No coordinates found
Reflection (physics)
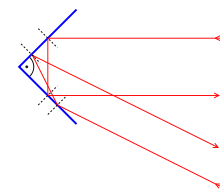
"Bouncing back" of waves at an interfaceReflection is the change in direction of a wavefront at an interface between two different media so that the wavefront returns into the medium from which it originated. Common examples include the reflection of light, sound and water waves. The law of reflection says that for specular reflection the angle at which the wave is incident on the surface equals the angle at which it is reflected.
Read article
Top Questions
AI generatedMore questions