Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Baird's flycatcher
Species of bird From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Baird's flycatcher (Myiodynastes bairdii) is a species of bird in the family Tyrannidae, the tyrant flycatchers. It is found in Ecuador and Peru.[2]
Remove ads
Taxonomy and systematics
Baird's flycatcher has a complicated taxonomic history. It was originally described as Saurophagus bairdii, placing it with the great kiskadee.[3] It was later renamed Tyrannus atrifrons, placing it with the kingbirds, then was renamed Myiodynastes atrifrons, and finally in 1883 achieved its present binomial Myiodynastes bairdii. The species' type locality was described as California, a clear error, and a correction to Guayaquil, Ecuador, was proposed in 1926.[4]
The English name and specific epithet of Baird's flycatcher honor Spencer Fullerton Baird, a 19th-century naturalist and the first curator and later Secretary of the Smithsonian Institution.
Remove ads
Description
Baird's flycatcher is about 23 cm (9.1 in) long; one female weighed 45 g (1.6 oz). The sexes have the same plumage. Adults have a pale sandy brown to whitish forecrown and sandy brown crown with light gray streaks and a usually hidden yellow patch in the center. They have a wide black "mask" that extends to the dusky ear coverts. Their upperparts are mostly olive-brown with a more rufous rump. Their wings are dusky with wide cinnamon-rufous edges on the coverts and flight feathers. Their tail is mostly rufous with some dusky edges on the outermost feathers. Their throat is whitish with faint thin grayish streaks. Their breast is pale creamy yellow with an ochraceous cast and faint thin grayish streaks. Their belly is unmarked pale creamy yellow. They have a chestnut-brown to gray-brown iris, a black bill with a dusky white base to the mandible, and gray to black legs and feet.[5]
Remove ads
Distribution and habitat
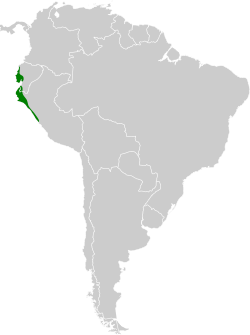
Baird's flycatcher is found in the lowlands from central Manabí Province in west-central Ecuador south to Peru's Lima Department. It inhabits somewhat dry deciduous forest and woodlands, gallery forest, secondary forest, arid scrublands, and towns. In elevation it ranges from sea level to 1,000 m (3,300 ft) in Ecuador and to 1,200 m (3,900 ft) in Peru.[5][6][7]
Behavior
Movement
Baird's flycatcher is a year-round resident across its range.[5]
Feeding
Baird's flycatcher feeds on insects, though details are lacking. It usually forages in pairs. It perches in the forest canopy and takes prey at all levels with short sallies to glean it from vegetation and sometimes the ground.[5][6]
Breeding
The breeding season of Baird's flycatcher has not been defined but includes February. Five nests in Ecuador were made from twigs lined with thin plant stems and roots; all were in cavities in human structures. The clutch size is four to five unmarked white eggs. The incubation period, time to fledging, and details of parental care are not known.[5]
Vocalization
The dawn song of Baird's flycatcher has been described as "wrrr-yeeít...wrrr-yeeít..." repeated several times and sometimes "followed by an ascending jumbled phrase".[6] Another description is "a loud, accelerating series of burry notes, until a final rising chatter" rewTCHI! rewTCHI! reTCHIrewTCHIrewTCHI-tip'ti'chip-awee?". Its call is a "single rewTCHI!".[7]
Remove ads
Status
The IUCN has assessed Baird's flycatcher as being of Least Concern. Its population size is not known and is believed to be stable. No immediate threats have been identified.[1] It is considered generally common in both Ecuador and Peru.[6][7] However, as of 2020 it appears thinly spread south of Peru's central La Libertad Department and its status there is uncertain.[5]
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads