Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
PFP (enzyme)
Class of enzymes From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
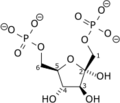
Diphosphate—fructose-6-phosphate 1-phosphotransferase also known as PFP is an enzyme of carbohydrate metabolism in plants and some bacteria. The enzyme (EC 2.7.1.90) catalyses the reversible interconversion of fructose 6-phosphate and fructose 1,6-bisphosphate using inorganic pyrophosphate as the phosphoryl donor:
- diphosphate + D-fructose 6-phosphate phosphate + D-fructose 1,6-bisphosphate
In plants, the PFP is located in the cytosol of the cell and is strongly activated by the signal molecule fructose 2,6-bisphosphate.
PFP is an exclusively cytosolic enzyme that catalyses the phosphorylation of fructose-6-phosphate to fructose-1,6-bisphosphate in the glycolytic direction, and the de-phosphorylation of fructose-1,6-bisphosphate to fructose-6-phosphate in the gluconeogenic reaction. Reeves[2] first isolated PFP from Entamoeba histolytica, a lower eukaryote. The first plant PFP isolated was from the leaves of pineapples by Carnal and Black[3] and it has since been isolated from a variety of plant species and tissues.[4]
Remove ads
Nomenclature
This enzyme belongs to the family of transferases, specifically those transferring phosphorus-containing groups (phosphotransferases) with an alcohol group as acceptor. The systematic name of this enzyme class is diphosphate:D-fructose-6-phosphate 1-phosphotransferase. Other names in common use include:
- 6-phosphofructokinase (pyrophosphate),
- inorganic pyrophosphate-dependent phosphofructokinase,
- inorganic pyrophosphate-phosphofructokinase,
- pyrophosphate-dependent phosphofructo-1-kinase, and
- pyrophosphate-fructose 6-phosphate 1-phosphotransferase,
- pyrophosphate-fructose 6-phosphate phosphotransferase
Remove ads
See also
References
Further reading
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads