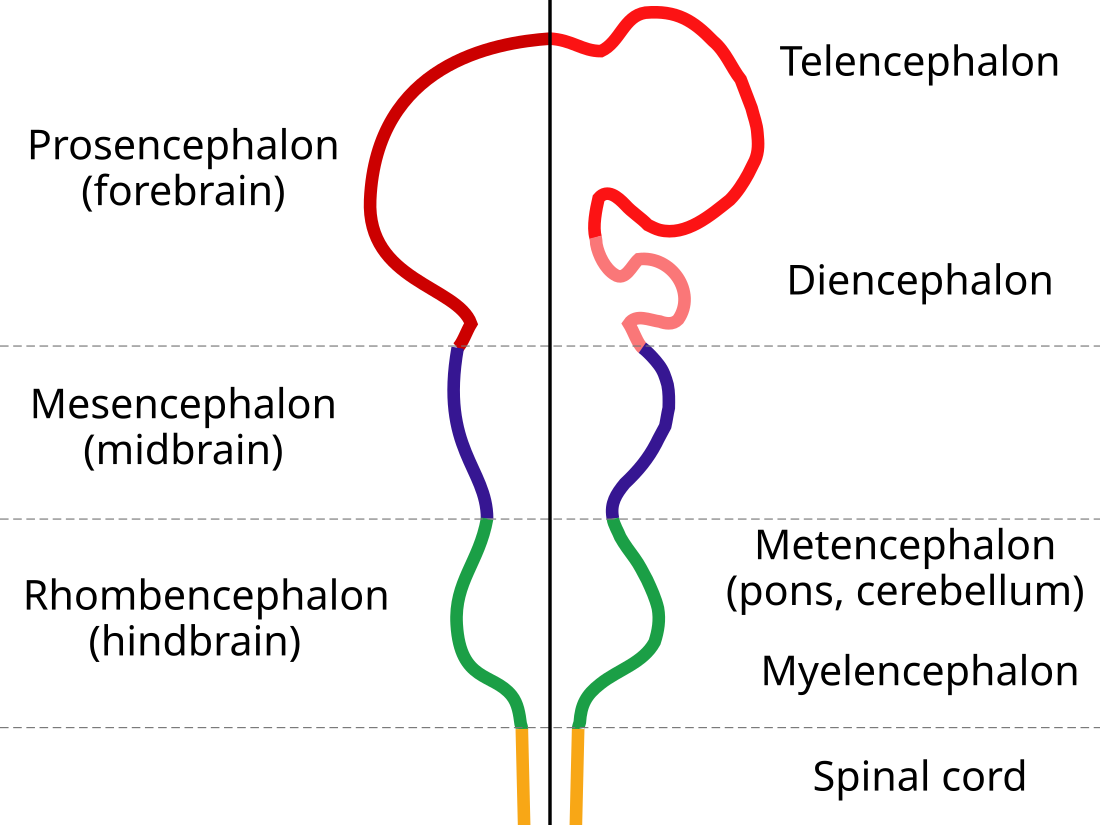Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Hindbrain
Part of the embryonic brain From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
The hindbrain, rhombencephalon (shaped like a rhombus) is a developmental categorization of portions of the central nervous system in vertebrates. It includes the medulla, pons, and cerebellum. Together they support vital bodily processes.[1]
Remove ads
Metencephalon
Rhombomeres Rh3-Rh1 form the metencephalon.
The metencephalon is composed of the pons and the cerebellum; it contains:
- a portion of the fourth (IV) ventricle,
- the trigeminal nerve (CN V),
- abducens nerve (CN VI),
- facial nerve (CN VII),
- and a portion of the vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII).
Myelencephalon
Rhombomeres Rh8-Rh4 form the myelencephalon.
The myelencephalon forms the medulla oblongata in the adult brain; it contains:
- a portion of the fourth ventricle,
- the glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX),
- vagus nerve (CN X),
- accessory nerve (CN XI),
- hypoglossal nerve (CN XII),
- and a portion of the vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII).
Evolution
The hindbrain is homologous to a part of the arthropod brain known as the sub-oesophageal ganglion, in terms of the genes that it expresses and its position in between the brain and the nerve cord.[2] It has been suggested that the hindbrain first evolved in the urbilaterian—the last common ancestor of chordates and arthropods—between 570 and 555 million years ago.[2][3]
Hindbrain diseases
A rare brain disease of the cerebellum is rhombencephalosynapsis characterized by an absent or partially formed vermis. Symptoms can include truncal ataxia. The disorder is a main feature of Gomez-Lopez-Hernandez syndrome.
References
Further reading
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads