Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Prostaglandin H2
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Prostaglandin H2 (PGH2), or prostaglandin H2 (PGH2), is a type of prostaglandin and a precursor for many other biologically significant molecules. It is synthesized from arachidonic acid in a reaction catalyzed by a cyclooxygenase enzyme.[2] The conversion from arachidonic acid to prostaglandin H2 is a two-step process. First, COX-1 catalyzes the addition of two free oxygens to form the 1,2-dioxane bridge and a peroxide functional group to form prostaglandin G2 (PGG2).[3] Second, COX-2 reduces the peroxide functional group to a secondary alcohol, forming prostaglandin H2. Other peroxidases like hydroquinone have been observed to reduce PGG2 to PGH2.[4] PGH2 is unstable at room temperature, with a half life of 90–100 seconds,[1] so it is often converted into a different prostaglandin. PGH2 is produced by every type of cell except for red blood cells and has a wide range of effects in the body.[5]
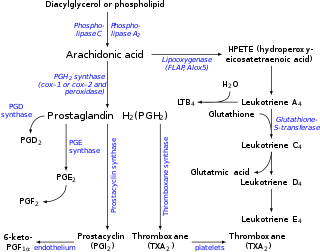
It is acted upon by:
- prostacyclin synthase to create prostacyclin
- thromboxane-A synthase to create thromboxane A2 and 12-(S)-hydroxy-5Z,8E,10E-heptadecatrienoic acid (HHT) (see 12-Hydroxyheptadecatrienoic acid)
- prostaglandin D2 synthase to create prostaglandin D2
- prostaglandin E synthase to create prostaglandin E2
- prostaglandin F synthase to create prostaglandin F2α[6]
It rearranges non-enzymatically to:
- A mixture of 12-(S)-hydroxy-5Z,8E,10E-heptadecatrienoic acid (HHT) and 12-(S)-hydroxy-5Z,8Z,10E-heptadecatrienoic acid (see 12-hydroxyheptadecatrienoic acid)
- These breakdown products are associated with increased aggregation of Amyloid beta peptides and Alzheimer's disease.[7]
Functions of prostaglandin H2:
- regulating the constriction and dilation of blood vessels
- stimulating platelet aggregation
- binds to thromboxane receptor on platelets' cell membranes to trigger platelet migration and adhesion to other platelets[8]
Effects of aspirin on prostaglandin H2:
- Aspirin has been hypothesized to block the conversion of arachidonic acid to prostaglandin

Remove ads
History
Prostaglandin H2 was discovered in 1973 by Diederik H. Nugteren and Elly Christ-Hazelhof while they were researching the formation of prostaglandin E2 from arachidonic acid using enzymes found in vesicular glands.[9]
Synthesis
The original synthesis of prostaglandin H2 by Diederik H. Nugteren and Elly Christ-Hazelhof was performed in 1973.[9] Sheep vesicular glands were homogenized with 1M KH2PO4 and 0.001 M EDTA buffer and then centrifuged to isolate the COX-1 enzymes. Pure arachidonic acid was added to a solution containing the enzymes, and the mixture was shaken. Thin-layer chromatography was used to isolate a band of prostaglandin H2.
In 1986, due to low prostaglandin H2 product purity from thin-layer chromatography and column chromatography, high-performance liquid chromatography with hexane and isopropanol as solvents was developed as an alternative means of isolating the prostaglandin with 98% purity.[10]
Remove ads
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads

