Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
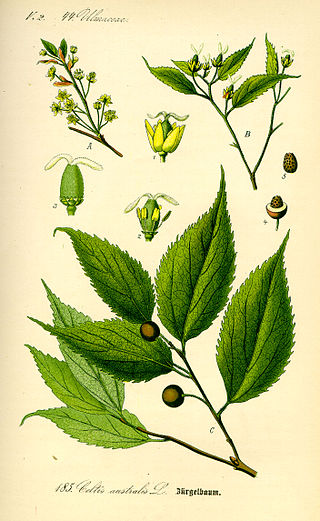
Celtis australis
Species of flowering plant From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Celtis australis, the European nettle tree, European hackberry, Mediterranean hackberry, lote tree, southern nettle tree, or honeyberry,[3][4] is a deciduous tree native to Southern Europe, North Africa, and Asia Minor.
Remove ads
Description
The tree can grow to 25 metres (82 ft) in height, though 10 m (33 ft) is more common in cooler climates. The bark is smooth and grey, almost elephantine.[5]
The alternate leaves are narrow and sharp-toothed, rugose above and tomentose below, 5–15 centimetres (2–6 in) long and dark grey/green throughout the year, fading to a pale yellow before falling in autumn.
The apetalous wind-pollinated flowers are perfect (hermaphrodite, having both male and female organs), small and green, either singly or in small clusters.
The fruit is a small, dark-purple berry-like drupe, 1 cm wide, hanging in short clusters.
Remove ads
Distribution and habitat
The plant prefers light well-drained (sandy) and medium (loamy) soils, including those nutritionally poor; it can tolerate drought but not shade. The Mediterranean climate is especially suitable for the plant but it can tolerate colder climate (USDA Zone 7B). An article on Nettle tree cultivation is brought down in Ibn al-'Awwam's 12th-century agricultural work, Book on Agriculture.[6]
The tree was introduced to England in 1796.[7]
Remove ads
Ecology
The drupes are extremely popular with birds and other wildlife.
Uses
Summarize
Perspective
Trade names for the species include nettle wood and brimji.[8] It is often planted as an ornamental as it is long-living and resistant to air pollution.
The fruit is sweet and edible raw or cooked. The leaves and fruit are astringent, lenitive, and stomachic. A decoction of both the leaves and fruit is used in the treatment of amenorrhoea, heavy menstrual and inter-menstrual bleeding, and colic. The decoction can also be used to astringe the mucous membranes in the treatment of diarrhea, dysentery, and peptic ulcers. A yellow dye is obtained from the bark.
The wood is very tough, pliable, durable, and widely used by turners; the flexible, thin shoots are used as walking sticks.
Secondary metabolites
The leaves of Celtis australis are a rich source of flavonoid C-glycosides.[9][10] Young leaves of C. australis from Northern Italy were found to contain the highest amounts of phenolics per gram dry weight. Amounts rapidly decreased until mid-May and after this date the level of phenolics fluctuated but showed no discernible trend. This general trend of high amounts of phenolics in the early growing season and a fast decline affected both caffeic acid derivatives and flavonoids.[11]
Remove ads
In culture
Celtis australis is supposed to have been the Lotus of the ancients, whose fruit Herodotus, Dioscorides, and Theophrastus describe as sweet, pleasant, and wholesome. Homer has Ulysses refer to the "Lotus-eaters" and the "lotus" in Odyssey, Book IX.[12]

In Islamic tradition, hackberry trees are considered holy and amulets made from their wood are employed to exorcise demons. The hackberry trees on the Temple Mount in Jerusalem are said to be the oldest in the world.[13]
A large specimen planted in 1550 stands before the church in the village perché of Fox-Amphoux in the Provence region of southern France. The tree was 18 m (59 ft) in height with a circumference at breast height of 5 m in 2013.[14]
The fruit and its effects are described in Alfred Tennyson's poem The Lotos-Eaters.
Remove ads
Gallery
- In Muntić, Croatia, planted in the early 16th century
- In Panchkhal, Nepal
- Flower
- Autumn leaves
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads