Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Geography of the Cayman Islands
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
The Cayman Islands are a British dependency and island country. It is a three-island archipelago in the Caribbean Sea, consisting of Grand Cayman, Cayman Brac, and Little Cayman. Georgetown, the capital of the Cayman Islands is 438 km (272 mi) south of Havana, Cuba,[1] and 504 km (313 mi) northwest of Kingston, Jamaica,[2] northeast of Costa Rica, north of Panama and are between Cuba and Central America. Georgetown's geographic coordinates are 19.300° north, 81.383° west.[2]
The Cayman Islands have a land area of 264 km2 (102 sq mi) approximately 1.5 times the size of Washington, D.C., and just 3 km2 (1.2 sq mi) larger than Saint Kitts and Nevis. The Cayman Islands have a coastline of 160 km (99 mi). The Cayman Islands make a maritime claim of a 200-nautical-mile (370.4 km; 230.2 mi) exclusive fishing zone and a territorial sea of 12 nautical miles (22.2 km; 13.8 mi).[3][4]
Remove ads
Geology
The islands are located on the Cayman Rise which forms the northern margin of the Cayman Trough. The trough is the deepest point in the Caribbean Sea and forms part of the tectonic boundary between the North American Plate and the Caribbean Plate. The Cayman Rise extends from southeastern Cuba along the northern margin of the Cayman Trough toward Costa Rica and resulted from Paleocene to Eocene island arc formation with associated volcanism along an extinct subduction zone.[5] The islands are formed of marine limestone and dolomite that was uplifted during the late Miocene epoch.[6] Due to the islands' location, the Cayman Islands do get earthquakes.
Remove ads
Climate
Summarize
Perspective
The Cayman Islands have a tropical wet and dry climate, with a wet season from May to December, and a dry season that runs from January to April. Terrain is mostly a low-lying limestone base surrounded by coral reefs.
Besides earthquakes another major natural hazard is the tropical cyclones that form during the Atlantic hurricane season from June to November.
Remove ads
Environmental issues
An important environmental issue is the lack of fresh water resources. Drinking water supplies must be met by rainwater catchment and desalination. There is also a problem with trash washing up on the beaches or being deposited by there by residents. The Cayman Islands have no recycling or waste treatment facilities.[13]
Natural resources
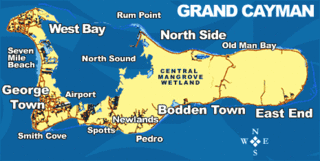

Natural resources include fish and a climate and beaches that foster tourism, which is the islands' major industry. A 2012 estimate of land use determined that the Cayman Islands' had 0.83 percent arable land and 2.08 percent permanent crops.
In Cayman Islands forest cover is around 53% of the total land area, equivalent to 12,720 hectares (ha) of forest in 2020, down from 13,130 hectares (ha) in 1990. In 2020, naturally regenerating forest covered 12,720 hectares (ha) and planted forest covered 0 hectares (ha). Of the naturally regenerating forest 0% was reported to be primary forest (consisting of native tree species with no clearly visible indications of human activity). For the year 2015, 0% of the forest area was reported to be under public ownership, 12% private ownership and 88% with ownership listed as other or unknown.[14][15]
Remove ads
Districts
The territory is subdivided into six districts that are governed by district managers and that have a role as electoral districts and as regional units for statistics. Five of the districts are located on the main island, Grand Cayman. The sixth, Sister Islands, comprises the islands of Little Cayman and Cayman Brac.
The population is concentrated in the three (south-)western districts George Town (capital), West Bay, and Bodden Town. Those have a population density many times higher than all remaining districts.
Remove ads
Extreme points
- Northernmost point – Booby Point, Cayman Brac
- Easternmost point – North East Point, Cayman Brac
- Southernmost point – Great Pedro Point, Grand Cayman
- Westernmost point – North West Point, Grand Cayman
- Lowest point – Caribbean Sea (0m)
- Highest point – 1 km SW of The Bluff, Cayman Brac (50m)
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads

