Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Rectified 9-simplexes
Type of geometric object From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
In nine-dimensional geometry, a rectified 9-simplex is a convex uniform 9-polytope, being a rectification of the regular 9-simplex.
These polytopes are part of a family of 271 uniform 9-polytopes with A9 symmetry.
There are unique 4 degrees of rectifications. Vertices of the rectified 9-simplex are located at the edge-centers of the 9-simplex. Vertices of the birectified 9-simplex are located in the triangular face centers of the 9-simplex. Vertices of the trirectified 9-simplex are located in the tetrahedral cell centers of the 9-simplex. Vertices of the quadrirectified 9-simplex are located in the 5-cell centers of the 9-simplex.
Remove ads
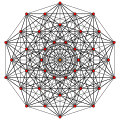
Rectified 9-simplex
| Rectified 9-simplex | |
|---|---|
| Type | uniform 9-polytope |
| Schläfli symbol | t1{3,3,3,3,3,3,3,3} |
| Coxeter-Dynkin diagrams | |
| 8-faces | 20 |
| 7-faces | 135 |
| 6-faces | 480 |
| 5-faces | 1050 |
| 4-faces | 1512 |
| Cells | 1470 |
| Faces | 960 |
| Edges | 360 |
| Vertices | 45 |
| Vertex figure | 8-simplex prism |
| Petrie polygon | decagon |
| Coxeter groups | A9, [3,3,3,3,3,3,3,3] |
| Properties | convex |
The rectified 9-simplex is the vertex figure of the 10-demicube.
Alternate names
- Rectified decayotton (reday) (Jonathan Bowers)[1]
Coordinates
The Cartesian coordinates of the vertices of the rectified 9-simplex can be most simply positioned in 10-space as permutations of (0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1). This construction is based on facets of the rectified 10-orthoplex.
Images
Remove ads
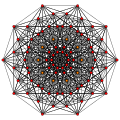
Birectified 9-simplex
This polytope is the vertex figure for the 162 honeycomb. Its 120 vertices represent the kissing number of the related hyperbolic 9-dimensional sphere packing.
Alternate names
- Birectified decayotton (breday) (Jonathan Bowers)[2]
Coordinates
The Cartesian coordinates of the vertices of the birectified 9-simplex can be most simply positioned in 10-space as permutations of (0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,1). This construction is based on facets of the birectified 10-orthoplex.
Images
Remove ads
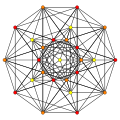
Trirectified 9-simplex
Alternate names
- Trirectified decayotton (treday) (Jonathan Bowers)[3]
Coordinates
The Cartesian coordinates of the vertices of the trirectified 9-simplex can be most simply positioned in 10-space as permutations of (0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,1). This construction is based on facets of the trirectified 10-orthoplex.
Images
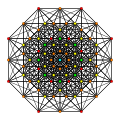
Quadrirectified 9-simplex
Alternate names
- Quadrirectified decayotton
- Icosayotton (icoy) (Jonathan Bowers)[4]
Coordinates
The Cartesian coordinates of the vertices of the quadrirectified 9-simplex can be most simply positioned in 10-space as permutations of (0,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,1,1). This construction is based on facets of the quadrirectified 10-orthoplex.
Images
Remove ads
Notes
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads