Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Nordenfelt gun
Organ gun From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
The Nordenfelt gun was a multiple-barrel organ gun that had a row of up to twelve barrels. It was fired by pulling a lever back and forth and ammunition was gravity fed through chutes for each barrel. It was produced in a number of different calibres up to 25 mm (0.98 in). Larger calibres were also used, but for these calibres the design simply permitted rapid manual loading rather than true automatic fire. This article covers the anti-personnel rifle-calibre (typically 0.45 in [11 mm]) gun.


Sailor operating 10-barrel rifle calibre gun, with right hand on lever
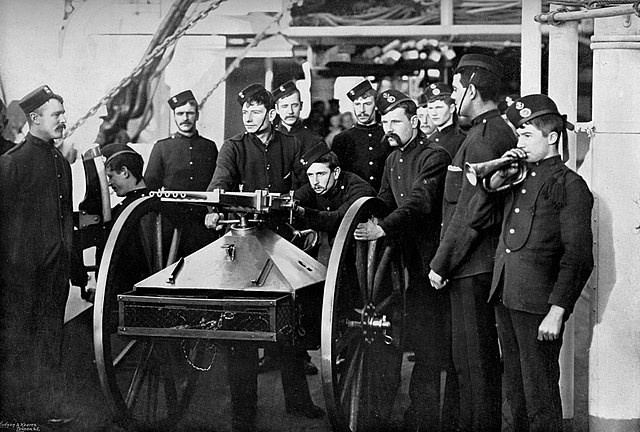

Remove ads
Development
The weapon was designed by a Swedish engineer, Helge Palmcrantz. He created a mechanism to load and fire a multiple-barreled gun by simply moving a single lever backwards and forwards. It was patented in 1873.
Production of the weapon was funded by a Swedish steel producer and banker (later weapons maker) named Thorsten Nordenfelt, who was working in London. The name of the weapon was changed to the Nordenfelt gun. A plant producing the weapon was set up in England with sales offices in London and long demonstrations were conducted at several exhibitions. The weapon was adopted by the British Royal Navy, as an addition to their Gatling and Gardner guns.
During a demonstration held at Portsmouth, a ten-barrelled version of the weapon, firing rifle-calibre cartridges, fired 3,000 rounds of ammunition in 3 minutes and 3 seconds without stoppage or failure.
However, with the development of the Maxim gun, the weapon was eventually outclassed. Nordenfelt merged in 1888 with the Maxim Gun Company to become Maxim Nordenfelt Guns and Ammunition Company Limited.
Remove ads
Surviving examples
At least one Nordenfelt was re-activated for the 1966 film Khartoum and can be seen firing in the river boat sequence.
The Bundeswehr Museum of German Defense Technology in Koblenz has one of this specimen in its collection.
Another one is exhibited in the Romanian Naval Museum in Constanța.
Users
 Brazil[1][2]
Brazil[1][2] British Empire
British Empire Chile[3]
Chile[3] Egypt[4]
Egypt[4] Kingdom of Montenegro: Seven were in use at the time of the Balkan Wars.[5]
Kingdom of Montenegro: Seven were in use at the time of the Balkan Wars.[5] Peru[3]
Peru[3] Portuguese Empire[2][6]
Portuguese Empire[2][6] Qajar Iran: Had a battery of four guns in the 1890s.[7]
Qajar Iran: Had a battery of four guns in the 1890s.[7] Qing Empire[8]
Qing Empire[8] Uruguay[9]
Uruguay[9] Kingdom of Spain
Kingdom of Spain
Conflicts
- Egyptian-Ethiopian War[4]
- War of The Pacific[3]
- Mahdist Wars[10]
- Revolution of Quebracho[9]
- Jebu War[11]
- Philippine-American War
- Federalist Revolution[1][2]
- Revolta Da Armada[1]
- First Matabele War[12]
- First Sino-Japanese War[8]
- War of Canudos[1][13]
- Revolution of 1897[9]
- Boxer Rebellion[14]
- Balkan Wars[5]
See also
Weapons of comparable role, performance and era
- Gardner gun: similar hand-cranked machine gun
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads

