Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
East Chadic languages
Afro-Asiatic language branch From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
The three dozen East Chadic languages of the Chadic family are spoken in Chad and Cameroon.[1]
Speakers of various East Chadic languages are locally known as Hadjarai peoples.[2][3] The largest East Chadic language is Nancere.[4]
Remove ads
Languages
Summarize
Perspective
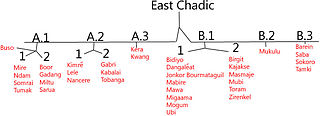
The branches of East Chadic go either by names or by letters and numbers in an outline format.[5]
The East Chadic B classification follows that of Lovestrand (2012).
Peust (2018), however, has a somewhat different phylogenetic classification for East Chadic.[4] The most striking change is the repositioning of Mokilko (B.2) from East Chadic B to East Chadic A, where it now constitutes the first branch to separate, followed by Lele-Nancere (A.2.1). Within East Chadic B, he treats the Mubi group (B.1.2) as the first primary branching, with all the rest forming a subgroup divided between Dangla (B.1.1) in the north and Barain plus Sokoro (B.3 and B.4) in the south.
East Chadic A is distributed primarily in Tandjilé and neighbouring regions. East Chadic B is distributed primarily in Guéra and neighbouring regions.[10]
Remove ads
Numerals
Summarize
Perspective
Comparison of numerals in individual languages:[11]
Remove ads
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads