Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
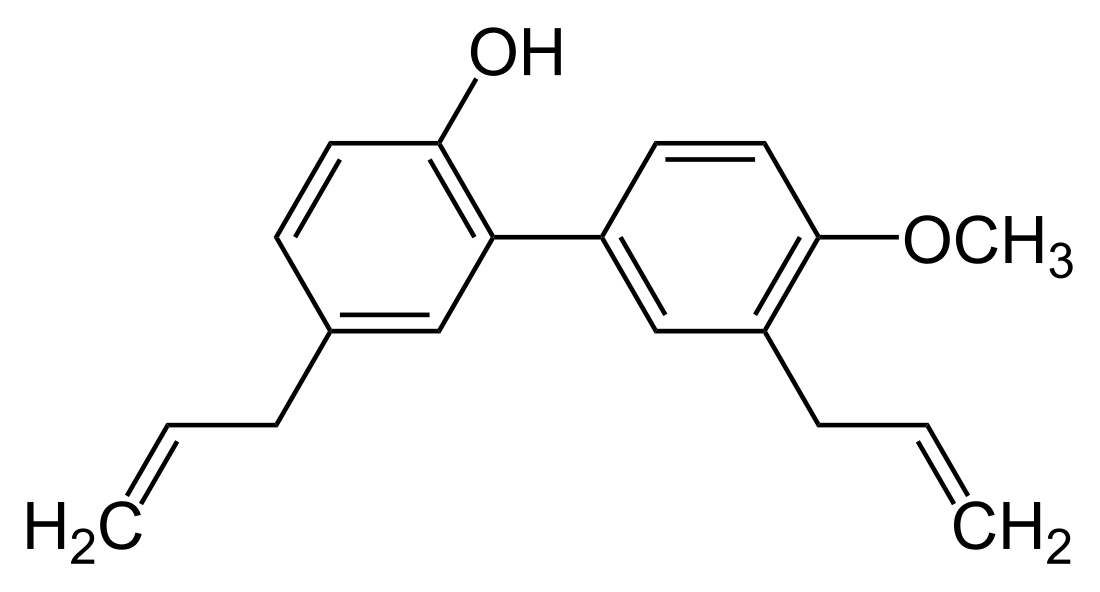
4-O-Methylhonokiol
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
4-O-Methylhonokiol is a neolignan, a type of phenolic compound. It is found in the bark of Magnolia grandiflora[1] and in M. virginiana flowers.[2] Recent studies shows the presence of 4-O-Methylhonokiol in a few other Magnolia species such as; Magnolia officinalis, Magnolia obovata, and Magnolia garrettii.[3]
4-O-Methylhonokiol is a CB2 receptor ligand (Ki = 50 nM), showing inverse agonism and partial agonism via different pathways (cAMP and Ca2+), which potently inhibits osteoclastogenesis.[4] 4-O-Methylhonokiol further attenuates memory impairment in presenilin 2 mutant mice through reduction of oxidative damage and inactivation of astrocytes and the ERK pathway.[5] The different neuroprotective effects reported in rodent models may be mediated via CB2 receptors.[6] 4-O-Methylhonokiol activates CB2 receptors and also inhibits the oxygenation of the major endocannabinoid 2-AG via COX-2 in a substrate-selective manner, thus leading to potential synergistic effects at CB receptors.[7] The same study also provided data that 4-O-methylhonokiol can readily pass the blood–brain barrier.
Remove ads
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads