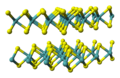Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Strukturbericht designation
System of detailed crystal structure classification From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
In crystallography, a Strukturbericht designation or Strukturbericht type is a system of detailed crystal structure classification by analogy to another known structure. The designations were intended to be comprehensive but are mainly used as supplement to space group crystal structures designations, especially historically.[1][2] Each Strukturbericht designation is described by a single space group, but the designation includes additional information about the positions of the individual atoms, rather than just the symmetry of the crystal structure. While Strukturbericht symbols exist for many of the earliest observed and most common crystal structures, the system is not comprehensive, and is no longer being updated. Modern databases such as Inorganic Crystal Structure Database index thousands of structure types directly by the prototype compound (i.e. "the NaCl structure" instead of "the B1 structure").[3] These are essentially equivalent to the old Stukturbericht designations.
Remove ads
History
The designations were established by the journal Zeitschrift für Kristallographie – Crystalline Materials, which published its first round of supplemental reviews under the name Strukturbericht from 1913-1928.[4] These reports were collected into a book published in 1931 by Paul Peter Ewald and Carl Hermann which became Volume 1 of Strukturbericht.[5] While the series was continued after the war under the name Structure reports, which was published through 1990,[6] the series stopped generating new symbols. Instead, some new additional designations were given in books by Smithels,[7] and Pearson.[8]
For the first volume, the designation consisted of a capital letter (A,B,C,D,E,F,G,H,L,M,O) specifying a broad category of compounds, and then a number to specify a particular crystal structure. In the second volume, subscript numbers were added, some early symbols were modified (e.g. what was initially D1 became D01, noted in the tables below as "D1 → D01"), and the categories were modified (types I,K,S were added). In the third volume, the class I was renamed J. Later designations began to use a lower case letter in subscripts as well.[9]
Remove ads
A-compounds
Summarize
Perspective
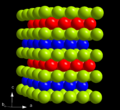
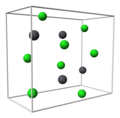
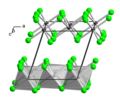
The 'A' compounds are reserved for structures made up of atoms of all the same chemical element.
Remove ads
B-compounds
Summarize
Perspective
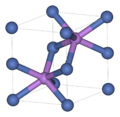
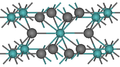
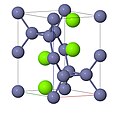
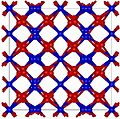
'B' designates compounds of two elements with equal numbers of atoms.
C-compounds
Summarize
Perspective
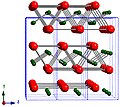
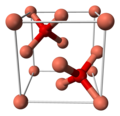
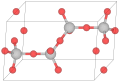
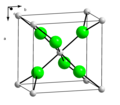
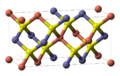
'C' designates compounds of the stoichiometry AB2.
Remove ads
D-compounds
Summarize
Perspective
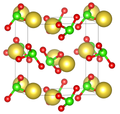
'D' designates compounds of arbitrary stoichiometry. Originally, D1-D10 were set aside for stoichiometry AB3, D11-D20 for stoichiometry ABn for n > 3, D31-D50 for (ABn)2, and D51 up for the AmBn for arbitrary m and n.[9]
Remove ads
E to K compounds
Summarize
Perspective
Letters between 'E' and 'K' designate more complex compounds.
Remove ads
L-compounds
'L' designates intermetallic compounds.
Remove ads
S-compounds
Remove ads
See also
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads