Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Tungsten diselenide
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
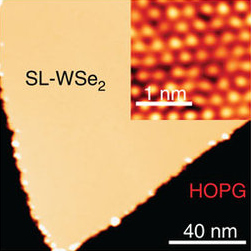
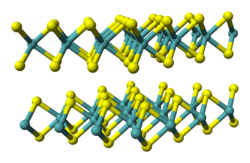
Tungsten diselenide is an inorganic compound with the formula WSe2.[6] The compound adopts a hexagonal crystalline structure similar to molybdenum disulfide. The tungsten atoms are covalently bonded to six selenium ligands in a trigonal prismatic coordination sphere while each selenium is bonded to three tungsten atoms in a pyramidal geometry. The tungsten–selenium bond has a length of 0.2526 nm, and the distance between selenium atoms is 0.334 nm.[7] It is a well studied example of a layered material. The layers stack together via van der Waals interactions. WSe2 is a very stable semiconductor in the group-VI transition metal dichalcogenides.
Remove ads
Structure and properties
The hexagonal (P63/mmc) polymorph 2H-WSe2 is isotypic with hexagonal MoS2. The two-dimensional lattice structure has W and Se arranged periodically in layers with hexagonal symmetry. Similar to graphite, van der Waals interactions hold the layers together; however, the 2D-layers in WSe2 are not atomically thin. The large size of the W cation renders the lattice structure of WSe2 more sensitive to changes than MoS2.[8]
In addition to the typical semiconducting hexagonal structure, a second metallic polymorph of WSe2 exists. This phase, 1T-WSe2, is based on a tetragonal symmetry with one WSe2 layer per repeating unit. The 1T-WSe2 phase is less stable and transitions to the 2H-WSe2 phase.[8][9] WSe2 can form a fullerene-like structure.
The Young's modulus varies greatly as a function of the number of layers in a flake. For a single monolayer, the reported Young's modulus is 258.6 ± 38.3 GPa.[10]
Remove ads
Synthesis
Heating thin films of tungsten under pressure from gaseous selenium and high temperatures (>800 K) using the sputter deposition technique leads to the films crystallizing in hexagonal structures with the correct stoichiometric ratio.[11]
- W + 2 Se → WSe2
Potential applications

The potential applications of transition metal dichalcogenides in solar cells and photonics are often discussed.[13] Bulk WSe
2 has an optical band gap of ~1.35 eV with a temperature dependence of −4.6×10−4 eV/K.[14] WSe
2 photoelectrodes are stable in both acidic and basic conditions, making them potentially useful in electrochemical solar cells.[15][16][17]
The properties of WSe
2 monolayers differ from those of the bulk state, as is typical for semiconductors. Mechanically exfoliated monolayers of WSe
2 are transparent photovoltaic materials with LED properties.[18] The resulting solar cells pass 95 percent of the incident light, with one tenth of the remaining five percent converted into electrical power.[19][20] The material can be changed from p-type to n-type by changing the voltage of an adjacent metal electrode from positive to negative, allowing devices made from it to have tunable bandgaps.[21]
Superconductivity has been reported in twisted bilayer WSe
2, with a transition temperature of 200 mK.[22]
See also
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads