Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Rail transport in Bangkok
Railway system in the Thai capital From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Thailand's capital Bangkok has been served by rail transit since 1897 and today hosts a full complement of intercity, commuter and metro lines.
History
Summarize
Perspective
Bangkok's first rail line was the private Paknam Railway linking Bangkok to Samut Prakan which opened in 1893.
Electric trams served Bangkok from 1894 to 1968. At the turn of the 20th century, King Rama V's new tram network employed foreign engineers and technicians, especially from Denmark.
The State Railway of Thailand (SRT) was founded in 1890[1] and operated its first train service in 1897[1] The SRT remains the only railway operator that operates services between Bangkok Metropolitan Region and other parts of the country.
Proposals for the development of rapid transit in Bangkok date back to 1975.[2] One such was for the failed Lavalin Skytrain. A rapid-transit network finally opened in 1999, with the Sukhumvit Line and Silom Line of the BTS Skytrain.
Since then, a number of additional lines have opened. In 2004, the Blue Line became the first with an underground section. In 2010 the Airport Rail Link connected Phaya Thai station with Suvarnabhumi Airport. In that year Bangkok BRT also began operation. In 2016, the Purple Line opened. In 2020, the Gold Line opened. In 2021, the SRT Red Lines, consisting of SRT Dark Red Line and SRT Light Red Line, began operation.
In 2023, the country's first two monorail lines, the Yellow Line and Pink Line, opened.
Remove ads
Rapid transit
Summarize
Perspective
Bangkok is currently served by four rapid-transit systems: the BTS Skytrain, the MRT, the Airport Rail Link, and the SRT Red Lines.
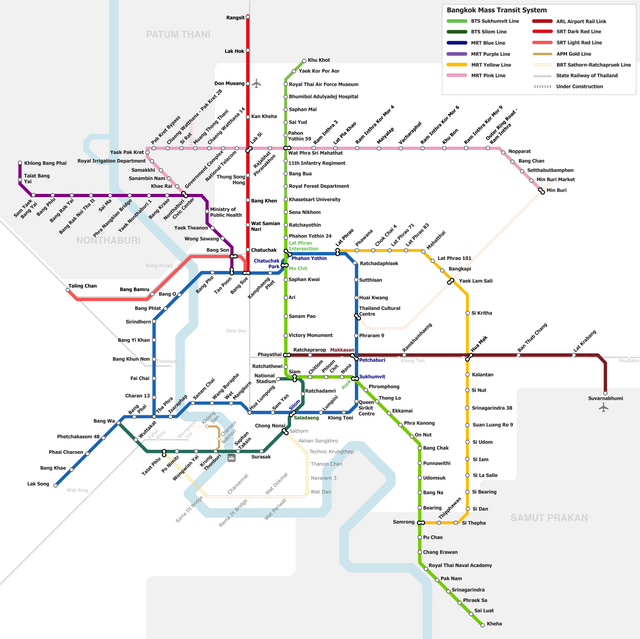
Networks
BTS Skytrain
The Skytrain consists of three lines, totalling 70.05 kilometers (43.53 mi). The Sukhumvit Line runs southwards from Khu Khot Station along Phahon Yothin Road and then eastwards along Sukhumvit Road to Kheha Station in Samut Prakan. The Silom Line runs eastwards from National Stadium Station in Pathum Wan District, then southwest along Ratchadamri, Si Lom, Narathiwat Ratchanakharin and Sathon Roads, crossing the Chao Phraya passing Wong Wian Yai Station in Khlong San towards Bang Wa Station in Phasi Charoen District. Both lines are elevated, and interchange at Siam Station in Pathum Wan. The Gold Line runs along Charoen Nakhon Road in Khlong San from Krung Thon Buri Station, which interchanges with the Silom Line, to Khlong San Station.
MRT (Metro)
The MRT (Metropolitan Rapid Transit) system opened in July 2004, and currently consists of four lines, the Blue Line (partially underground heavy rail), Purple Line (above-ground medium capacity rail) and Yellow Line and Pink Line (monorail). The Blue Line runs for 37.1 kilometres (23.1 mi) from Tao Poon Station in a southward arc through the east along Ratchadaphisek Road, via Hua Lamphong, where it connects to the central railway station, to Lak Song. It has 38 stations, and connects to the BTS system at BTS stations Mo Chit, Asok, Sala Daeng and Bang Wa. The Blue Line was extended to form a circle in 2020. The Purple Line opened in 2016.
Although initial passenger numbers were low, these systems have become indispensable to many commuters. The BTS reported an average of 392,167 daily trips in 2010, while the MRT had 178,334 passenger trips per day. However, relatively high fare prices have kept these systems inaccessible to a portion of the population. The Pink and Yellow monorail lines opened in 2023.
Airport Rail Link
The Airport Rail Link, opened in August 2010 after many delays, connects the city centre to Suvarnabhumi Airport in Samut Prakan Province to the east. It is operated by the SRT, and offers services between the airport and Makkasan where it connects with Phetchaburi Station of the MRT. It terminates at Phaya Thai Station, where it connects to the BTS. Its eight stations span a distance of 29 kilometres (18 mi).
SRT and commuter rail
The SRT Red Lines, which opened in 2021 along with the Bang Sue Grand Station, serve the Bangkok Metropolitan Region. It consists of two lines, the Dark Red Line and Light Red Line.
Lines in operation
Future expansion
The entire Mass Rapid Transit Master Plan in Bangkok Metropolitan Region consists of eight main lines and four feeder lines totalling 508 kilometres (316 mi) to be completed by 2029.
New lines under construction are the Orange Line and an extension to the Purple Line and extensions to the Airport Rail Link.
Rolling stock
Ticketing and fare rates
MRT Blue line
There are many types of stored-value cards according to passenger age. An Adult card is equivalent to full fare. An Elder card for over-65s provides a 50% discount. A Student card for under-23s provides a 10% discount. A Child card for under-14s (and under 120 cm tall) provides a 50% discount.
The fare rates are counted by the number of stations, starting from 16 baht for a station, increasing by 2-3 baht for each station up to 42 baht for 17 stations.[7]
MRT Purple line
This line uses the same stored-value cards as MRT Blue Line. Fares start from 15 baht for a station, increasing 1 baht for each station up to 29 baht for 15 stations.[8]
For passengers without cards, fares start from 17 baht for a station, increasing 2-3 baht for each station, reaching the maximum values at 42 baht for 11 stations.[9]
Airport Rail Link
For the city line, the fare rates start from 15 baht for a station, increase 5 baht for each station up to 45 baht for 7 stations.[10]
BTS
BTS (not to be confused with the K-pop group) has its own stored value cards called "Rabbit card". There are 3 types of Rabbit card: adult, student, and senior, with 100 baht initial stored value.[11]
BTS fare rates start from 16 baht. The costs is based on the distance travelled. Travelling between Wongwian Yai - Bang Wa stations, On-Nut - Bearing stations costs 15 baht. 15 baht will also be added when travelling between these stations to the other station on the main line.
Remove ads
Inter-city and high-speed rail

Bangkok is the location of the Krung Thep Aphiwat Central Terminal, the central rail hub for most long-distance trains as of 2023, as well as the older Hua Lamphong station, both operated by the State Railway of Thailand (SRT). From Bangkok, trains travel on the Northern Line to Chiang Mai, the Northeastern Line to Nong Khai and Ubon Ratchathani, and the Eastern Line to Aranyaprathet, and the Southern Line, which terminates at Su-ngai Kolok and has a connection to Malaysia (the other Southern terminus is Thonburi).
Planned high-speed rail terminus
There are multiple planned high-speed rail lines in Thailand. The Bangkok–Nong Khai high-speed railway and Don Mueang–Suvarnabhumi–U-Tapao high-speed railway are under construction as of 2023. The Krung Thep Aphiwat Central Terminal will act as a future hub for all high-speed services.
See also
Notes
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads













