Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
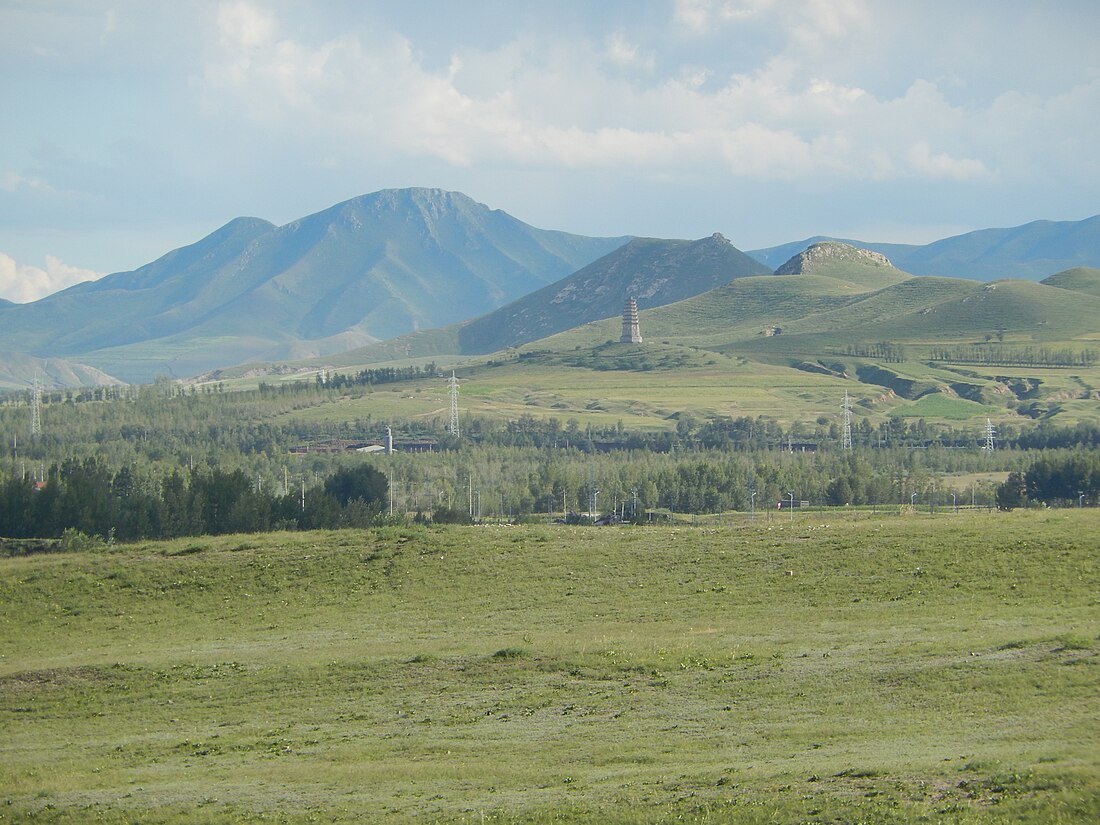
Bairin Left Banner
Banner in Inner Mongolia, China From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Baarin Left Banner (Mongolian: ᠪᠠᠭᠠᠷᠢᠨ ᠵᠡᠭᠦᠨ ᠬᠣᠰᠢᠭᠤ; Chinese: 巴林左旗), or Bairin, is a banner of eastern Inner Mongolia, China, under the administration of the prefecture-level city of Chifeng.[2][3] The banner spans an area of 6,644 square kilometers,[3] and as of 2018, has a population of 340,020.[4] Baarin Mongols live here.[citation needed] The distinct Mongolian dialect of this region is called Baarin.[citation needed] It is located at the intersection of two national highways: China National Highway 303 and 305.
Remove ads
History
Summarize
Perspective

Balin Left Banner has a long history, with archaeological digs dating to the 40th Century BC.[5] Archaeological relics uncovered in the banner are believed to include those of the Hongshan culture and the Fuhe culture.[5]
Around the time China was undergoing the Warring States period, the area of Bairin Left Banner was home to the Shanrong and Donghu people.[5] Later, the area would be home to the Wuhuan and the Xianbei.[5]
During the first few centuries of the Common Era, the area was home to the Khitan people and the Kumo Xi.[5]
In 918 CE, the capital of the Khitan-led Liao Dynasty, Shangjing (Chinese: 上京), was built in present-day Bairin Left Banner.[5] From 918 CE to 938 it was known as Huangdu (皇都).[5]
During the time of the Republic of China, many Han Chinese began moving to the area.[5]
On March 1, 1933, the banner, then known as Lindong County (林东县; 林東縣), was invaded by Japanese forces, who occupied the county until August 10, 1945.[5]
On June 1, 1946, the Chinese Communist Party established its local government in the area, the Lindong Administrative Committee (林东行政委员会; 林東行政委員會).[5]
From the establishment of the People's Republic of China throughout the early 1980s, the area underwent numerous administrative reorganizations, culminating in October 1983, with the placement of the Bairin Left Banner under the prefecture-level city of Chifeng.[5]
Remove ads
Climate
Summarize
Perspective
Baarin Left Banner has a continental, semi-arid climate (Köppen BSk), with very cold and dry winters, hot, somewhat humid summers, and strong winds, especially in spring. The monthly 24-hour average temperature ranges from −13.1 °C (8.4 °F) in January to 22.8 °C (73.0 °F) in July, with the annual mean at 5.89 °C (42.6 °F). The annual precipitation is approximately 370 millimetres (14.6 in), with more than half of it falling in July and August alone. Due to the aridity and elevation, diurnal temperature variation often exceeds 15 °C (27 °F) in spring, averaging 13.7 °C (24.7 °F) annually. There are 2,934 hours of bright sunshine annually, with each of the winter months having over 70% of the possible total, and this percentage falling to 52 in July.
Remove ads
Administrative divisions
Summarize
Perspective
Bairin Left Banner is divided into 2 subdistricts, 7 towns, 2 townships and 2 sums.[9] The banner's seat of government is the town of Lindong.[3]
Demographics
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads