Big Bang
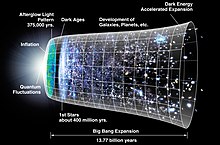
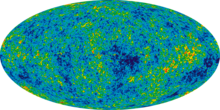
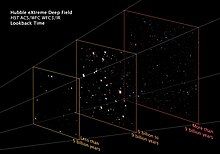
Physical theoryThe Big Bang is a physical theory that describes how the universe expanded from an initial state of high density and temperature. Various cosmological models based on the Big Bang concept explain a broad range of phenomena, including the abundance of light elements, the cosmic microwave background (CMB) radiation, and large-scale structure. The uniformity of the universe, known as the horizon and flatness problems, is explained through cosmic inflation: a phase of accelerated expansion during the earliest stages. Detailed measurements of the expansion rate of the universe place the Big Bang singularity at an estimated 13.787±0.02 billion years ago, which is considered the age of the universe. A wide range of empirical evidence strongly favors the Big Bang event, which is now widely accepted.
- 1912Vesto Slipher measured the first Doppler shift of a "spiral nebula."
- 1922Alexander Friedmann introduced the concept of an expanding universe with the Friedmann equations.
- 1924Edwin Hubble's measurement of the great distance to the nearest spiral nebulae showed they were other galaxies.