Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Hotend
Fused-filament 3D printer component From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
A hotend is a component of fused filament deposition 3D printers. Its purpose is to heat up and melt filament material for depositing into the intended shape.
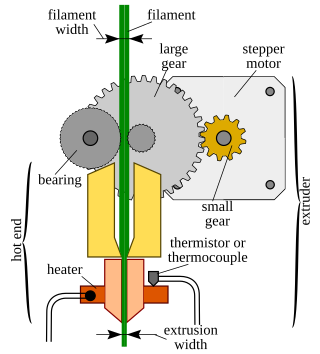
The hotend is usually made of a bulk heat-conductive material with an internal resistive heater, coupled with a thermistor or thermocouple for precise temperature control. In common desktop 3D printer designs, the heater is located near the nozzle, and a heatsink is attached upstream (on the colder side).[1] A heatbreak component made of dissimilar metals (bimetal) can be used to limit heat transfer to the cold filament above, increasing the controllability of the melted filament.[2][3]
Remove ads
Nozzle
The nozzle is an interchangeable tip attached to the hotend with a small diameter hole through which the melted filament is extruded. In desktop fused filament deposition printers, different sized nozzle holes can be used to balance between printing speed and precision. Common large sized ones (1.0mm) extrude more material per travel length whereas smaller sized nozzles (0.2mm) result in higher quality.[4]
In consumer desktop printers, the nozzle is often made of brass or stainless steel. Desired characteristics include abrasion resistance, as the nozzle frequently slides across the printed object, and thermal conductivity. To improve thermal conductivity, nozzles can be perforated with multiple holes on the intake side, forming an internal structure with more contact area between the heated nozzle body and the filament.[5] This results in a higher maximum volumetric flow, which can improve printing speed.
Remove ads
See also
- 3D printer cabinet, encapsulation that can provide better control of the environment around a 3D printer
- 3D printer extruder, feeding mechanism for filament in certain types of 3D printers
- PTC heating element, type of heating element with self-regulating properties to prevent thermal runaway
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads
