Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
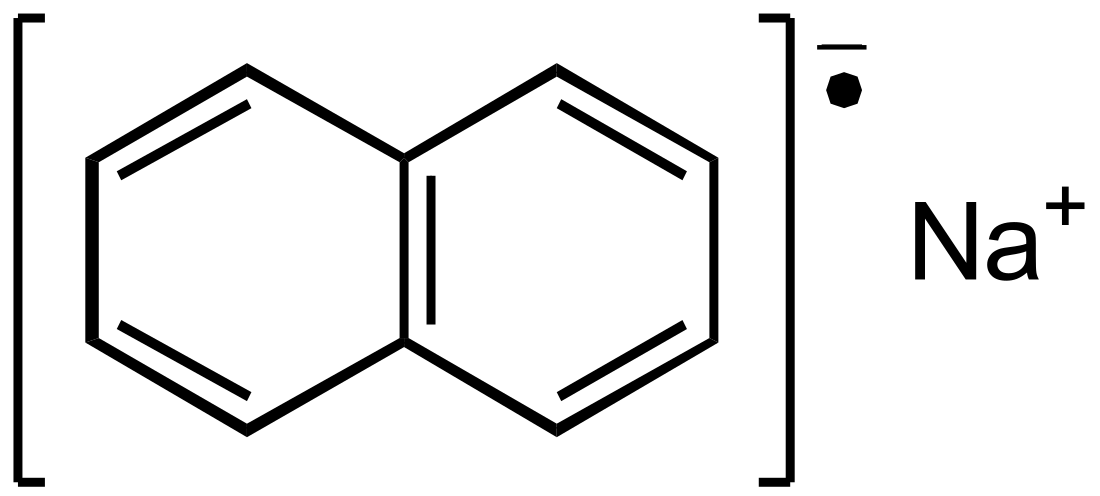
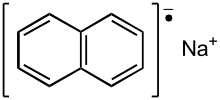
Sodium naphthalene
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Sodium naphthalene is an organic salt with the chemical formula Na+[C10H8]−. In the research laboratory, it is used as a reductant in the synthesis of organic, organometallic, and inorganic chemistry. It is usually generated in situ. When isolated, it invariably crystallizes as a solvate with ligands bound to Na+.[1]
Remove ads
Preparation and properties

The alkali metal naphthalene salts are prepared by stirring the metal with naphthalene in an ethereal solvent, usually as tetrahydrofuran or dimethoxyethane. The resulting salt is dark green.[2][3][4] The anion is a radical, giving a strong EPR signal near g = 2.0. Its deep green color arises from absorptions centered at 463 and 735 nm.
Several solvates of sodium naphthalenide have been characterized by X-ray crystallography. The effects are subtle, the outer pair of CH−CH bonds contract by 3 pm and the other nine C−C bonds elongate by 2–3 pm. The net effect is that reduction weakens the bonding.[5][6]
Remove ads
Reactions
Redox
With a reduction potential near −2.5 V vs NHE, the naphthalene radical anion is a strong reducing agent.[1] It is capable of defluorinating PTFE and is commonly used for chemically etching PTFE to allow adhesion.[7]
Protonation
The anion is strongly basic, and a typical degradation pathway involves reaction with water and related protic sources such as alcohols. These reactions afford dihydronaphthalene:
As a ligand
Alkali metal salts of the naphthalene radical anion are used to prepare complexes of naphthalene.[8]
Remove ads
Related reagents
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads