Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
L-serine ammonia-lyase
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
The enzyme L-serine ammonia-lyase (EC 4.3.1.17) catalyzes the chemical reaction
- L-serine = pyruvate + NH3 (overall reaction)
- (1a) L-serine = 2-aminoprop-2-enoate + H2O
- (1b) 2-aminoprop-2-enoate = 2-iminopropanoate (spontaneous)
- (1c) 2-iminopropanoate + H2O = pyruvate + NH3 (spontaneous)
This enzyme belongs to the family of lyases, specifically ammonia lyases, which cleave carbon-nitrogen bonds. The systematic name of this enzyme class is L-serine ammonia-lyase (pyruvate-forming). Other names in common use include serine deaminase, L-hydroxyaminoacid dehydratase, L-serine deaminase, L-serine dehydratase, and L-serine hydro-lyase (deaminating). This enzyme participates in glycine, serine, threonine and cysteine metabolism. It employs one cofactor, pyridoxal phosphate.
Remove ads
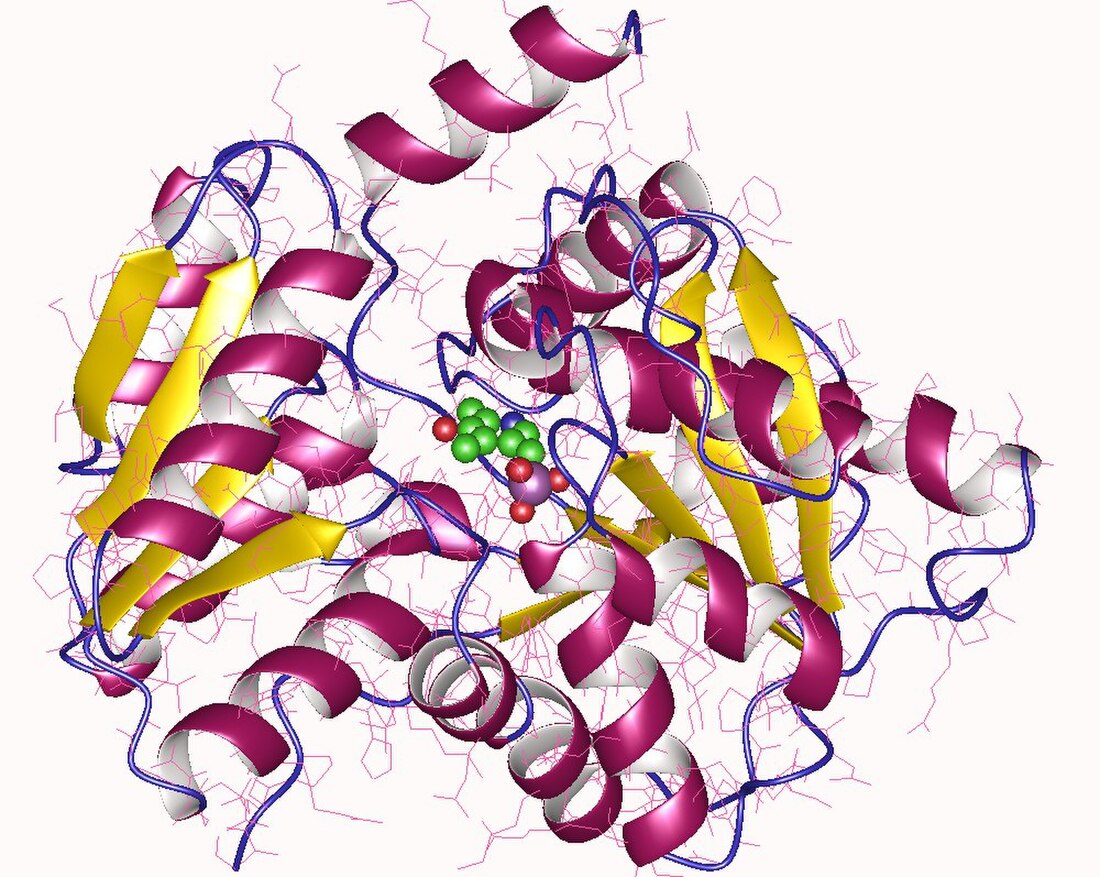
Structural studies
As of late 2007, 4 structures have been solved for this class of enzymes, with PDB accession codes 1P5J, 1PWE, 1PWH, and 2IQQ.
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads