Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
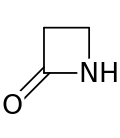
Lactam
Cyclic amide From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
A lactam is a cyclic amide, formally derived from an amino carboxylic acid through cyclization reactions.[1] The term is a portmanteau of the words lactone + amide.

Nomenclature
Greek prefixes in alphabetical order indicate ring size.
This ring-size nomenclature stems from the fact that hydrolysis of an α-lactam gives an α-amino acid and that of a β-Lactam gives a β-amino acid, and so on.
Remove ads
Synthesis
Summarize
Perspective
General synthetic methods are used for the organic synthesis of lactams.
Beckmann rearrangement
Lactams form by the acid-catalyzed rearrangement of oximes in the Beckmann rearrangement.
Schmidt reaction
Lactams form from cyclic ketones and hydrazoic acid in the Schmidt reaction. Cyclohexanone with hydrazoic acid, forms ε - Caprolactum, which upon treatment with excess acid forms Cardiazole, a heart stimulant.
Cyclization of amino acids
Lactams can be formed from cyclisation of amino acids via the coupling between an amine and a carboxylic acid within the same molecule. Lactamization is most efficient in this way if the product is a γ-lactam. For example, Fmoc-Dab(Mtt)-OH, although its side-chain amine is sterically protected by extremely bulky 4-Methyltrityl (Mtt) group, the amine can still intramolecularly couple with the carboxylic acid to form a γ-lactam. This reaction almost finished within 5 minutes with many coupling reagents (e.g. HATU and PyAOP).[2]
Intramolecular nucleophilic substitution
Lactams form from intramolecular attack of linear acyl derivatives from the nucleophilic abstraction reaction.
Iodolactamization
An iminium ion reacts with a halonium ion formed in situ by reaction of an alkene with iodine.[3]
Kinugasa reaction
Lactams form by copper-catalyzed 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition of alkynes and nitrones in the Kinugasa reaction
Diels-Alder reaction
Diels-Alder reaction between cyclopentadiene and chlorosulfonyl isocyanate (CSI) can be utilized to obtain both β- as well as γ-lactam. At lower temp (−78 °C), β-lactam is the preferred product. At optimum temperatures, a highly useful γ-lactam known as Vince Lactam[4] is obtained.[5]
Remove ads
Lactam–lactim tautomerism
A lactim is a cyclic imidic acid compound characterized by an endocyclic carbon-nitrogen double bond. They are formed when lactams undergo tautomerization.
Reactions
- Lactams can polymerize to polyamides.
See also
- Lactone, a cyclic ester.
- β-Lactam
- β-Lactam antibiotics, which includes penicillins
- 2-Pyrrolidone
- 2-Piperidinone
- Caprolactam
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads