Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Bucinator muscle
Muscle From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
The buccinator (/ˈbʌksɪneɪtər/[2][3] or musculus bucinatorius) is a thin quadrilateral muscle occupying the interval between the maxilla and the mandible at the side of the face. It forms the anterior part of the cheek or the lateral wall of the oral cavity.[4]
Remove ads
Structure
It arises from the outer surfaces of the alveolar processes of the maxilla and mandible, corresponding to the three pairs of molar teeth and in the mandible, it is attached upon the bucinator crest posterior to the third molar;[5] and behind, from the anterior border of the pterygomandibular raphe which separates it from the constrictor pharyngis superior.
The fibers converge toward the angle of the mouth, where the central fibers intersect each other, those from below being continuous with the upper segment of the orbicularis oris, and those from above with the lower segment; the upper and lower fibers are continued forward into the corresponding lip without decussation.
Innervation
Motor innervation is from the buccal branch of the facial nerve (cranial nerve VII). Sensory innervation is supplied by the buccal branch (one of the muscular branches) of the mandibular part of the trigeminal (cranial nerve V).[6]
Remove ads
Function
Its purpose is to pull back the angle of the mouth and to flatten the cheek area, which aids in holding the cheek to the teeth during chewing. This action causes the muscle to keep food pushed back on the occlusal surface of the posterior teeth, as when a person chews. By keeping the food in the correct position when chewing, the bucinator assists the muscles of mastication.[4]
It aids whistling and smiling, and in neonates it is used to suckle.
Remove ads
Structures piercing the bucinator
- Parotid duct (Stenson's duct)
- Molar glands of cheeks
- Buccal branch of mandibular nerve
Etymology
A buccinator in classical Latin is a trumpeter,[7] or more precisely, the person who blows the bucina.[7] The name bucina could refer in Roman antiquity to a crooked horn or trumpet,[7] a shepherd's horn[7] or a war-trumpet.[7] Despite its similarity to the classical Latin name for cheek, i.e. bucca,[7] the words bucinator, bucina, and bucinere (to blow the bucina[7]) are not related to bucca,[8] hence some disapproved the spelling buccinator.[8] Although the name bucinator is not derived from bucca, this muscle is also called musculus buccae [9] or musculus buccalis [10] in Latin and muscle of the cheek [9] in English.
The first edition of Terminologia Anatomica,[11] and preceding editions (Nomina Anatomica)[12][13] [14][15] dictate the spelling 'buccinator' with double 'c', with the exception of the Jena Nomina Anatomica, authorized in 1935, which writes 'musculus bucinatorius' [8] with a single 'c'. The second edition of Terminologia Anatomica published in 2019 adopted the spelling 'bucinator' with a single 'c'.[16]
Remove ads
Additional images
- Left maxilla, outer surface
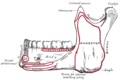
- Mandible, outer surface, side view
- Scheme showing arrangement of fibers of orbicularis oris
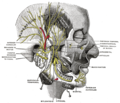
- The internal carotid and vertebral arteries, right side
- Distribution of the maxillary and mandibular nerves and the submaxillary ganglion
- Mandibular division of the trifacial nerve
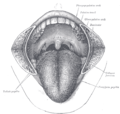
- The mouth cavity: The cheeks have been slit transversely and the tongue pulled forward.
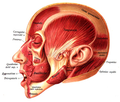
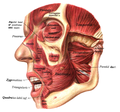
- Position of buccinator muscle (red)
- Position of buccinator muscle (red)
- Position of buccinator muscle (red)
- Buccinator muscle
Remove ads
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads