Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
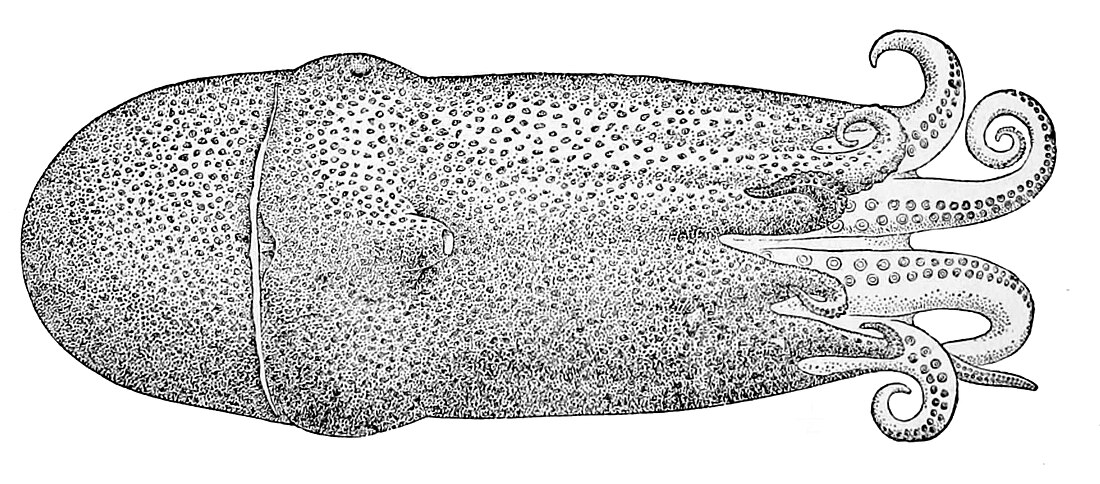
Seven-arm octopus
Species of cephalopod From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
The seven-arm octopus (Haliphron atlanticus), also known as the blob octopus or sometimes called septopus, is one of the two largest known species of octopus; the largest specimen ever discovered had an estimated total length of 3.5 m (11 ft) and mass of 75 kg (165 lb).[3][4] The only other similarly large extant species is the giant Pacific octopus, Enteroctopus dofleini.
The genera Alloposina (Grimpe, 1922), Alloposus (Verrill, 1880) and Heptopus (Joubin, 1929) are junior synonyms of Haliphron, a monotypic genus in the monotypic family Alloposidae, part of the superfamily Argonautoidea in the suborder Incirrata of the order Octopoda.[2]
Remove ads
Description

The seven-arm octopus is so named because in males, the hectocotylus (a specially modified arm used in egg fertilization) is coiled in a sac beneath the right eye. Due to this species' thick, gelatinous tissue, the arm is easily overlooked, giving the appearance of just seven arms. However, like other octopuses, it actually has eight.[5]
Remove ads
Distribution
H. atlanticus is found worldwide in tropical and temperate waters.[6]
The type specimen was collected in the Atlantic Ocean at 38°N 34°W (west of the Azores). It is deposited at the University of Copenhagen Zoological Museum.[7]
Since then, several specimens have been caught throughout the Atlantic, as far as the Azores archipelago[8] and near South Georgia Island.[9]
In 2002, a single specimen of giant proportions was caught by fishermen trawling at a depth of 920 m (3,020 ft) off the eastern Chatham Rise, New Zealand. This specimen, the largest of this species and of all octopuses, was the first validated record of Haliphron from the South Pacific. It had a mantle length of 0.69 m (2.3 ft), a total length of 2.90 m (9.5 ft), and a weight of 61.0 kg (134.5 lb), although it was incomplete.[3][4]
There have also been multiple sightings of H. atlanticus in Monterey Bay in the Northeast Pacific Ocean.[10]
Remove ads
Ecology
Isotopic,[9] photographic and video evidence[8] have shown complex interactions between H. atlanticus and jellyfish and other gelatinous zooplankton, from feeding to protection, respectively.
Predators of H. atlanticus include the blue shark, sperm whale, and swordfish.[11][12][13][14][15]
Beak morphology
Lower (left) and upper beaks of female Haliphron atlanticus (estimated 150 mm ML) in lateral view
 3D red cyan glasses are recommended to view this image correctly.
3D red cyan glasses are recommended to view this image correctly.
See also
References
Further reading
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads