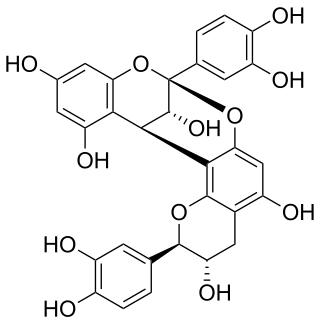
Procyanidin A1 is an A type proanthocyanidin dimer.
Quick facts Names, Identifiers ...
Procyanidin A1
 Chemical structure of procyanidin A1 Chemical structure of procyanidin A1 |
| Names |
| IUPAC name
(2R,3S,8S,14R,15R)-2,8-bis(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2,3,4,14-tetrahydro-8,14-methanobenzo[7,8][1,3]dioxocino[4,5-h]chromene-3,5,11,13,15-pentaol |
| Identifiers |
|
|
|
|
| ChemSpider |
|
|
|
| UNII |
|
|
|
InChI=1S/C30H24O13/c31-12-6-17(35)23-21(7-12)42-30(11-4-18(36)26(39)19(37)5-11)29(40)25(23)24-22(43-30)9-15(33)13-8-20(38)27(41-28(13)24)10-1-2-14(32)16(34)3-10/h1-7,9,20,25,27,29,31-40H,8H2/t20-,25-,27-,29-,30+/m1/s1 Key: WODBGULXKVZGQF-QCPBNORNSA-N
|
O[C@@H]1[C@@H](C2=C(O[C@H](C3=CC(O)=C(O)C=C3)[C@@H](O)C4)C4=C(O)C=C2O5)C6=C(C=C(O)C=C6O)O[C@]15C7=CC(O)=C(O)C=C7
|
| Properties |
|
C30H24O12 |
| Molar mass |
576.510 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). |
Close
It is an epicatechin-(2β→7,4β→8)-catechin dimer found in Rhododendron spiciferum,[1] in peanut skins[2] and in Ecdysanthera utilis.[3]
Procyanidin B1 can be converted into procyanidin A1 by radical oxidation using 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radicals under neutral conditions.[4]