Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
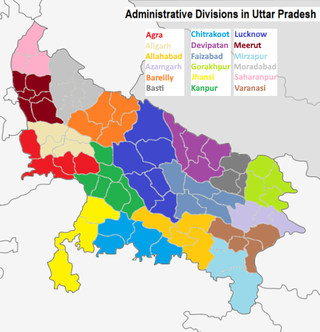
Administrative divisions of Uttar Pradesh
Divisions in Uttar Pradesh From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
The northern Indian state of Uttar Pradesh, which borders Nepal, comprises 18 administrative divisions. Within these 18 divisions, there are a total of 75 districts.[1] The following table shows the name of each division, its administrative capital city, its constituent districts, and a map of its location.
This article needs additional citations for verification. (December 2023) |
Remove ads
Current divisions
Summarize
Perspective
Currently 75 districts are divided into 18 divisions.
| Divisions | Formed | Headquarters | Districts | Map |
| Agra division | Pre-Independence | Agra |  | |
| Aligarh division | 17 April 2008 (Separated From Agra division) | Aligarh |  | |
| Ayodhya division | Pre-Independence | Ayodhya | 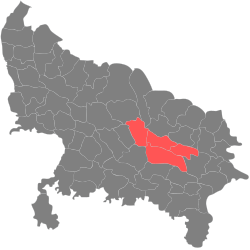 | |
| Azamgarh division | 15 November 1994 (Separated from Gorakhpur and Varanasi divisions) | Azamgarh | 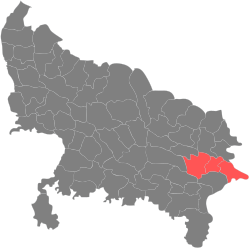 | |
| Bareilly division | Pre-Independence | Bareilly | 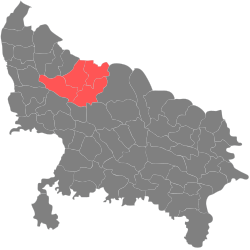 | |
| Basti division | 14 June 1997 (Separated from Gorakhpur division) | Basti |  | |
| Chitrakootdham division | 21 November 1997 (Separated from Jhansi division) | Banda |  | |
| Devipatan division | 21 November 1997 (Separated from Ayodhya division) | Gonda |  | |
| Gorakhpur division | Pre-Independence | Gorakhpur |  | |
| Jhansi division | Pre-Independence | Jhansi | 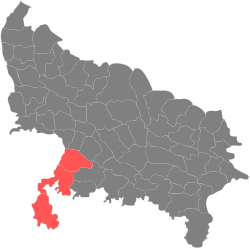 | |
| Kanpur division | 15 August 1988 (Separated from Allahabad division) | Kanpur |  | |
| Lucknow division | Pre-Independence | Lucknow | 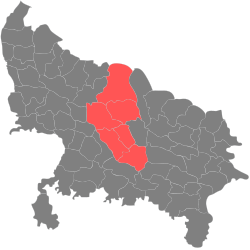 | |
| Meerut division | Pre-Independence | Meerut |  | |
| Moradabad division | 14 September 1980 (Separated from Bareilly Division) | Moradabad |  | |
| Prayagraj division | Pre-Independence | Prayagraj | 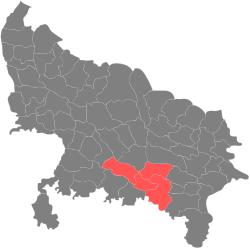 | |
| Saharanpur division | 21 November 1997 (Separated from Meerut Division) | Saharanpur |  | |
| Varanasi division | Pre-Independence | Varanasi | 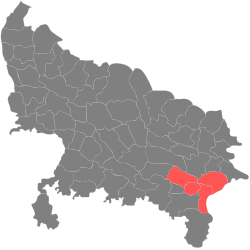 | |
| Vindhyachal division | 14 June 1997 (Separated from Varanasi division) | Mirzapur |  |
Remove ads
Original Divisions with their original districts during Independence
Summarize
Perspective
During the formation of State of Uttar Pradesh, it consisted of 49 districts divided into 10 divisions.
| Divisions | Headquarters | Districts |
| 2nd or Agra division | Agra | |
| 10th or Ayodhya division (Faizabad division) | Faizabad | |
| 3rd or Bareilly division (Rohilkhand division) | Bareilly | |
| 7th or Gorakhpur division | Gorakhpur | |
| 5th or Jhansi division | Jhansi | |
| 9th or Lucknow division | Lucknow | |
| 8th or Kumaon division | Nainital | |
| 1st or Meerut division | Meerut | |
| 4th or Prayagraj division (Allahabad division) | Allahabad | |
| 6th or Varanasi division (Benaras division) | Benaras |
There were three native principalities (Rampur State, Benaras State and Tehri Garhwal State) which existed outside the regular revenue administration which were later incorporated into it. Rampur State was made a district and was transferred to Rohilkhand division and later to newly formed Moradabad division. Benaras State was integrated with Varanasi district and Varanasi division. Tehri Garhwal State was carved into several hilly districts and a new Garhwal division was created in 1969 with Pauri district as its headquarters along with transferring of Dehradun district from Meerut division to Garhwal division. Pratapgarh district was transferred from Ayodhya division to Prayagraj division in 1988. Ballia district was transferred from Varanasi division when Azamgarh division was formed after separation from Gorakhpur division in 1994. When Uttarakhand got separated from Uttar Pradesh in 2000, Kumaon division and Garhwal division were incorporated into it along with newly formed Haridwar district which was transferred from Saharanpur division to Garhwal division.
Remove ads
Divisional Officers
Summarize
Perspective
Almost every department in Uttar Pradesh Government has its divisional level officers who supervise, review and guide its district level officers. There are many important divisional level committees and meetings chaired by concerned Divisional Commissioner which take inter-departmental decisions such as divisional crime and law & order review meeting, divisional security committee, divisional level monitoring committee for development work, regional transport authority etc. Every divisional headquarter district has a state guest-house known as Circuit House.
Remove ads
Demand for integrated Divisional Office Complexes
After the state government approved integrated divisional office complexes for Gorakhpur and Varanasi division which will have offices of all divisional officers under one roof.[2] The opposition alleged favouritism for these two divisions as they are located in Chief Minister’s and Prime Minister’s constituencies.
See also
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads
