Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
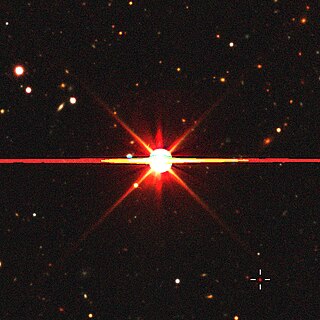
Ross 458
Star in the constellation Virgo From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Ross 458, also referred to as DT Virginis, is a binary star system in the constellation of Virgo. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 9.79[3] and is located at a distance of 37.6 light-years from the Sun. Both of the stars are low-mass red dwarfs with at least one of them being a flare star. This binary system has a circumbinary sub-stellar companion.
Remove ads
Description
Summarize
Perspective

This star was mentioned as a suspected variable by M. Petit in 1957.[14] In 1960, O. J. Eggen classified it as a member of the Hyades moving group based on the system's space motion;[15] it is now considered a likely member of the Carina Near Moving Group.[16] Two flares were reported from this star in 1969 by N. I. Shakhovskaya, confirming it as a flare star.[12] It was identified as an astrometric binary in 1994 by W. D. Heintz, who found a period of 14.5 years.[5] The pair were resolved using adaptive optics in 1999.[5] Early mass estimates placed the companion near the substellar limit, and it was initially proposed as a brown dwarf[17] but is now considered late-type red dwarf.[4]
The primary member, component A, is an M-type main-sequence star with a stellar classification of M0.5.[4] It is young, magnetically very active star with a high rate of rotation[17] and strong Hα emission.[4] The star experiences star spots that cover 10–15% of the surface[3] It is smaller and less massive than the Sun. The star is radiating just 4.4%[7] of the luminosity of the Sun from its photosphere at an effective temperature of 3,484 K.[16]
Remove ads
Substellar companion
A distant sub-stellar companion to the binary star system was discovered in 2010 as part of a deep infrared sky survey. This is most likely a T8 spectral type brown dwarf with an estimated rotation period of 6.75±1.58 h. The object varies slightly in brightness, which may be due to patchy clouds.[4] The companion lacks detectable oxygen in the atmosphere, implying its formation from sequestrated source or peculiar atmospheric chemistry.[18] Analysis of its chemical composition show it to be similar to that of Ross 458 A, indicating that the object formed in a stellar-like manner.[6]
Remove ads
See also
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads

![{\displaystyle {\begin{smallmatrix}\left[{\mathrm {M} }/{\mathrm {H} }\right]\end{smallmatrix}}}](http://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/d9a106d03666c72cc54c1dff07a5637d3adda9a1)