Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
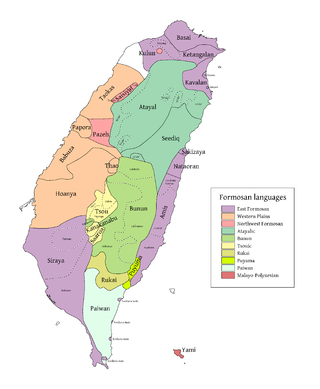
Tsouic languages
Language family From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
The Tsouic languages (also known as the Central Formosan languages) are three Formosan languages, Tsou proper and the Southern languages Kanakanavu and Saaroa. The Southern Tsouic languages of Kanakanavu and Saaroa have the smallest phonemic inventories out of all the Formosan languages, with each language having only 13 consonants and 4 vowels (Blust 2009:165).[1] These two languages are highly endangered, as many Southern Tsouic speakers are shifting to Bunun and Mandarin Chinese.
The Proto-Tsouic language was reconstructed by Japanese linguist Shigeru Tsuchida in 1976, and is supported by Blust (1999), Li (2008), and Sagart (2014). However, Chang (2006)[2] and Ross (2009)[3] deny that Tsouic is a valid group; Ross places Southern Tsouic within Nuclear Austronesian (the family of the various proto-Austronesian reconstructions), but the Tsou language as a more divergent branch.
Sagart (2014) supports Tsouic on the basis on shared irregular phonological reflexes confined to specific terms, in addition to over 57 terms reconstructed by Tsuchida that appear in no other Austronesian clade.[4]
Remove ads
Classification
- Tsou
- Southern Tsouic
Sound changes
The following sound changes from Proto-Austronesian occurred in the Tsouic languages (Li 2008:215).[5]
- *C, *d > c
- *y > Proto-Tsouic *z
- *R > r
References
Further reading
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads