Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
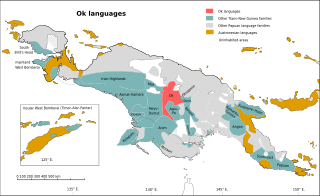
Ok languages
Trans–New Guinea language family From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
The Ok languages are a family of about a dozen related Trans–New Guinea languages spoken in a contiguous area of eastern Irian Jaya and western Papua New Guinea. The most numerous language is Ngalum, with some 20,000 speakers; the best known is probably Telefol.
This article should specify the language of its non-English content using {{lang}} or {{langx}}, {{transliteration}} for transliterated languages, and {{IPA}} for phonetic transcriptions, with an appropriate ISO 639 code. Wikipedia's multilingual support templates may also be used. (December 2021) |
The Ok languages have dyadic kinship terms.[2]
Remove ads
History of classification
The Ok languages are clearly related. Alan Healey identified them as a family in 1962. He later noted connections with the Asmat languages and Awyu–Dumut families (Healey 1970).
Voorhoeve developed this into a Central and South New Guinea (CSNG) proposal. As part of CSNG, the Ok languages form part of the original proposal for Trans–New Guinea, a position tentatively maintained by Malcolm Ross, though reduced nearly to Healey's original conception. Ross states that he cannot tell if the similarities in CSNG are shared innovations or retentions from proto-TNG. Voorhoeve argues specifically for an Awyu–Ok relationship, and Foley believes that these two families may be closest to Asmat among the TNG languages.
Loughnane and Fedden (2011)[3] claim to have demonstrated that the erstwhile TNG isolate Oksapmin is related to the Ok family. However, this has not been generally accepted because loans from Mountain Ok have not been accounted for.
Van den Heuvel & Fedden (2014) argue that Greater Awyu and Greater Ok are not genetically related, but that their similarities are due to intensive contact.[4]
Remove ads
Languages
The languages are:
Reconstruction
Summarize
Perspective
Phonology
The following are consonants of Proto-Ok:[5]
Vowels may be /*iː *ʉ *uː *e *a *o/, but this reconstruction may be biased toward Telefol.
Pronouns
Healey & Ross reconstruct the pronouns of proto-Ok are as follows:[citation needed]
Usher (2020) reconstructs the independent pronouns as,[5]
and the subject suffixes as,
Evolution
Proto-Mountain Ok reflexes of proto-Trans-New Guinea (pTNG) etyma, as quoted by Pawley & Hammarström (2018) from Healey (1964):[6][7]
- *beːn ‘arm’ < *mbena
- *mburuŋ ‘fingernail’ < *mb(i,u)t(i,u)C
- *katuun ‘knee’ < *(ng,k)atVk
- *maŋkat ‘mouth’ < *maŋgat[a]
- *gitak ‘neck’ < *k(a,e)ndak
- *kum ‘side of neck’ < *kuma(n,ŋ)
- *mutuum ‘nose’ < *mundu
- *falaŋ ‘tongue’ < *mbilaŋ
- *kaliim ‘moon’ < *kal(a,i)m
Lexicon
Usher (2020)
Some lexical reconstructions by Usher (2020) are:[5]
Loughnane and Fedden (2011)
Proto-Ok-Oksapmin reconstructions from Loughnane and Fedden (2011):[3]
Remove ads
Further reading
- Proto-Ok-Oksapmin. TransNewGuinea.org. From Loughnane, R. & Fedden, S. 2011. Is Oksapmin Ok?—A Study of the Genetic Relationship between Oksapmin and the Ok Languages. Australian Journal of Linguistics 31:1, 1-42.
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads