Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
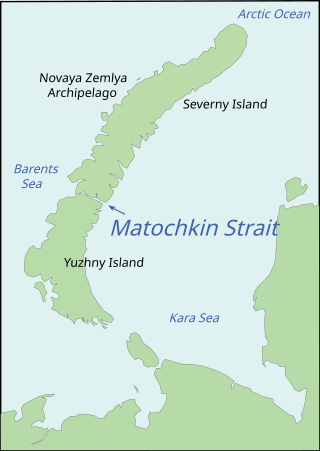
Matochkin Strait
Strait between the Severny and Yuzhny Islands of Novaya Zemlya From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Matochkin Strait or Matochkin Shar (Russian: Ма́точкин Шар) is a narrow waterway separating Severny and Yuzhny Islands on Russia's Novaya Zemlya archipelago. It links the Barents Sea on the west to the Kara Sea on the east in the Arctic Circle. It is under ice cover for most of the year and is navigable only for a short time. It is located in a region of strategic importance, and the surrounding region was a major nuclear test site during the Cold War.
Remove ads
Geography
Matochkin is a narrow strait separating Severny and Yuzhny islands on Russia's Novaya Zemlya archipelago. Located north of the Russian mainland, in the northeastern Europe, it links the Barents Sea on the west to the Kara Sea on the east in the Arctic Circle.[1][2] It is one of the largest sounds in the world.[3] It is part of Russia's exclusive economic zone in the Arctic.[4]
Surveys have documented diverse gastropod molluscs in the region.[5] Studies also indicate the presence of various benthos community structures in the ecosystem.[6][7] A 2021 study has indicated that the benthic communities continue to thrive in the region despite the fragility of the environment due to multiple nuclear tests.[8]
Remove ads
Navigation
The strait remains frozen for most of the year. Ice begins to form in late October, and it becomes completely frozen in mid-November. The western part of the strait begins to clear in May, once warm water from the west breaks the ice caps. It becomes clearer in June, while the eastern part becomes clear of ice in July. It is navigable from July to October, while the navigation is limited to midsize ships during the ice-free months.[9][10] A 2024 report indicates that strait remains ice-bound seasonally restricting maritime transit in the region.[11]
Remove ads
History
The first-recorded navigation of this sound was done by the Dutch explorer Willem Barentsz in 1596. It is, however, believed that Pomor traders and hunters know of this region well before this Western explorer came to this area. However, the name of the sound came later, possibly in the 1700s, when a recorded local person endured hunting in the area.
The sound is located in a strategic region, and during the Cold War, the surrounding region became a major nuclear test site.[9] Nearly 40 nuclear tests were conducted here from 1961 to 1990 including the Tsar Bomba, the largest-ever test conducted. While it was abandoned in the 1990s, the Russian government started to reactivate the test site in the 2000s to conduct subcritical hydronuclear experiments.[12]
See also
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads
