Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Neighbor-net
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
NeighborNet[1] is an algorithm for constructing phylogenetic networks which is loosely based on the neighbor joining algorithm. Like neighbor joining, the method takes a distance matrix as input, and works by agglomerating clusters. However, the NeighborNet algorithm can lead to collections of clusters which overlap and do not form a hierarchy, and are represented using a type of phylogenetic network called a splits graph. If the distance matrix satisfies the Kalmanson combinatorial conditions then Neighbor-net will return the corresponding circular ordering.[2][3] The method is implemented in the SplitsTree and R/Phangorn[4][5] packages.
This article may be too technical for most readers to understand. (December 2019) |
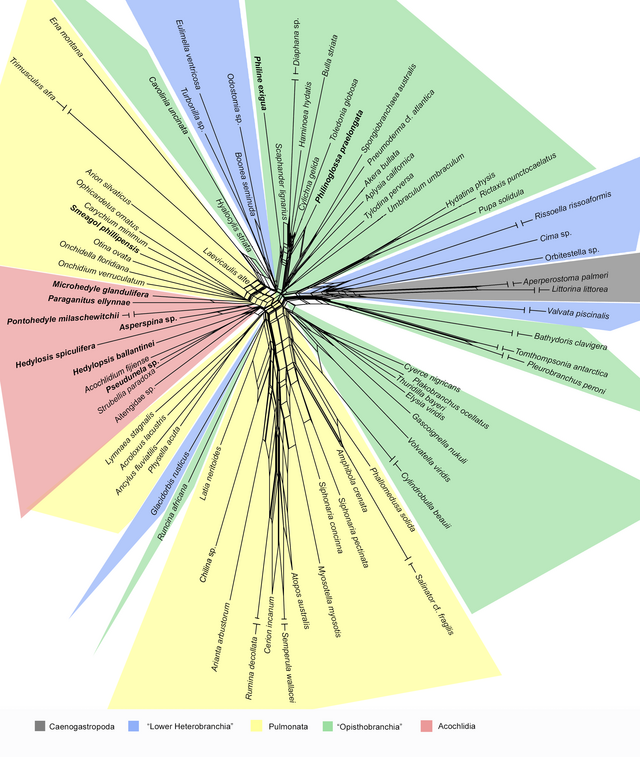
Examples of the application of Neighbor-net can be found in virology,[6] horticulture,[7] dinosaur genetics,[8] comparative linguistics,[9] and archaeology.[10]
Remove ads
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads
