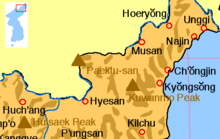
Paektu Mountain
Mountain on the China–North Korea borderPaektu Mountain or Baekdu Mountain (Korean: 백두산) is an active stratovolcano on the Chinese–North Korean border. In China, it is known as Changbai Mountain. At 2,744 m (9,003 ft), it is the tallest mountain in North Korea and Northeast China and the tallest mountain of the Baekdu-daegan and Changbai mountain ranges. The highest peak, called Janggun Peak, belongs to North Korea. The mountain notably has a caldera that contains a large crater lake called Heaven Lake, and is also the source of the Songhua, Tumen, and Yalu rivers. Korean and Manchu people assign a mythical quality to the mountain and its lake, and consider the mountain to be their ancestral homeland.
Read article
Top Questions
AI generatedMore questions
Timeline
AI Generated- 946The mountain's caldera was created by the colossal (VEI 6) "Millennium" or "Tianchi" eruption.
- 1597The Joseon dynasty recorded a volcanic eruption.