Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
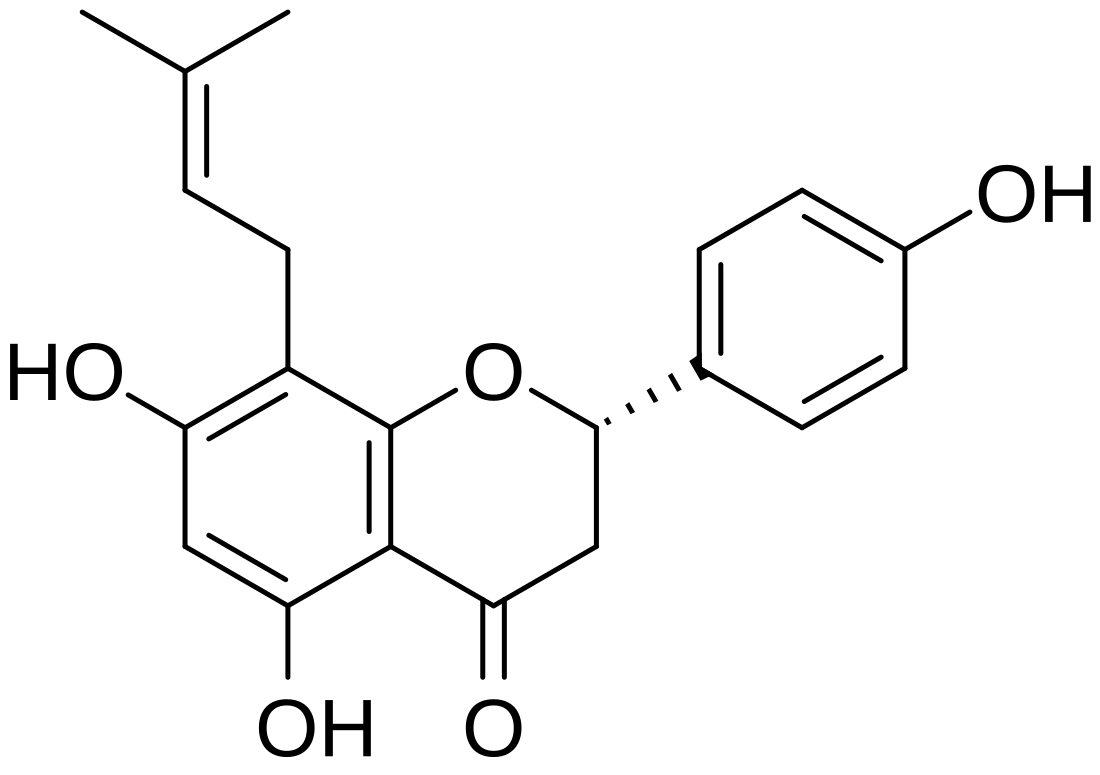
8-Prenylnaringenin
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
8-Prenylnaringenin (8-PN; also known as flavaprenin, (S)-8-dimethylallylnaringenin, hopein, or sophoraflavanone B) is a prenylflavonoid phytoestrogen. It is reported to be the most estrogenic phytoestrogen known.[1] The compound is equipotent at the two forms of estrogen receptors, ERα and ERβ,[2] and it acts as a full agonist of ERα.[3] Its effects are similar to those of estradiol, but it is considerably less potent in comparison.[2]
8-PN is found in hops (Humulus lupulus) and in beer, and is responsible for the estrogenic effects of the former.[2][4] It can be produced from isoxanthohumol in fungal cells cultures,[5] and by flora in the human intestine.[1][6]
Remove ads
Properties
Summarize
Perspective
Estrogenic
8-PN was shown to preserve bone density[1] and has been demonstrated to reduce hot flashes.[1][7] 8-PN also induces the secretion of prolactin, and increases other estrogenic responses.[8] The compound binds to and activates ERα more times[clarification needed] than it does to ERβ.[1][2][9]
This prenylflavanoid has drawn interest in the study of hormone replacement therapy, and it is comparable to some selective estrogen-receptor modulators.[10][11]
In an in vivo study, 8-PN has activated proliferation of mammary cells.[8] At the concentration found in beer, it is unlikely to have an estrogenic effect in breast tissue.[12] Similar to other estrogens, 8-PN induces the expression of the progesterone receptor in various tissues.[8]
Luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) are suppressed by 8-PN, indicating that it possesses antigonadotropic properties.[8] 8-PN adversely affects male sperm.[13] The role 8-PN plays in fertility requires further research.
Other
In an in vitro study, 8-PN and synthetic derivatives demonstrated anticancer properties.[14] More recently, a radioligand binding study showed enhancements in GABAA receptor activity by 8-PN[15]
Prenylflavonoids from hops, including 8-PN, are ingredients in some breast enlargement supplements,[16] though there is no evidence of its effectiveness for this purpose.[17]
Remove ads
Chemistry
The enzyme naringenin 8-dimethylallyltransferase uses dimethylallyl diphosphate and (−)-(2S)-naringenin to produce diphosphate and sophoraflavanone B (8-prenylnaringenin).
The enzyme 8-dimethylallylnaringenin 2'-hydroxylase uses sophoraflavanone B (8-prenylnaringenin), NADPH, H+ and O2 to produce leachianone G, NADP+ and H2O.
Synthesized derivatives of 8-PN are: 7,4′-di-O-methyl-8-prenylnaringenin; 7-O-pentyl-8-prenylnaringenin; 7,4′-Di-O-allyl-8-prenylnaringenin; 7,4′-Di-O-acetyl-8-prenylnaringenin; and 7,4′-Di-O-palmitoyl-8-prenylnaringenin.[14]
8-Neopentylnaringenin and 8-n-heptylnaringenin are synthetic derivatives of 8-PN.[18]
Remove ads
Etymology
There is another compound, 8-isopentenylnaringenin,[1] also known as sophoraflavanone B, from Sophora flavescens, that could properly be called 8-prenylnaringenin by scientific naming convention.[19]
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads