Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Trolleybuses in Chișinău
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
The Chișinău trolleybus system forms an important part of the public transport network in Chișinău, the capital of Moldova. The system was created shortly after the end of the World War II to replace the old electric tram system that suffered extensive damage during the war.[1] Along with the network of minibuses known as rutierele, it forms the backbone of the Chișinău transport system, with the average daily ridership reaching 250,000 passengers per day.[2][3]
Remove ads
History
The history of the trolleybus network in Chișinău goes back to 1949 when the city council took the decision to introduce it as a substitute for the tram network that was heavily damaged during World War II and could only be rebuilt to a limited extent. The first line connecting the Chişinău Railway Station with the University of Medicine ran along the Stephen the Great boulevard, where the former tram tracks were removed, and was served by six MTB-82D units. In 1959 the tram depot was transferred to serve the trolleybus system that comprised over 50 units at that time, and by 1961 trolleybuses had completely replaced the trams. The second and the third depots were introduced into service in 1966 and 1986, respectively.[1]
Remove ads
Lines
Summarize
Perspective
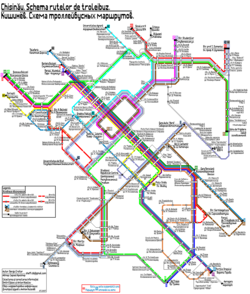
The trolleybus network consists of 22 lines covering all the city districts and the suburb of Durlești.[4]
| Line | Route | |
| 2 | bd. Traian – str. Pușkin | circular route |
| 3 | șos. Balcani – str. Miorița | |
| 4 | Grădina Botanică – str. Constituţiei | |
| 5 | Trolleybus depot 2 – str. Bariera Sculeni | |
| 7 | A.B.A.-4 – str. 31 August 1989 | |
| 8 | bd. Traian – parcul "La izvor" | |
| 9 | Schinoasa-2 – Autogara Nord | |
| 10 | str. Studenților – str. Miorița | |
| 11 | str. Studenților – parcul "La izvor" | |
| 13 | str. Ion Dumeniuc – str. Dokuceaev | |
| 16 | Uzina de frigidere – str. 31 August 1989 | |
| 17 | Schinoasa 2 – Gara | |
| 20 | Trolleybus depot 2 – Autogara Nord | |
| 21 | Uzina de frigidere – șos. Balcani | |
| 22 | șos. Balcani – Grădina Botanică | |
| 23 | str. Ion Dumeniuc – parcul "La izvor" | |
| 24 | str. Ion Dumeniuc – str. Mioriţa | |
| 25 | str. Ceucari – str. 31 August 1989 | |
| 26 | str. Ceucari – str. Ion Dumeniuc | |
| 27 | str. Ceucari – str. Ion Creangă | |
| 28 | or. Durlești – str. Sarmizegetusa | |
| 29 | Universitatea Agrară – parcul "Ștefan cel Mare" | |
| 30 | Aeroportul Internațional Chișinău – str. 31 August 1989 |
Remove ads
Fleet
Summarize
Perspective



The fleet consists mainly of the various modification of the Soviet-built ZiU-9 and the recently purchased low-floor vehicles AKSM-321 manufactured by Belkommunmash in Belarus (Chișinău is the third-largest user of this model, after Minsk and Moscow). In addition, the network also operates a number of the Czech-produced Škoda 14Tr (popular with the drivers) and Ukrainian-built YuMZ-T2.[5]
| Model[6] | Total / Active |
| ACSM-321 | 101 / 98 |
| RTEC 62321M2 | 65 / 59 |
| RTEC 62321M1 | 64 / 62 |
| RTEC 6232100DM3 | 40 / 40 |
| Škoda 14TrM | 39 / 32 |
| ZiU-682V variants | 23 / 20 |
| Škoda 24Tr Irisbus Citelis | 20 / 20 |
| YuMZ T2 | 20 / 19 |
| ZiU-682G variants | 17 / 13 |
| ZiU-683V01 | 5 / 3 |
| ACSM-433 Vitovt Max II | 5 / 5 |
| Solaris Trollino II 18 AC | 10 / 10 |
| Solaris Trollino II 18 Ganz | 5 / 5 |
| ACSM-213 | 2 / 2 |
| RTEC 624201M1 | 1 / 1 |
| VMZ-5298.00 (VMZ-375) | 1 / 1 |
| YuMZ T1 | 1 / 1 |
In 2021, two trolleybuses built by the now-defunct Dutch manufacturer APTS (Advanced Public Transport Systems), to its Phileas design, were acquired secondhand: A 2011 prototype for a planned new busway system in Pescara, Italy, and a 2014 prototype (with doors on both sides) for the Metromare busway then under construction in Rimini, Italy.[7] Neither ever entered service on the systems for which they had been purchased, and eventually they were sold to a dealer in secondhand vehicles.[8] They were given fleet numbers 1000 and 1001 in Chișinău, and No. 1001 entered service in June 2022.[9]
Payment system
Every vehicle has a fare collector who sells single-ride tickets valid for this particular ride only. Alternatively, one can purchase a monthly ticket, valid for a calendar month. A single-ride ticket costs (since September '22) 6 MDL, and the price of the monthly pass is 234 MDL. There are also: monthly ticket for scholars and students – 70 MDL, ticket for 15 days – 100 MDL, monthly ticket for students with social privileges – 70 MDL, monthly ticket for economic agents – 320 MDL.
Remove ads
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads