Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Thracians
Indo-European people in ancient southeast Europe From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
The Thracians (/ˈθreɪʃənz/; Ancient Greek: Θρᾷκες, romanized: Thrāikes; Latin: Thraci) were an Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Southeast Europe in ancient history.[1][2] Thracians resided mainly in Southeast Europe in modern-day Bulgaria, Romania, North Macedonia, northern Greece and European Turkey, but also in north-western Anatolia (Asia Minor) in Turkey.
This article needs additional citations for verification. (April 2022) |

The exact origin of the Thracians is uncertain, but it is believed that Thracians like other Indo-European speaking groups in Europe descended from a mixture of Proto-Indo-Europeans and Early European Farmers.[3]
During the 5th and 4th millennium BC, the inhabitants of the eastern region of the Balkans became organized in different groups of indigenous people that were later named by the ancient Greeks under the single ethnonym of "Thracians".[4][5][6][7]
The Thracian culture emerged during the early Bronze Age, which began about 3500 BC.[4][8][9][10] From it also developed the Getae, the Dacians and other regional groups of tribes. Historical and archaeological records indicate that the Thracian culture flourished in the 3rd and 2nd millennium BC.[4][11][12] Writing in the 6th century BC, Xenophanes described Thracians as "blue-eyed and red-haired".[13]
According to ancient Greek and Roman historians, the Thracians were uncivilized and remained largely disunited, until the establishment of their first permanent state the Odrysian kingdom in the very beginning of 5th century BC, founded by king Teres I, exploiting the collapse of the Persian presence in Europe due to the failed invasion of Greece in 480–79.[14] Teres and his son Sitalces pursued a policy of expansion, making the kingdom one of the most powerful of its time. Throughout much of its early history it remained an ally of Athens and even joined the Peloponnesian War on its side. By 400 BC the state showed first signs of fatigue, although Cotys I initiated a brief renaissance that lasted until his murder in 360 BC. Around 340 BC, the Odrysian kingdom lost independence to Macedon and became incorporated into the empire, but it regained independence following Alexander the Great's death. A much smaller Odrysian state was revived in around 330 BC by Seuthes III, who founded a new capital named Seuthopolis.
In the mid-2nd century BC, the Thracians faced gradual conquest by the Romans, under whom they faced internal strife.[ambiguous] They composed major parts of rebellions against the Romans along with the Macedonians up until the Third Macedonian War. The Odrysian kingdom was attacked by the Roman Republic in the late 1st century BC, when the Odrysian heartlands eventually became known as the Sapaean kingdom, a client state of the Roman Republic, which was finally abolished and converted into a Roman province of Thracia in 45-46 AD.

Thracians were described as "warlike" and "barbarians" by the Greeks and Romans since they were neither Romans nor Greeks, but in spite of this they were favored as excellent mercenaries. While the Thracians were perceived as unsophisticated by the Romans and Greeks, their culture was reportedly noted for its sophisticated poetry and music.[15] Since the 19th century-early 20th century, Bulgaria and Romania have used archaeology to learn more about Thracian culture and way of life.
Thracians followed a polytheistic religion with monotheistic elements. One of their customs was tattooing, common among both men and women.[16] The Thracians culturally interacted with the peoples surrounding them – Greeks, Persians, Scythians and Celts[17][18] Thracians spoke the now-extinct Thracian language and shared a common culture.[1] The last reported use of a Thracian language was by monks in the 6th century AD. The scientific study of the Thracians is known as Thracology.
Remove ads
Etymology
The first historical record of the ethnonym Thracian is found in the Iliad, where the Thracians are described as allies of the Trojans in the Trojan War against the Ancient Greeks.[19] The ethnonym Thracian comes from Ancient Greek Θρᾷξ (Thrāix; plural Θρᾷκες, Thrāikes) or Θρᾴκιος (Thrāikios; Ionic: Θρηίκιος, Thrēikios), and the toponym Thrace comes from Θρᾴκη (Thrāikē; Ionic: Θρῄκη, Thrēikē).[20] These forms are all exonyms as applied by the Greeks.[21]
Remove ads
Mythological foundation

In Greek mythology, Thrax (his name simply the quintessential Thracian) was regarded as one of the reputed sons of the god Ares.[22] In the Alcestis, Euripides mentions that one of the names of Ares himself was "Thrax". Since Ares was regarded as the patron of Thrace his golden or gilded shield was kept in his temple at Bistonia in Thrace.[23]
Remove ads
Origins
Summarize
Perspective
The origins of the Thracians remain obscure due to the absence of written historical records before they made contact with the Greeks.[24] Evidence of proto-Thracians in the prehistoric period depends on artifacts of material culture. Leo Klejn identifies proto-Thracians with the multi-cordoned ware culture that was pushed away from Ukraine by the advancing timber grave culture, also known as the Srubnaya. It is generally proposed that a Thracian people developed from a mixture of indigenous peoples and Indo-Europeans from the time of Proto-Indo-European expansion in the Early Bronze Age[25] when the latter, around 1500 BC, mixed with indigenous peoples.[26] According to one theory, their ancestors migrated in three waves from the northeast: the first in the Late Neolithic, forcing out the Pelasgians and Achaeans, the second in the Early Bronze Age, and the third around 1200 BC. They reached the Aegean islands, ending the Mycenaean civilization. They did not speak the same language.[24] The lack of written archeological records left by Thracians suggests that the diverse topography did not make it possible for a single language to form.[24]
Ancient Greek and Roman historians agreed that the ancient Thracians were superior fighters; only their constant political fragmentation prevented them from overrunning the lands around the northeastern Mediterranean.[27] Although these historians characterized the Thracians as "primitive" partly because they lived in simple, open villages, the Thracians in fact had a fairly advanced culture that was especially noted for its poetry and music. Their soldiers were valued as mercenaries, particularly by the Macedonians and Romans.[27]
Identity and distribution
Summarize
Perspective
Thracians inhabited parts of the ancient provinces of Thrace, Moesia, Macedonia, Beotia, Attica, Dacia, Scythia Minor, Sarmatia, Bithynia, Mysia, Pannonia, and other regions of the Balkans and Anatolia. This area extended over most of the Balkans region, and the Getae north of the Danube as far as beyond the Bug and including Pannonia in the west.[28]
According to Ethnica, a geographical dictionary by Stephanus of Byzantium, Thrace—the land of the Thracians—was known as Perki (Περκη) and Aria (Αρια) before being named Thrace by the Greeks,[29][30] presumably due to the affiliation of the Thracians with the god Ares[31] and Perki is the reflexive name of the god Ares as *Perkʷūnos.[32]

Thucydides[31] mentions about a period in the past, from his point of view, when Thracians had inhabited the region of Phocis, also known as the location of Delphi. He dates it to the lifetime of Tereus – mythological Thracian king and son of the god Ares.
Due to the lack of historical records that predate Classical Greece it's presumed that the Thracians did not form a lasting political organization until the Odrysian state was founded in the 5th century BC. In the 1st century BC, during King Burebista's rule, emerged the powerful state of Dacia.
Currently, there are about 200 identified Thracian tribes.[33] Thracian peoples from Moesia achieved significant importance during Roman rule.[34] Some peoples from Moesia practiced vegetarianism, feeding themselves on honey, milk, and cheese.[35]

Remove ads
Greek and Roman descriptions
Summarize
Perspective
Thracians were regarded by ancient Greeks and Romans as warlike, ferocious, bloodthirsty, and barbarian.[36][37][38] Plato in his Republic groups them with the Scythians,[39] calling them extravagant and high spirited; and in his Laws portrays them as a warlike nation, grouping them with Celts, Persians, Scythians, Iberians and Carthaginians.[40] Polybius wrote of Cotys's sober and gentle character being unlike that of most Thracians.[41] Tacitus in his Annals writes of them being wild, savage and impatient, disobedient even to their own kings.[42] The Thracians have been said to have "tattooed their bodies, obtained their wives by purchase, and often sold their children".[38] French historian Victor Duruy further notes that they "considered husbandry unworthy of a warrior, and knew no source of gain but war and theft".[38] He also states that they practiced human sacrifice,[38] which has been confirmed by archaeological evidence.[43]
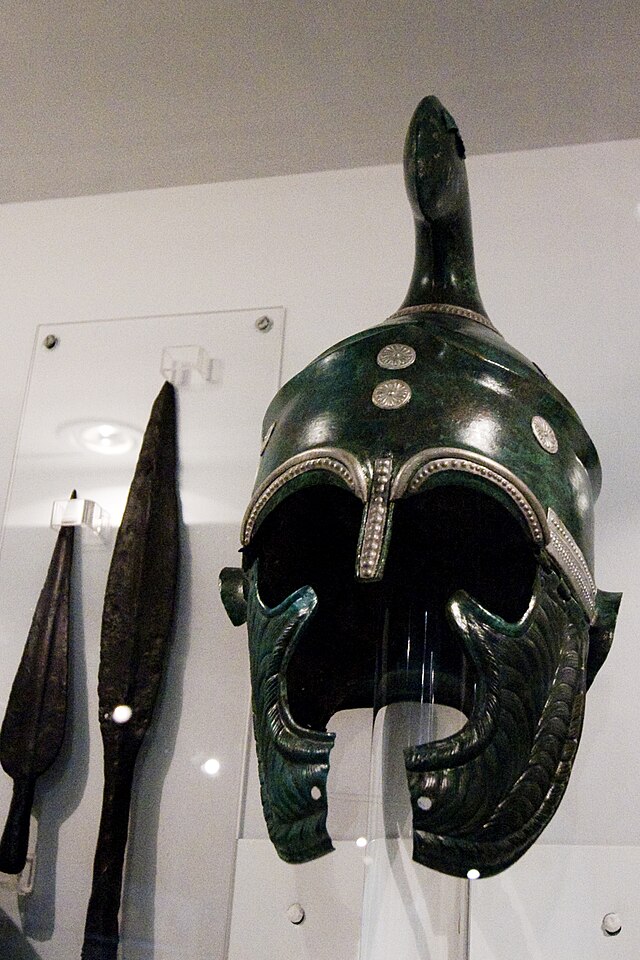

Polyaenus and Strabo write how the Thracians broke their pacts of truce with trickery.[44][45] Polyaneus testifies that the Thracians struck their weapons against each other before battle, "in the Thracian manner".[46] Diegylis, leader of the Caeni, was considered one of the most bloodthirsty chieftains by Diodorus Siculus. An Athenian club for lawless youths was named after the Thracian tribe Triballi[47] which might be the origin of the word tribe.
According to ancient Roman sources, the Dii[48] were responsible for the worst[49] atrocities in the Peloponnesian War, killing every living thing, including children and dogs in Tanagra and Mycalessos.[48] The Dii would impale Roman heads on their spears and rhomphaias such as in the Kallinikos skirmish at 171 BC.[49] Strabo treated the Thracians as barbarians, and held that they spoke the same language as the Getae.[50] Some Roman authors noted that even after the introduction of Latin they still kept their "barbarous" ways.[38] Herodotus writes that "the Thracians sell their children and let their maidens commerce with whatever men they please".[51]
The accuracy and impartiality of these descriptions have been called into question in modern times, given the seeming embellishments in Herodotus's histories, for one.[52][53][54] Archaeologists have attempted to piece together a fuller understanding of Thracian culture through the study of their artifacts.[55]
Remove ads
Physical appearance
Summarize
Perspective


Several Thracian graves or tombstones have the name Rufus inscribed on them, meaning "redhead" – a common name given to people with red hair[56]–and consequently the Romans came to associate the name with slaves.[57] Ancient Greek artwork often depicts Thracians as redheads.[58] Rhesus of Thrace, a mythological Thracian king, was so named because of his red hair and is depicted on Greek pottery as having red hair and a red beard.[58] Ancient Greek writers also described the Thracians as red-haired. A fragment by the Greek poet Xenophanes describes the Thracians as blue-eyed and red haired:
...Men make gods in their own image; those of the Ethiopians are black and snub-nosed, those of the Thracians have blue eyes and red hair.[59]
Bacchylides described Theseus as wearing a hat with red hair, which classicists believe was Thracian in origin.[60] Other ancient writers who described the hair of the Thracians as red include Hecataeus of Miletus,[61] Galen,[62] Clement of Alexandria,[63] and Julius Firmicus Maternus.[64]

Nevertheless, academic studies[citation needed] have concluded that people often had different physical features from those described by primary sources. Ancient authors described as red-haired several groups of people. They claimed that all Slavs had red hair, and likewise described the Scythians as red haired. According to Beth Cohen, Thracians had "the same dark hair and the same facial features as the Ancient Greeks."[65] However, Aris N. Poulianos states that Thracians, like modern Bulgarians, belonged mainly to the Aegean anthropological type.[66]
Remove ads
History
Summarize
Perspective
Homeric period
The earliest known mention of Thracians is in the second song of Homer's Iliad, where the population inhabiting the Thracian Chersonesus is said to have participated in the Trojan War, which is believed to have taken place around 12th century BC. This population is referred to with the following name:
"...And Hippothous led the tribes of the Pelasgi, that rage with the spear, even them that dwelt in deep-soiled Larisa; these were led by Hippothous and Pylaeus, scion of Ares, sons twain of Pelasgian Lethus, son of Teutamus. But the Thracians Acamas led and Peirous, the warrior, even all them that the strong stream of the Hellespont encloseth."[67][68][69]
Archaic period
The first Greek colonies along the Thracian coasts (first the Aegean, then the Marmara and Black Seas) were founded in the 8th century BC.[70] Thracians and Greeks lived side-by-side. Ancient sources record a Thracian presence on the Aegean islands and in Hellas (the broader "land of the Hellenes").[71]
At some point in the 7th century BC, a portion of the Thracian Treres tribe crossed the Thracian Bosporus and invaded Anatolia.[72] In 637 BC, the seventh year of the reign of the Lydian king Ardys, the Treres under their king Kobos (Ancient Greek: Κώβος Kṓbos; Latin: Cobus), in alliance with the Cimmerians and the Lycians, attacked Lydia.[73] They defeated the Lydians and captured the Lydian capital, Sardis, except for its citadel, and Ardys might have been killed in this attack.[74] In another Cimmerian attack on Lydia, Ardys's son and successor, Sadyattes, might also have been killed.[74] Soon after 635 BC, with Assyrian approval[75] the Scythians under Madyes entered Anatolia. In alliance with Sadyattes's son, the Lydian king Alyattes,[76][77] Madyes expelled the Treres from Asia Minor and defeated the Cimmerians, following which the Scythians extended their domination to Central Anatolia[78] until they were themselves expelled from Western Asia by the Medes in the 600s BC.[73]
Achaemenid Thrace

In the 6th century BC the Persian Achaemenid Empire conquered Thrace, starting in 513 BC, when the Achaemenid king Darius I amassed an army and marched from Achaemenid-ruled Anatolia into Thrace, crossing the Arteskos river and then proceeding through the valley-route of the Hebros river. Darius sought to create a new satrapy in the Balkans, and had sent emissaries to many Thracian tribes on the path of his army and elsewhere. Many Thracians, including the Odrysae, submitted to Darius until his army reached the territory of the Getae who lived just south of the Danube and who vainly attempted to resist Achaemenid conquest. After the Getae were defeated and were forced to provide the Achaemenid army with soldiers, all the Thracian tribes between the Aegean Sea and the Danube river had been subjected by the Achaemenid Empire. Darius crossed the Danube and campaigned against the Scythians, after which he returned to Anatolia through Thrace and left a large army in Europe under the command of his general Megabazus.[79]
Following Darius I's orders to create a new satrapy for the Achaemenid Empire in the Balkans, Megabazus forced the Greek cities who had refused to submit to the Achaemenid Empire, starting with Perinthus, after which led military campaigns throughout Thrace to impose Achaemenid rule over every city and tribe in the area. With the help of Thracian guides, Megabazus was able to conquer Paeonia up to but not including the area of Lake Prasias, and he gave the lands of the Paeonians inhabiting these regions up to the Lake Prasias to Thracians loyal to the Achaemenid Empire. The last endeavours of Megabazus included his the conquest of the area between the Strymon and Axius rivers, and at the end of his campaign, the king of Macedonia, Amyntas I, accepted to become a vassal of the Achaemenid Empire. Within the satrapy itself, the Achaemenid king Darius granted to the tyrant Histiaeus of Miletus the district of Myrcinus on the Strymon's east bank until Megabazus persuaded him to recall Histiaeus after he returned to Asia Minor, after which the Thracian tribe of the Edoni retook control of Myrcinus.[79] The new satrapy, once created, was named Skudra (𐎿𐎤𐎢𐎭𐎼), derived from Scythian the name Skuδa, which was the self-designation of the Scythians who inhabited the northern parts of the satrapy.[80] Once Megabazus had returned to Asia Minor, he was succeeded in Skudra by a governor whose name is unknown, and Darius appointed the general Otanes to oversee the administrative division of the Hellespont, which extended on both sides of the sea and included the Bosporus, the Propontis, and the Hellespont proper and its approaches. Otanes then proceeded to capture Byzantium, Chalcedon, Antandrus, Lamponeia, Imbros, and Lemnos for the Achaemenid Empire.[79]

The area included within the satrapy of Skudra included both the Aegean coast of Thrace, as well as its Pontic coast till the Danube. In the interior, the Western border of the satrapy consisted of the Axius river and the Belasica-Pirin-Rila mountain ranges till the site of modern-day Kostenets. The importance of this satrapy rested in that it contained the Hebros river, where a route in the river valley connected the permanent Persian settlement of Doriscus with the Aegean coast, as well as with the port-cities of Apollonia, Mesembria and Odessos on the Black Sea, and with the central Thracian plain, which gave this region an important strategic value. Persian sources describe the province as being populated by three groups: the Saka Paradraya ("Saka beyond the sea", the Persian term for all Scythian peoples to the north of the Caspian and Black Seas [81][82]); the Skudra themselves (most likely the Thracian tribes), and Yauna Takabara. The latter term, which translates as "Ionians with shield-like hats", is believed to refer to Macedonians. The three ethnicities (Saka, Macedonian, Thracian) enrolled in the Achaemenid army, as shown in the Imperial tomb reliefs of Naqsh-e Rostam, and participated in the Second Persian invasion of Greece on the Achaemenid side.[83]
When Achaemenid control over its European possessions collapsed once the Ionian Revolt started, the Thracians did not help the Greek rebels, and they instead saw Achaemenid rule as more favourable because the latter had treated the Thracians with favour and even given them more land, and also because they realised that Achaemenid rule was a bulwark against Greek expansion and Scythian attacks. During the revolt, Aristagoras of Miletus captured Myrcinus from the Edones and died trying to attack another Thracian city.[79]

Once the Ionian Revolt had been fully quelled, the Achaemenid general Mardonius crossed the Hellespont with a large fleet and army, re-subjugated Thrace without any effort and made Macedonia full part of the satrapy of Skudra. Mardonius was however attacked at night by the Bryges in the area of Lake Doiran and modern-day Valandovo, but he was able to defeat and submit them as well. Herodotus's list of tribes who provided the Achaemenid army with soldiers included Thracians from both the coast and from the central Thracian plain, attesting that Mardonius's campaign had reconquered all the Thracian areas which were under Achaemenid rule before the Ionian Revolt.[79]
When the Greeks defeated a second invasion attempt by the Persian Empire in 479 BC, they started attacking the satrapy of Skudra, which was resisted by both the Thracians and the Persian forces. The Thracians kept on sending supplies to the governor of Eion when the Greeks besieged it. When the city fell to the Greeks in 475 BC, Cimon gave its land to Athens for colonisation. Although Athens was now in control of the Aegean Sea and the Hellespont following the defeat of the Persian invasion, the Persians were still able to control the southern coast of Thrace from a base in central Thrace and with the support of the Thracians. Thanks to the Thracians co-operating with the Persians by sending supplies and military reinforcements down the Hebrus river route, Achaemenid authority in central Thrace lasted until around 465 BC, and the governor Mascames managed to resist many Greek attacks in Doriscus until then.[79]
Around this time, Teres I, the king of the Odrysae tribe, in whose territory the Hebrus flowed, was starting to organise the rise of his kingdom into a powerful state. With the end of Achaemenid power in the Balkans, the Thracian Odrysian kingdom, the Kingdom of Macedonia, and the Athenian thalassocracy filled the ensuing power vacuum and formed their own spheres of influence in the area.[79]
Odrysian Kingdom
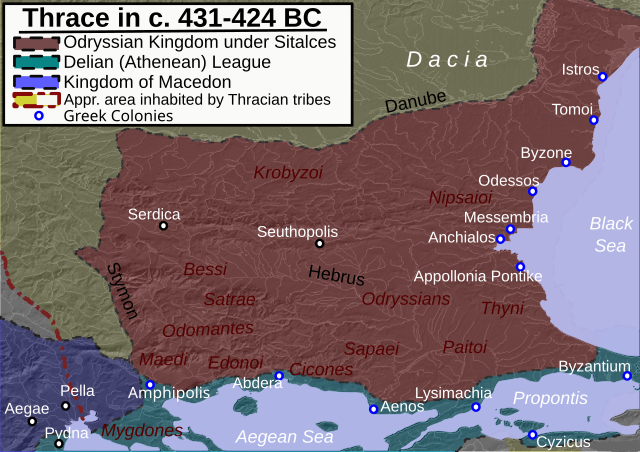
The Odrysian Kingdom was a state union of over 40 Thracian tribes[84] and 22 kingdoms[85] that existed between the 5th century BC and the 1st century AD. It consisted mainly of present-day Bulgaria, spreading to parts of Southeastern Romania (Northern Dobruja), parts of Northern Greece and parts of modern-day European Turkey.[citation needed]
By the 5th century BC, the Thracian population was large enough that Herodotus called them the second-most numerous people in the part of the world known by him (after the Indians), and potentially the most powerful, if not for their lack of unity.[86] The Thracians in classical times were broken up into a large number of groups and tribes, though a number of powerful Thracian states were organized, the most important being the Odrysian kingdom of Thrace, and also the short lived Dacian kingdom of Burebista. The peltast is a type of soldier of this period that originated in Thrace.[87]
At this time, a subculture of celibate ascetics called the "ctistae" lived in Thrace, where they served as philosophers, priests and prophets. They were held in a place of honor by the Thracians, with their lives being dedicated to the gods.[88]
Macedonian Thrace
During this period, contacts between the Thracians and Classical Greece intensified.[citation needed]
After the Persians withdrew from Europe and before the expansion of the Kingdom of Macedon, Thrace was divided into three regions (east, central, and west). A notable ruler of the East Thracians was Cersobleptes, who attempted to expand his authority over many of the Thracian tribes. He was eventually defeated by the Macedonians.[citation needed]
The Thracians were typically not city-builders[89][90] and their only polis was Seuthopolis.[91][92]
The conquest of the southern part of Thrace by Philip II of Macedon in the 4th century BC made the Odrysian kingdom extinct for several years. After the kingdom was reestablished, it was a vassal state of Macedon for several decades under generals such as Lysimachus of the Diadochi.[citation needed]

In 336 BC, Alexander the Great began recruiting Thracian cavalry and javelin men in his army, who accompanied him on his continuous conquest to expand the borders of the Macedonian Empire.[93] The strength of the thracian cavalry quickly grew from 150 men, to 1000 men by the time Alexander advanced into Egypt, and numbered 1600 when he reached the persian city of Susa. The thracian infantry was under the command of the Odrysian prince Sitalces II who led them in the siege of Telmissus and in the battles of Issus and Gaugamela.[93]
In 279 BC, Celtic Gauls advanced into Macedonia, southern Greece and Thrace. They were soon forced out of Macedonia and southern Greece, but they remained in Thrace until the end of the 3rd century BC. From Thrace, three Celtic tribes advanced into Anatolia and established the kingdom of Galatia.[citation needed]
As evident from the archaeological findings of pits and treasures, spanning from the 3rd century BC to the 1st century BC in northwestern Bulgaria and northeastern Serbia, Scordiscian communities lived next to the Thracian ones.[94]
Greek raids to enslave Thracians
Slave raids were a specific form of banditry that was the primary method employed by the ancient Greeks for gathering slaves. In regions such as Thrace and the eastern Aegean, natives, or "barbarians", captured in these raids were the main source of slaves, rather than prisoners of war. As described by Xenophon, and Menander in Aspis, after the slaves were captured in raids, their actual enslavement took place when they were resold through slave-dealers to Athenians and other slaveowners throughout Greece. The fragmentary list of slaves confiscated from the property of the mutilators of the Hermai mentions 32 slaves whose origins have been ascertained: 13 came from Thrace, 7 from Caria, and the others came from Cappadocia, Scythia, Phrygia, Lydia, Syria, Ilyria, Macedon, and Peloponnese. The names given to slaves in the comedies often had a geographical link, thus Thratta, used by Aristophanes in The Wasps, The Acharnians, and Peace, simply meant a Thracian woman. The ethnicity of a slave was a significant criterion for major purchasers: Ancient practice was to avoid a concentration of too many slaves of the same ethnic origin in the same place, in order to limit the risk of revolt.
Roman Thrace

During the Macedonian Wars, conflict between Rome and Thrace was unavoidable. The rulers of Macedonia were weak, and Thracian tribal authority resurged. But after the Battle of Pydna in 168 BC, Roman authority over Macedonia seemed inevitable, and the governance of Thrace passed to Rome.[citation needed]
Initially, Thracians and Macedonians revolted against Roman rule. For example, the revolt of Andriscus in 149 BC drew the bulk of its support from Thrace. Incursions by local tribes into Macedonia continued for many years, though a few tribes, such as the Deneletae and the Bessi, willingly allied with Rome.[citation needed]
After the Third Macedonian War, Thrace acknowledged Roman authority. The client state of Thracia comprised several tribes.[citation needed]

The next century and a half saw the slow development of Thracia into a permanent Roman client state. The Sapaei tribe came to the forefront initially under the rule of Rhascuporis. He was known to have granted assistance to both Pompey and Caesar, and later supported the Republican armies against Mark Antony and Octavian in the final days of the Republic.[citation needed]
The heirs of Rhascuporis became as deeply enmeshed in political scandal and murder as were their Roman masters. A series of royal assassinations altered the ruling landscape for several years in the early Roman imperial period. Various factions took control with the support of the Roman Emperor.[citation needed]
After Rhoemetalces III of the Thracian Kingdom of Sapes was murdered in AD 46 by his wife, Thracia was incorporated as an official Roman province to be governed by Procurators, and later Praetorian prefects. The central governing authority of Rome was in Perinthus, but regions within the province were under the command of military subordinates to the governor. The lack of large urban centers made Thracia a difficult place to manage, but eventually the province flourished under Roman rule. However, Romanization was not attempted in the province of Thracia.[citation needed]
Roman authority in Thracia rested mainly with the legions stationed in Moesia, though the province's rural nature and distance from Roman authority complicated the maintenance of that authority. Over the next few centuries, the province was periodically and increasingly attacked by migrating Germanic tribes. The reign of Justinian saw the construction of over 100 legionary fortresses to supplement the defense.[citation needed]
Remove ads
Aftermath
Summarize
Perspective

Repeated invasions of the Balkans by Romans, Celts, Huns, Goths, Scythians, Sarmatians and Slavs, accompanied by, hellenization, romanization and later slavicisation, remade the ethnicity, language, and culture of Thrace. Regardless, writers continued to speak of a separate Thracian nationality until the Early Middle Ages.[95] Towards the end of the 4th century, Nicetas the Bishop of Remesiana brought the gospel to "those mountain wolves", the Bessi.[96] Reportedly his mission was successful, and Christianity eventually replaced the worship of Dionysus and other Thracian gods.

In 570, Antoninus Placentius said that in the valleys of Mount Sinai there was a monastery in which monks spoke Greek, Latin, Syriac, Egyptian and Bessian. The origin of the monastery is explained in Simeon Metaphrastes's medieval hagiography Vita Sancti Theodosii Coenobiarchae, which says that Theodosius the Cenobiarch founded a monastery on the shore of the Dead Sea with four churches, in each of which a different language was spoken, Bessian being one of them. The site of the monastery was called "Cutila", which may be a Thracian name.[97]

The further fate of the Thracians is a matter of dispute. German historian Gottfried Schramm speculated that the Albanians descended from the Christianized Thracian tribe Bessi, after Bessi remnants were allegedly pushed by Slavs and Bulgars westwards during the 9th century into modern day Albania.[96] There is no archaeological evidence, however, of a 9th-century migration of any population, such as the Bessi, from western Bulgaria to Albania.[98] There is likewise no linguistic support for Schramm's hypothesis. Little comparative linguistic material is available (the Thracian language is attested only marginally, while the Bessian is completely unknown), but the phonetic history of Albanian and Thracian indicates different sound developments inconsistent with Schramm's thesis. Furthermore, the Christian vocabulary of Albanian is mainly Latin, which speaks against the construct of a "Thracian-Bessian church language".[99] Most likely the Thracians were assimilated into Roman and Byzantine society, becomong one of the ancestral groups of modern Southeastern Europeans.[100]
The last mention of Thracians, in the 6th century, coincides with the first mention of Slavs, when the Slavic tribes inhabited large territories of Central and Eastern Europe.[101] After the 6th century Thracians who weren't already assimilated in the Byzantine Empire, were incorporated in the slavic speaking Bulgarian Empire.[102]

Bulgarian Thrace
Slavic tribes had mingled with the Thracian population, prior to the formation of the Bulgarian state.[102] Under the leadership of Asparuh, in 680 AD the Thracians, Bulgars and Slavs readily united to establish the First Bulgarian Empire.[103][104] These three ethnic groups mingled to produce the Bulgarian people.[105] The Byzantine Empire, retained control over Thrace until the 7th century when the northern half of the entire region was claimed by the First Bulgarian Empire and the remainder was reorganized in the Thracian theme.
Remove ads
Legacy
A recent Bulgarian study on the heritage of Thracian mounds in Bulgaria claims historical, cultural and ethnic links between Thracians and Bulgarians.[106][105] Genetic studies on modern Bulgarians show that approximately 55% of Bulgarian autosomal genetic legacy is of Paleo-Balkan and Mediterranean origin which can be attributed to Thracians and other indigenous Balkan populations predating Slavs and Bulgars.[107][108][109][110]
Greek Thrace
Turkish Thrace
Culture
Summarize
Perspective

Language
The records of Thracian writing are very scarce. There are only four inscriptions that have been discovered. One of them is a gold ring unearthed in the village of Ezerovo, Bulgaria. The thracian inscription is written using the Greek script and consists of 8 lines. Attempts to decipher the inscription have proven inconclusive.[111]
Religion

One notable cult that existed in Thrace, Moesia, Phrygia and the lands of the Dacians and the Getae (Scythia Minor, now Dobrudja) was that of the "Thracian horseman", also known as Sabazios or "Thracian Heros" known by a Thracian name as Heros Karabazmos, a god of the underworld, who was usually depicted on funeral statues as a horseman slaying a beast with a spear.[112][113][114] Getae and Dacians potentially had a monotheistic religion based on the god Zalmoxis, though this is heavily debated in the anthropological community.[115] The supreme Balkan thunder god Perkon was part of the Thracian pantheon, although cults of Orpheus and Zalmoxis likely overshadowed his.[citation needed]
The Thracians are considered the first to worship the god of wine called Dionysus in Greek or Zagreus in Thracian.[116] Later this cult reached Ancient Greece.[117][118] Some consider Thrace as the motherland of wine culture.[119] The works of Homer, Herodotus and other historians of Ancient Greece also refer to the ancient Thracians' love for winemaking and consumption, also related to religion[120] as early as 6000 years ago.[121]
Marriage
The male Thracians were polygamous. Menander puts it: "All Thracians, especially us and the Getae, are not much abstaining, because no one takes less than ten, eleven, twelve wives, some even more. If one dies and has only four or five wives he is called ill-fated, unhappy and unmarried."[122] According to Herodotus virginity among women was not valued, and unmarried Thracian women could have sex with any man they wished to.[122] There were men perceived as holy Thracians, who lived without women and were called "ktisti".[122] In myth, Orpheus rebuked the sexual advances of the Bistones women after the death of Eurydice, and was killed for not engaging in the activities promoted by the followers of Dionysus.
Warfare

The Thracians were a warrior people, known as both horsemen and lightly armed skirmishers with javelins.[123] Thracian peltasts had a notable influence in Ancient Greece.[124]
The history of Thracian warfare spans from c. 10th century BC up to the 1st century AD in the region defined by Ancient Greek and Latin historians as Thrace. It concerns the armed conflicts of the Thracian tribes and their kingdoms in the Balkans and in the Dacian territories. Emperor Traianus, also known as Trajan, conquered Dacia after two wars in the 2nd century AD. The wars ended with the occupation of the fortress of Sarmisegetusa and the death of the king Decebalus. Besides conflicts between Thracians and neighboring nations and tribes, numerous wars were recorded among Thracian tribes too.[citation needed]
Remove ads
Genetics
Summarize
Perspective
A genetic study published in Scientific Reports in 2019 examined the mtDNA of 25 Thracian remains in Bulgaria from the 3rd and 2nd millennia BC. They were found to harbor a mixture of ancestry from Western Steppe Herders (WSHs) and Early European Farmers (EEFs), supporting the idea that Southeast Europe was the link between Eastern Europe and the Mediterranean.[3]
A Bulgarian study from 2013 claims genetic similarity between Thracians (8-6 century BC), medieval Bulgarians (8–10 century AD), and modern Bulgarians, highlighting highest resemblance between them and Romanians, Northern Italians and Northern Greeks.[125]
Examinations of Iron Age and ancient Thracian remains in Bulgaria were found to mainly carry the Y-DNA haplogroup E-V13.[126] The tested samples were further specifically listed as: E-BY3880 x 3, E-L618 x 2, E-M78 x 2, R-Z93, E-CTS1273, E-BY14160.[126] Six of the samples were predicted for having brown eyes while two for having blue eyes, while majority of the samples were predicted for an intermediate skin color and hair color prediction ranged from majority brown on detailed, to light and dark.[127]
Remove ads
Notable people
Summarize
Perspective


This is a list of historically important personalities being entirely or partly of Thracian and Dacian ancestry:
- Orpheus, mythological figure considered chief among poets and musicians; king of the Thracian tribe of Cicones
- Rhesus of Thrace, mythical king of Thrace in the Iliad who fought on the side of Trojans
- Eumolpus, legendary king of Thrace described as having come to Attica either as a bard, a warrior, or a priest of Demeter and Dionysus
- Tereus, mythological Thracian king,[128][129] son of Ares and the naiad Bistonis
- Spartacus, Thracian gladiator who led a large slave uprising in south Italy in 73–71 BC and defeated several Roman legions in what is known as the Third Servile War
- Sitalces, king of the Odrysian kingdom; an ally of the Athenians during the Peloponnesian War
- Teres I, Thracian king who united many tribes of Thrace under the banner of the Odrysian state
- Amadocus I, Thracian king, the Amadok Point was named after him
- Seuthes I
- Seuthes II
- Seuthes III
- Cotys I
- Burebista, king of Dacia
- Decebalus, king of Dacia
- Maximinus Thrax, Roman emperor from 235 to 238.[130]
- Aureolus, Roman military commander
- Galerius, Roman emperor from 305 to 311; born to a Thracian father and Dacian mother
- Constantine the Great, Roman emperor from 306 to 337. Born to Thracian father[131][132] from Naissus, and Greek mother from Bithynia
- Licinius, Roman emperor from 308 to 324
- Maximinus Daza, Roman emperor from 308 to 313
- Justin I, Byzantine emperor and founder of the Justinian dynasty
- Justinian I, Byzantine emperor; Thracian origin,[133][134][135] born in Dardania
- Belisarius, Byzantine general; either Illyrian[136][137][138][139] or Thracian[140][141] origin
- Marcian, Byzantine emperor from 450 to 457; either Illyrian or Thracian origin
- Leo I the Thracian, Byzantine emperor from 457 to 474
- Bouzes, Byzantine general active during the reign of Justinian I (527–565)
- Coutzes, Byzantine general during the reign of Justinian I (527–565)
Thracology
Summarize
Perspective
Archaeology
The branch of science that studies the ancient Thracians and Thrace is called Thracology. Archaeological research on the Thracian culture started in the 20th century, especially after World War II, mainly in southern Bulgaria. As a result of intensive excavations in the 1960s and 1970s a number of Thracian tombs and sanctuaries were discovered. Most significant among them are: the Getic burial complex and the Tomb of Sveshtari, the Valley of the Thracian Rulers and the Tomb of Kazanlak, Tatul, Seuthopolis, Perperikon, Tomb of Aleksandrovo in Bulgaria, Sarmizegetusa in Romania and others.[citation needed] Also a large number of elaborately crafted gold and silver treasure sets from the 5th and 4th century BC were unearthed. In the following decades, those were exhibited in museums around the world, thus calling attention to ancient Thracian culture. Since the year 2000, Bulgarian archaeologist Georgi Kitov has made discoveries in Central Bulgaria, in an area now known as "The Valley of the Thracian Kings". The residence of the Odrysian kings was found in Starosel in the Sredna Gora mountains.[142][143] A 1922 Bulgarian study claimed that there were at least 6,269 necropolises[clarification needed] in Bulgaria.[144]
Multidisciplinary Studies
The dominant stance of history and archaeology as the two main disciplines dealing with the Thracians as a subject of research has been succeeded by a clear shift towards new multidisciplinary and more inclusive scientific perspectives. An example of this new trend was the large-scale multidisciplinary project "Thracians – Genesis and Development of the Ethnos, Cultural Identities, Civilization Relations and Heritage of the Antiquity", launched in 2016 in Bulgaria. The project was the first comprehensive study of the Thracian heritage including 72 scholars from 18 institutes of the Bulgarian Academy of Science, as well as researchers from Canada, Italy, Germany, Japan and Switzerland. The project studied 13 scientific themes among which: formation of the Thracian ethnos, outlining of its ethno-cultural territory, continuity of the gene pool and related DNA studies, architectural, botanical, microbiological, astronomical, acoustic and linguistic aspects, mining and ceramics technologies, food and drink customs, that resulted in an extensively illustrated book including 33 scientific articles.[145]
Gallery
- Thracian tribes and heroes
- Map of the territory of Philip II of Macedon
- Kingdom of Lysimachus and the Diadochi
- Map of the Diocese of Thrace (Dioecesis Thraciae) c. 400 AD
- Golden Dacian helmet of Cotofenesti, in Romania
- Gold coins that have been minted by the Dacians, with the legend ΚΟΣΩΝ
- A gold Thracian treasure from Panagyurishte, Bulgaria
- Thracian tomb Shushmanets, built in 4th century BC
- The interior of the Sveshtari tomb
- Interior of Tomb of Seuthes III
- Bronze head of Seuthes III
- Thracian Cavalry
- Thracian Horseman Relief
- Coin of Seuthes III
- The Thracian Horseman on the modern Bulgarian currency
See also
References
Sources
Further reading
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads



























