Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Injun (satellite)
Series of satellites by the University of Iowa From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
The Injun program was a series of six satellites designed and built by researchers at the University of Iowa to observe various radiation and magnetic phenomena in the ionosphere and beyond.
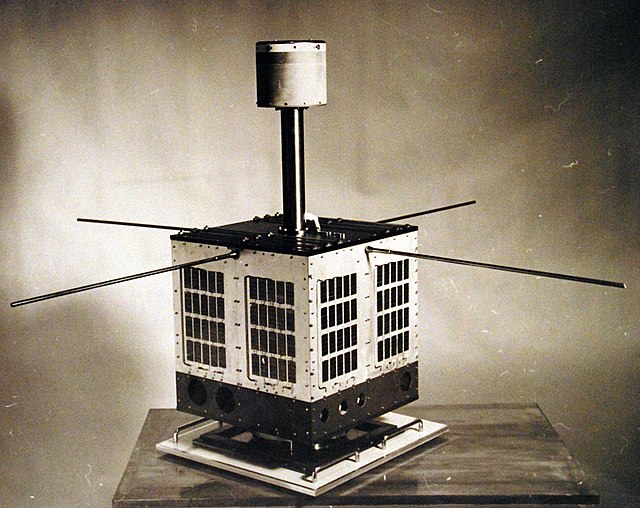
The design specifics of the satellites had little in common, though all were solar-powered and the first five used magnetic stabilization to control spacecraft attitude. (The last in the series was spin-stabilized.) Instruments included particle detectors of varying types, magnetometers, and photometers for observing auroras.[1] The last three satellites were launched as part of the Explorer program of NASA.
In spite of various hardware difficulties and the loss of Injun 2 due to an upper stage failure, the program was generally successful. In particular, they produced data on the Van Allen radiation belts including electrical convection in the magnetosphere,[2] and the radiation after effects of the Starfish Prime high-altitude nuclear test.[3]
Remove ads
Launch
Remove ads
See also
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads






