Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Combined gas and gas
Two-turbine, one-shaft marine propulsion From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
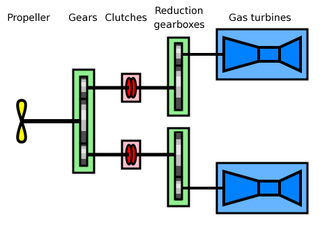
Combined gas turbine and gas turbine (COGAG) is a type of propulsion system for ships using two gas turbines connected to a single propeller shaft. A gearbox and clutches allow either of the turbines to drive the shaft or both of them combined. Marine usage of COGAG systems are similar to those found ashore.[1]
Description
| Combined marine propulsion |
|---|
|
Combined diesel or gas (CODOG) |
A COGAG system consists of two gas turbines, each connected to a reduction gearbox. These are each attached to a coupling with both connected to larger gearbox and then to the ship's propeller.[2]
Remove ads
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages of the system include a large degree of automation along with quick startup time, they are easier to silence and protect from shock.[3] Compared to combined diesel and gas (CODAG) or combined diesel or gas (CODOG), COGAG systems have a smaller footprint but a much lower fuel efficiency at cruise speed and for CODAG systems it is also somewhat lower for high speed dashes.[4] Issues with COGAG systems include their complexity and gearbox issues and high fuel use.[5]
Remove ads
List of COGAG ships
- Kolkata-class guided-missile destroyer (Indian Navy)
- INS Vikrant (aircraft carrier) (Indian Navy)
- Type 22 frigate (Batch 3) (Royal Navy)
- Invincible-class aircraft carrier (Royal Navy)
- Cavour-class aircraft carrier (Italian Navy)
- Asagiri-class destroyer (Japan Maritime Self-Defense Force), and subsequent destroyer classes
- Hyūga-class helicopter destroyer (Japan Maritime Self-Defense Force), helicopter carrier
- Izumo-class helicopter destroyer (Japan Maritime Self-Defense Force), helicopter carrier
- Type 055 destroyer (People's Liberation Army Navy)
- Neustrashimy-class frigate (Russian Navy)
- Sejong the Great-class destroyer (Republic of Korea Navy)
- Skjold-class corvette (Royal Norwegian Navy)
- Arleigh Burke-class destroyer (United States Navy)
- Ticonderoga-class cruiser (United States Navy)
Citations
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads
