Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Beta Boötis
Star in the constellation Boötes From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
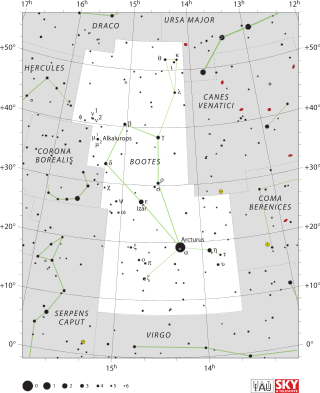
Beta Boötis is a star in the northern constellation of Boötes. Its name is a Bayer designation that is Latinized from β Boötis, and abbreviated Beta Boo or β Boo. The star has the official name Nekkar, pronounced /ˈnɛkɑːr/, which is derived from an Arabic name for 'the Herdsman'.[11] It has an apparent visual magnitude of 3.5,[2] making it visible to the naked eye and one of the brighter members of the constellation. In the modern constellation, it marks the head of Boötes the herdsman.[12] Based upon parallax measurements obtained by the Gaia spacecraft, this star is approximately 235 light-years (72 parsecs) from the Sun.[1] It is drawing closer to the Sun with a radial velocity of −18 km/s.[5] The magnitude of the star is reduced by 0.06 from extinction caused by intervening gas and dust.[6]
Remove ads
Nomenclature
β Boötis (Latinised to Beta Boötis) is the star's Bayer designation.
It bore the traditional name Nekkar or Nakkar derived from the Arabic name for the constellation: Al Baḳḳār 'the Herdsman'.[12] In 2016, the International Astronomical Union organized a Working Group on Star Names (WGSN)[13] to catalogue and standardize proper names for stars. The WGSN approved the name Nekkar for this star on 21 August 2016 and it is now so included in the List of IAU-approved Star Names.[11]
Remove ads
Properties
Summarize
Perspective
This star had its angular diameter measured using interferometric observations by the Navy Precision Optical Interferometer. The angular diameter, together with the star's distance, yield a radius 18 times the radius of the Sun.[8] Beta Boötis is 3.2 times more massive than the Sun. At the estimated age of 320 million years,[7] it has evolved into a giant star with a stellar classification of G8 IIIa Fe-0.5. In this notation, the a indicating a slightly higher luminosity class than a typical giant and the Fe-05 indicating slightly weak spectral lines of iron.[3] The star is radiating around 188[8] times as much luminosity as the Sun from its outer envelope at an effective temperature of 5,000 K.[9] This heat gives it the yellow-hued glow of a G-type star. It has an estimated rotation period of about 200 days and the pole is inclined 28° ± 6° to the plane of the sky.[4]
In 1993, the ROSAT satellite was used to observe an X-ray flare on Beta Boötis, which released an estimated 1.7 × 1032 erg. This was the first such observation for a low-activity star of this type. The flare may be explained by an as yet unobserved M-type dwarf companion star.[14] Beta Boötis is a mild barium star, which is evidence for a white dwarf companion.[15]
Remove ads
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads