Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
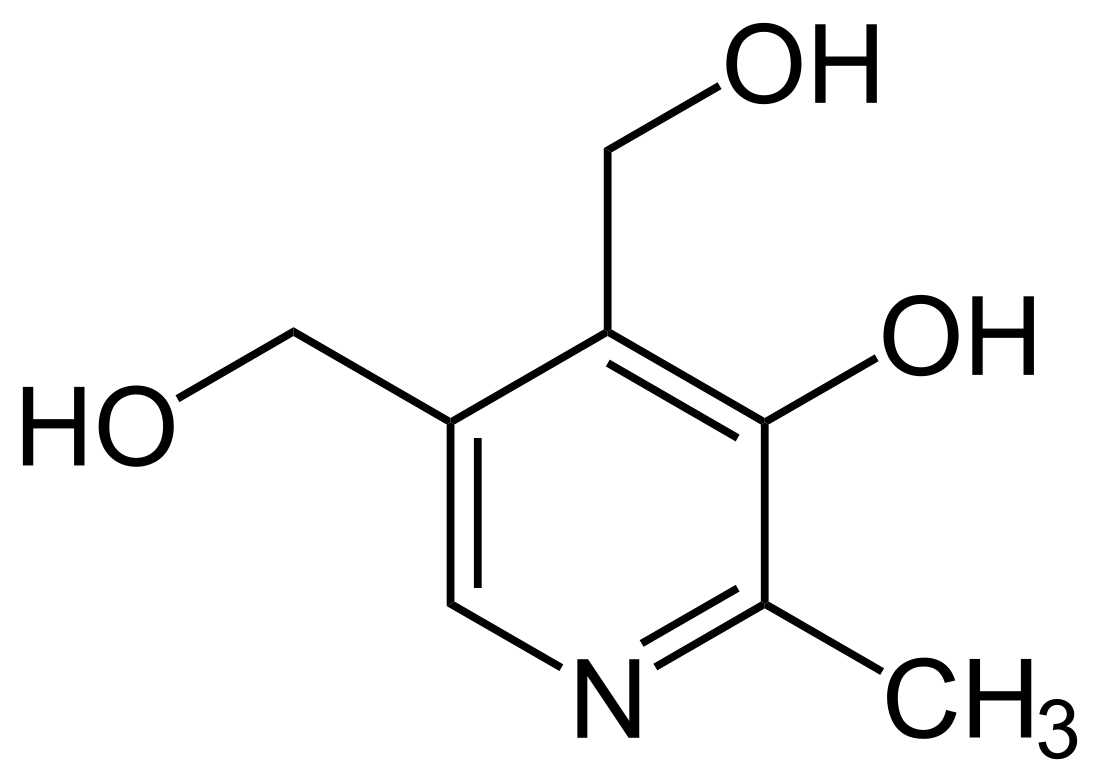
Pyridoxine
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Pyridoxine (PN)[4] is a form of vitamin B6 found commonly in food and used as a dietary supplement. As a supplement it is used to treat and prevent pyridoxine deficiency, sideroblastic anaemia, pyridoxine-dependent epilepsy, certain metabolic disorders, side effects or complications of isoniazid use, and certain types of mushroom poisoning.[5] It is used by mouth or by injection.[5]
It is usually well tolerated.[5] Occasionally side effects include headache, numbness, and sleepiness.[5] Normal doses are safe during pregnancy and breastfeeding.[5] Pyridoxine is in the vitamin B family of vitamins.[5] It is required by the body to metabolise amino acids, carbohydrates, and lipids.[5] Sources in the diet include meat, fish, fruit, vegetables, and grain.[6]
Remove ads
Medical uses
As a treatment (oral or injection), it is used to treat or prevent pyridoxine deficiency, sideroblastic anaemia, pyridoxine-dependent epilepsy, certain metabolic disorders, side effects of isoniazid treatment and certain types of mushroom poisoning.[5] Isoniazid is an antibiotic used for the treatment of tuberculosis. Common side effect include numbness in the hands and feet.[7] Co-treatment with vitamin B6 alleviates the numbness.[8] Pyridoxine-dependent epilepsy is a type of rare infant epilepsy that does not improve with typical anti-seizure medications.[9]
Pyridoxine in combination with doxylamine is used as a treatment for morning sickness in pregnant women.[10]
Remove ads
Side effects
It is usually well tolerated, though overdose toxicity is possible.[5] Occasionally side effects include headache, numbness, and sleepiness.[5] Pyridoxine overdose can cause a peripheral sensory neuropathy characterized by poor coordination, numbness, and decreased sensation to touch, temperature, and vibration.[11] Healthy human blood levels of pyridoxine are 2.1–21.7 ng/mL. Normal doses are safe during pregnancy and breastfeeding.[5]
Remove ads
Mechanism
Pyridoxine is in the vitamin B family of vitamins.[5] It is required by the body to make amino acids, carbohydrates, and lipids.[5] Sources in the diet include fruit, vegetables, and grain.[6] It is also required for muscle phosphorylase activity associated with glycogen metabolism.
Metabolism
The half-life of pyridoxine varies according to different sources: one source suggests that the half-life of pyridoxine is up to 20 days,[12] while another source indicates half-life of vitamin B6 is in range of 25 to 33 days.[13] After considering the different sources, it can be concluded that the half-life of pyridoxine is typically measured in several weeks.[12][13]
History
Pyridoxine was discovered in 1934, isolated in 1938, and first made in 1939.[14][15] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.[16] Pyridoxine is available both as a generic medication and over the counter product.[5] Foods, such as breakfast cereal have pyridoxine added in some countries.[6]
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads