Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Magnesium stearate
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
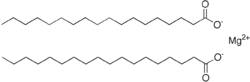
Magnesium stearate is a metal-organic compound, a salt of magnesium and stearic acid with the idealized chemical formula (C17H35CO2)2Mg. It is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid. Magnesium stearate is a white, water-insoluble powder. Its applications exploit its softness, insolubility in many solvents, and low toxicity. It is used as a release agent and as a component or lubricant in the production of pharmaceuticals and cosmetics.[1]
Remove ads
Speciation
Anhydrous magnesium stearate is known, with the formula (C17H35CO2)2Mg. More important are the hydrates, which have the formula (C17H35CO2)2Mg(H2O)n where n = 1, 2, 3. The latter has been characterized by X-ray crystallography.[2]
Manufacturing
Magnesium stearate is produced by the reaction of sodium stearate with magnesium salts or by treating magnesium oxide with stearic acid.[1][3]
Uses
Magnesium stearate is the most widely used additive in pharmaceuticals.[2] It is also used in food preparations as an anti-adherent and anticaking agent.[4] [5] in the manufacture of medical tablets, capsules and powders.[6] In this regard, the substance is also useful because it has lubricating properties, preventing ingredients from sticking to manufacturing equipment during the compression of chemical powders into solid tablets; magnesium stearate is the most commonly used lubricant for tablets.[7] However, it might cause lower wettability and slower disintegration of the tablets and slower and even lower dissolution of the drug.[8]
Magnesium stearate can also be used efficiently in dry coating processes.[9][10][11]
In the production of pressed candies, magnesium stearate serves as a release agent. It is also used to bind sugar in hard candies such as mints.[12]
Occurrence
When produced by soap and hard water, magnesium stearate and calcium stearate both form a white solid insoluble in water, and are collectively known as soap scum. This scum is a major component of the common “ring” of scum around a drained bathtub.
Safety
Magnesium stearate is generally considered safe for human consumption at levels below 2500 mg per kg of body weight per day[13] and is classified in the United States as generally recognized as safe (GRAS). In 1979, the FDA's Subcommittee on GRAS Substances (SCOGS) reported, "There is no evidence in the available information on ... magnesium stearate ... that demonstrates, or suggests reasonable grounds to suspect, a hazard to the public when they are used at levels that are now current and in the manner now practiced, or which might reasonably be expected in the future."[14]
Remove ads
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads