No coordinates found
Enlargement of the European Union
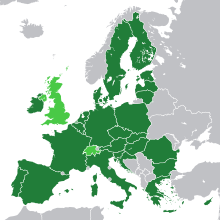
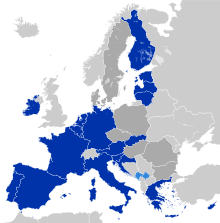
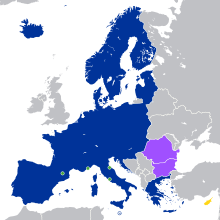
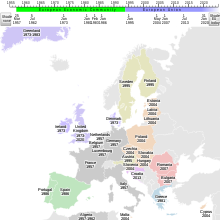
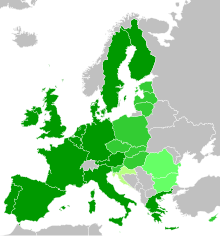
Accession of new countries to the EUThe European Union (EU) has expanded a number of times throughout its history by way of the accession of new member states to the Union. To join the EU, a state needs to fulfil economic and political conditions called the Copenhagen criteria, which require a stable democratic government that respects the rule of law, and its corresponding freedoms and institutions. According to the Maastricht Treaty, each current member state and the European Parliament must agree to any enlargement. The process of enlargement is sometimes referred to as European integration. This term is also used to refer to the intensification of co-operation between EU member states as national governments allow for the gradual harmonisation of national laws.
Read article
Top Questions
AI generatedMore questions