No coordinates found
PAL
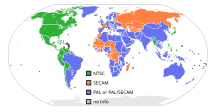
Color encoding system for analogue televisionPhase Alternating Line (PAL) is a colour encoding system for analogue television. It was one of three major analogue colour television standards, the others being NTSC and SECAM. In most countries it was broadcast at 625 lines, 50 fields (25 frames) per second, and associated with CCIR analogue broadcast television systems B, D, G, H, I or K. The articles on analog broadcast television systems further describe frame rates, image resolution, and audio modulation.
Read article
Top Questions
AI generatedMore questions