Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
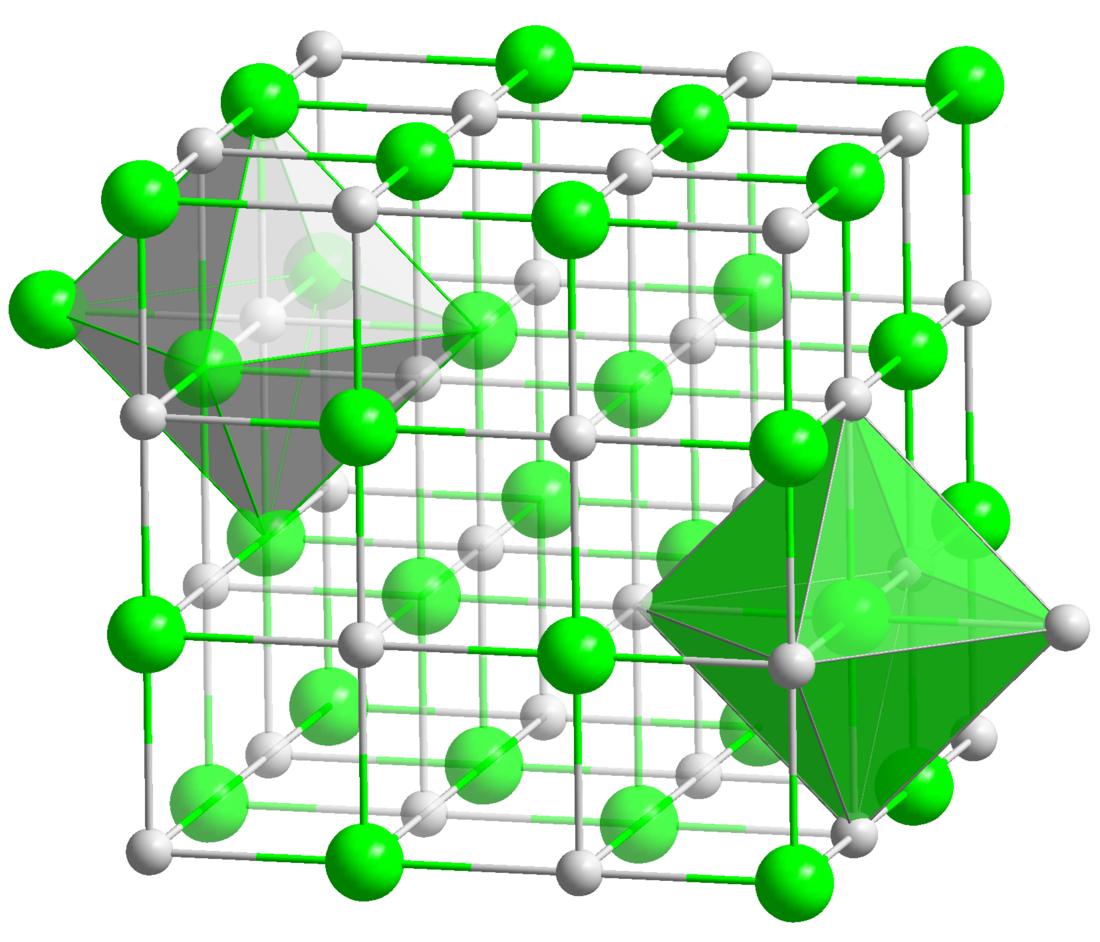
Gadolinium(III) nitride
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Gadolinium(III) nitride is a binary inorganic compound of gadolinium and nitrogen with the chemical formula GdN.[2]
Remove ads
Preparation
Gadolinium(III) nitride can be prepared by the direct reaction of gadolinium metal and nitrogen gas at 1600 °C and at a pressure of 1300 atm.[3]
- 2Gd + N2 → 2GdN
Properties
Physical
Gadolinium(III) nitride forms a black powder.[4] It is isomorphous with sodium chloride[5] with the space group of Fm3m.[6]
Chemical
Gadolinium(III) nitride hydrolyzes in humid air to form gadolinium(III) hydroxide and ammonia.[7] It is insoluble in water but soluble in acids.[8]
Uses
Gadolinium(III) nitride is used as a semiconductor.[9] It can also be used as a magnetic material, a catalyst in chemical reactions and a component in neutron converters for radiation detectors.[8]
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads