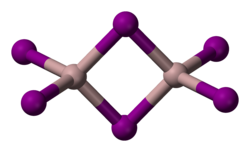
Solid AlI
3 is dimeric, consisting of Al
2I
6, similar to that of AlBr
3.[3] The structure of monomeric and dimeric forms have been characterized in the gas phase.[6] The monomer, AlI
3, is trigonal planar with a bond length of 2.448(6) Å, and the bridged dimer, Al
2I
6, at 430 K is a similar to Al
2Cl
6 and Al
2Br
6 with Al−I bond lengths of 2.456(6) Å (terminal) and 2.670(8) Å (bridging). The dimer is described as floppy with an equilibrium geometry of D2h.
Remove ads
Aluminium(I) iodide
The name "aluminium iodide" is widely assumed to describe the triiodide or its dimer. In fact, a monoiodide also enjoys a role in the Al–I system, although the compound AlI is unstable at room temperature relative to the triiodide:[7]
- 3 AlI → AlI3 + 2 Al
An illustrative derivative of aluminium monoiodide is the cyclic adduct formed with triethylamine, Al
4I
4(NEt
3)
4.
Remove ads
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads