Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Dicarboxylic acid
Organic compound with two –COOH groups From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
In organic chemistry, a dicarboxylic acid is an organic compound containing two carboxyl groups (−COOH). The general molecular formula for dicarboxylic acids can be written as HO2C−R−CO2H, where R can be aliphatic or aromatic.[1] In general, dicarboxylic acids show similar chemical behavior and reactivity to monocarboxylic acids.[1] Dicarboxylic acids are usually colorless solids. A wide variety of dicarboxylic acids are used in industry. Adipic acid, for example, is a precursor to certain kinds of nylon. A wide variety of dicarboxylic acids are found in nature. Aspartic acid and glutamic acid are two amino acids found in all life. Succinic and fumaric acids are essential for metabolism. A large inventory of derivatives are known including many mono- and diesters, amides, etc.[2]
Remove ads
Partial list of saturated dicarboxylic acids
Some common or illustrative examples
Remove ads
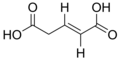
Unsaturated dicarboxylic acids
Remove ads
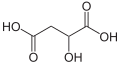
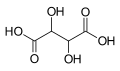
Substituted dicarboxylic acids
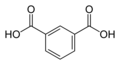
Aromatic dicarboxylic acids
Terephthalic acid is a commodity chemical used in the manufacture of the polyester known by brand names such as PET, Terylene, Dacron and Lavsan.
Remove ads
See also
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads