Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Bikol languages
Group of languages of the Philippines From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
The Bikol languages or Bicolano languages are a group of Central Philippine languages spoken mostly in the Bicol Peninsula in the southeastern part of Luzon, the neighboring island-province of Catanduanes, and the island of Burias in Masbate.
Remove ads
Internal classification
Summarize
Perspective
Ethnologue
Ethnologue groups the languages of Bikol as follows:
- Bikol
- Coastal Bikol (Northern)
- Inland Bikol (Southern)
- Mount Iriga Agta language
- Albay Bikol languages
- Buhinon language
- Libon language
- West Miraya language
- East Miraya language
- Rinconada Bikol language
- Highland/Sinabukid dialect
- Agta variant
- Iriga variant (standard)
- Lakeside/Sinaranəw dialect
- Baao variant
- Bato variant
- Bula–Pili variant
- Nabua–Balatan variant
- Highland/Sinabukid dialect
- Northern Catanduanes Bikol (Pandan Bikol)
McFarland (1974)
Curtis McFarland gives the following classification for the Bikol languages.[2]
| Bikol |
| |||||||||||||||||||||
Lobel (2000)
Clockwise from top-left: A signage barring people from hanging around the area; A signage barring vendors inside the churchyard; A signage reminding people of proper waste disposal; and a signage barring swimmers in Lake Bato. All are written in the Coastal Bikol language (Naga–Legazpi variant).
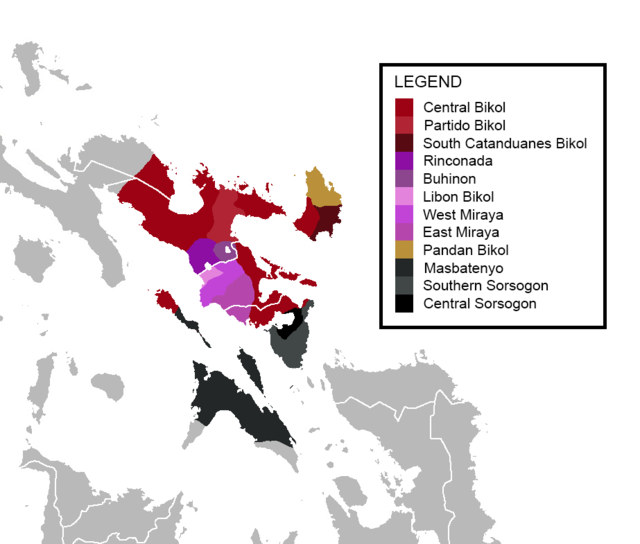
While McFarland (1974) splits Bikol into 11 dialects, Lobel (2000) splits Bikol into 12 different dialects (including Partido Bikol, which McFarland does not differentiate) and 4 main branches.[3]
- Bikol
- Northern Coastal Bikol
- Central Standard – spoken primarily in Naga City, Cam. Sur, Tabaco & Legazpi, Albay and Sorsogon City, Sorsogon. Also recognized (and sometimes understood) in Daet, Camarines Norte and many other areas of Camarines Sur, San Pascual, Masbate on Burias Island, first and second districts of Albay, southwestern coast of Catanduanes, and northeastern Sorsogon.
- Daet area variant
- Naga City area variant
- Tabaco–Legazpi–Sorsogon area variant
- Southwestern and northern town of San Andres and Caramoran, Catanduanes.
- Partido – spoken in the Camarines Sur municipalities of Ocampo, Goa, Tigaon, Lagonoy, Sagñay, and San Jose. This dialect has a mellow intonation and is heavily influenced by Rinconada Bikol.
- Southern Catanduanes – spoken in the southern half of Catanduanes.
- Virac area variant
- Bato area variant
- Baras area variant
- San Miguel variant (transitional to North Catanduanes)
- Central Standard – spoken primarily in Naga City, Cam. Sur, Tabaco & Legazpi, Albay and Sorsogon City, Sorsogon. Also recognized (and sometimes understood) in Daet, Camarines Norte and many other areas of Camarines Sur, San Pascual, Masbate on Burias Island, first and second districts of Albay, southwestern coast of Catanduanes, and northeastern Sorsogon.
- Southern Coastal and Inland Bikol
- Rinconada Bikol – spoken primarily in Iriga City, Baao, Bula, Balatan, Baao and Nabua, Camarines Sur. Also in some parts of Ocampo, Buhi and Pili in Camarines Sur and in parts of Polangui, Albay.
- Buhinon – spoken in Buhi, Camarines Sur. Contains features from both the Bikol of Polangui, Albay and the Iriga variant of Rinconada Bikol.
- Libon – spoken in Libon, Albay.
- West Miraya – spoken in Ligao City, Polangui, Oas, and Pio Duran, Albay.
- East Miraya – spoken in Guinobatan, Camalig, Daraga & Jovellar, Albay and Donsol & Pilar, Sorsogon.
- Central (Guinobatan)
- Far East (Camalig, Daraga)
- Southeast (Jovellar, Albay, Donsol, Pilar)
- Northern Catanduanes
- Pandan Bikol – spoken by about 80,000 people or the northern half of Catanduanes.
- Bisakol
- Northern Sorsogon – spoken in Sorsogon City, Castilla, Casiguran and Juban.
- Southern Sorsogon (also known as Gubat language) – spoken in Gubat; Barcelona, Bulusan, Santa Magdalena, Matnog, Irosin, and Bulan.
- Masbateño – spoken in Masbate City, Mobo, Uson, Dimasalang, Palanas, Masbate, Aroroy on the island of Masbate, all of Ticao Island, and Claveria on the southern half of Burias Island.
- Standard Masbateño
- Ticao Island variant
- Northern Coastal Bikol
Some dialects of Southern Bikol have the close central unrounded vowel /ɨ/ as a reflex of Proto-Austronesian *ə. However, Proto-Austronesian *ə is realized as /o/ in Libon. Two Bikol dialects have unique additional consonants, namely Southern Catanduanes, which has an interdental lateral consonant /l̟/ (also transcribed as l̪͆),[4][5] and Buhi-non, which has the voiced velar fricative /ɣ/.[6]
Remove ads
See also
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads





